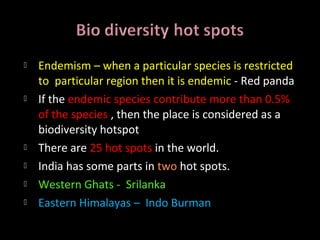
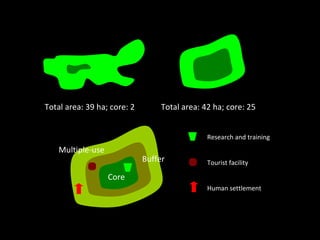
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth. It exists at genetic, species, ecosystem, and landscape levels. Species diversity is the number of different species in an area. Genetic diversity arises from sexual reproduction and mutations. Ecosystem diversity refers to the variety of habitats and communities in an area. India ranks high in terms of plant and animal diversity due to its various climates. However, human activities like habitat destruction threaten biodiversity. Conservation efforts must balance environmental protection with sustainable use of resources.