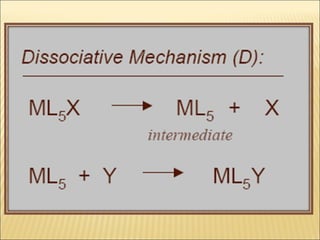
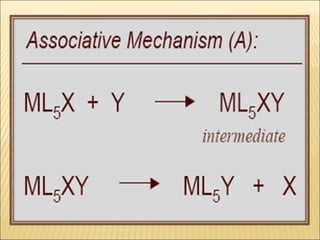
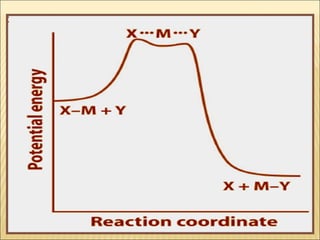
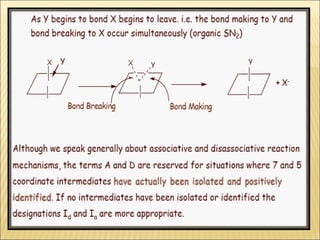
The document discusses the lability and inertness of coordination complexes. It defines labile complexes as those where ligand exchange occurs rapidly, while inert complexes have slow ligand exchange. Lability is determined by factors like the metal ion size, charge, and d-electron configuration, not thermodynamic stability. Smaller or higher charged metal ions and complexes with less than 3 d-electrons tend to be more labile. The rate of ligand substitution depends on both the leaving and entering ligands. Steric effects and solvent also influence the rate. Complexes may undergo dissociative or associative substitution based on their structure.


![ [Cu(NH3)4(H2O2)2]2+
is labile. Its aqueous
solution is blue in color.
When concentrated hydrochloric acid is
added to this solution, the blue solution
immediately turns green ,giving [CuCl4]2-
.
But when the complex is kept as such it
remains as such with out any decomposition
(i.e stable)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-3-320.jpg)
![ [Co(NH3)6]3+
reacts slowly. When this complex
is treated with concentrated HCl, no reaction
takes place. Only when it is heated with 6M
HCl for many hours, one NH3 is substituted by
Cl-
.
[Co(NH3)6]3+
+ HCl [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
+ NH4
+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-4-320.jpg)


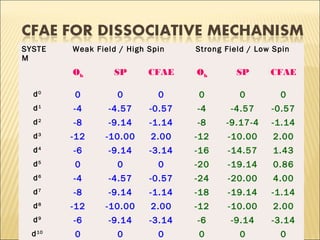
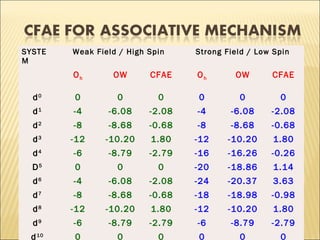
![No. of d electrons
& electron configuration
Nature Example
d0 Labile [CaEDTA]2-
d1
; t2g
1
eg
0
Labile [Ti(H2O)6]3+
d2
; t2g
2
eg
0
Labile [V(phen)3]3+
d3
; t2g
3
eg
0
Inert [V(H2O)6] 3+
d4
(high-spin); t2g
3
eg
1
Labile [Cr(H2O)6]3+
d4
(low-spin); t2g
4
eg
0
Inert [Cr(CN)6]4-
d5
(high-spin); t2g
3
eg
2
Labile [Mn(H2O)6]2+
d5
(low-spin); t2g
5
eg
0
Inert [Mn(CN)6]4-
d6
(high-spin); t2g
4
eg
2
Inert [Mn(H2O)6]2+
d6
(low-spin); t2g
6
eg
0
Inert [Fe(CN)6]4-
d7
, d8
, d9
, d10 Labile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-7-320.jpg)







