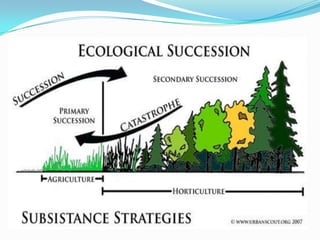
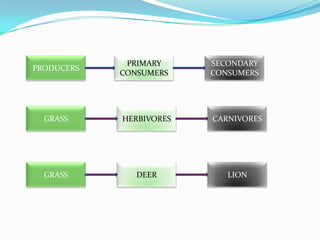
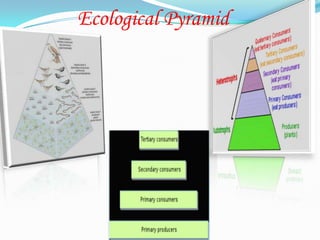
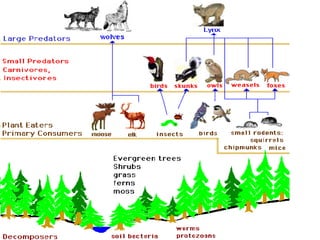
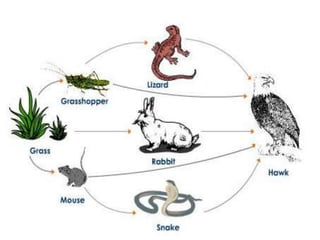
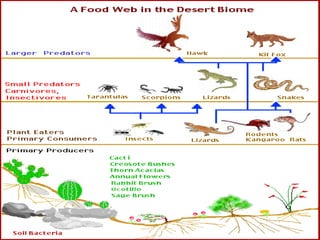
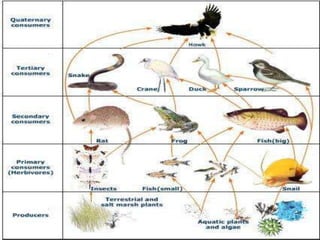
The document discusses various topics in ecology including ecosystems, ecological succession, food chains, food webs, and different types of ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, deserts, and aquatic ecosystems. It provides information on key concepts such as how ecosystems are defined, the process of ecological succession, how energy passes between producers and consumers in food chains and webs, and examples of different forest, grassland, desert and aquatic ecosystems. In the end, it emphasizes man's responsibility to conserve and protect ecosystems.