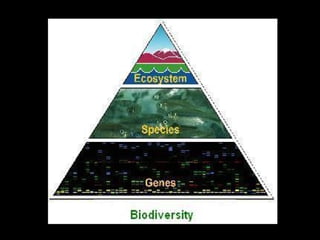
This document discusses biodiversity and its importance. It begins by defining biodiversity as the variety of all life forms, including different plants, animals and microorganisms, as well as their genes and ecosystems. It then discusses the three types of biodiversity: genetic, species, and ecological diversity. The document emphasizes the importance of biodiversity, noting how it increases ecosystem productivity and provides many benefits to humans like medicines, food, wood products, and more. It also outlines some major threats to biodiversity such as habitat destruction and pollution. Specific areas with high biodiversity, like rainforests and coral reefs, are highlighted. The conclusion provides suggestions for how individuals can help protect biodiversity.