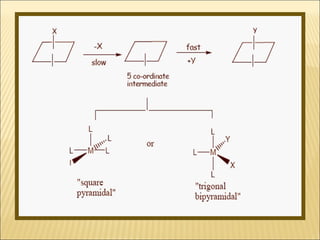

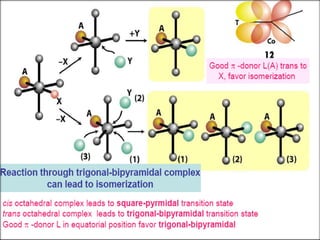

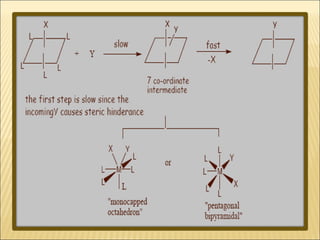







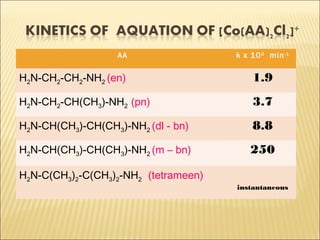
![ Ammine complexes of Co(III) are the most
studied.
Water is the medium of reaction.
Usually replacement of NH3 derivatives is
very slow, so only other ligands are
considered.
[Co(NH3)5X]2+
+ H2O [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+
+ X-
Rate = k. [Co(NH3)5X]2+
. [H2O]
Rate = k’. [Co(NH3)5X]2+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-36-320.jpg)

![ The increase in positive charge decreases the rate
of reaction following a dissociative mechanism
because the breaking the metal-ligand bond
becomes difficult.
For aquation of the Ru complexes the trend is as
shown
[RuCl6]3-
1.0 s-1
[RuCl3(H2O)3]0
2.1 x 10-6
s-
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-38-320.jpg)
![Complex Rate constant S-1
[Co(NH3)5(NO3)]2+
~ 10-5
[Co(NH3)5I]2+
~ 10-6
[Co(NH3)5F]2+
~ 10-8
Thus it is proved that M-X bond
breaking is very much important
in aquation reactions than bond
formation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-39-320.jpg)
![ The rate of aquation of [Co(NH3)5X]2+
depends on the
stability of M-X bond.
If the M-X bond is more stable rate of reaction is
low.
The order of reactivity is
HCO3
-
>NO3
-
>I-
>Br-
>Cl-
>SO4
2-
> F-
>SCN-
>NO2
-
This is the order of decreasing thermodynamic
stability of the complexes formed with these groups](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-40-320.jpg)

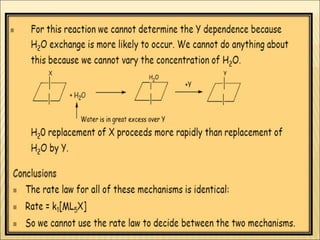
![ Another important experimental support for
this observation is that ligand exchange
reactions do not take place directly but
instead takes place through aquation and
then anation.
[Co(NH3)5X]2+
+ Y-
[Co(NH3)5Y]2+
+ X-
This indicates that the Co-X bond breaking is very much
significant and then whatever species is present at a higher
concentration will add in anation reaction. Thus, nature of Y-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-42-320.jpg)


![Complex k x 104
S-1
Complex k x 104
S-1
Cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
Very fast [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
(0)
4.0
Cis-[Co(en)2Cl2]+
150 [Co(en)2(NH3)Cl]2+
(2)
0.85
Cis-[Co(trien)Cl2]+
90 [Co(tren)(NH3)Cl]2+
(3)
0.40
trans-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+
1100 [Co(en)(dien)
(NH3)Cl]2+
(3) 0.31
trans-[Co(en)(NH3)2Cl2]+
130 [Co(tetren)Cl]2+
(4)
0.15
trans-[Co(en)2Cl2]+
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/san-rxn-161013152648/85/Reactions-of-complexes-45-320.jpg)