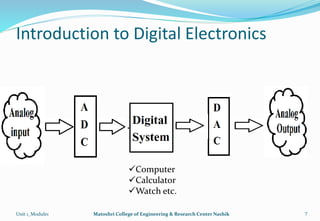
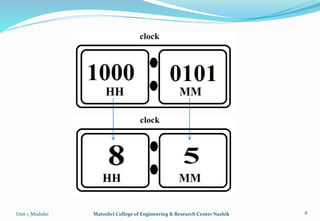
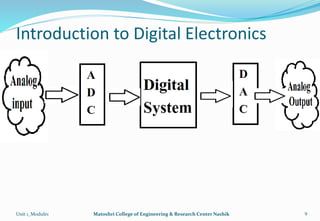
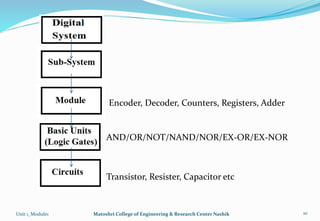
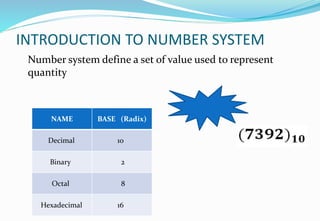
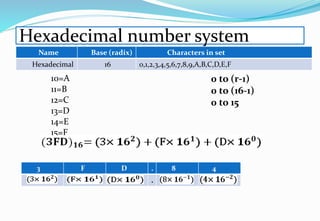
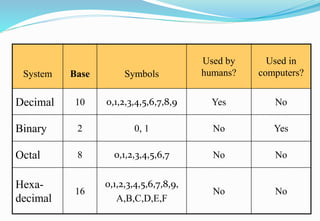
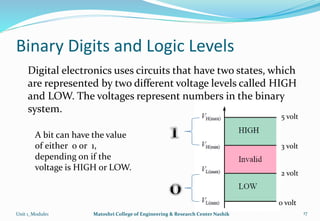
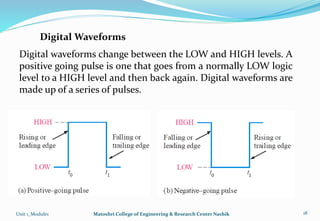
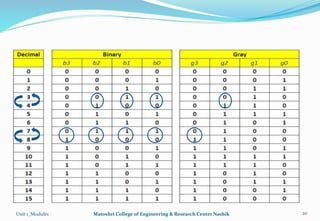
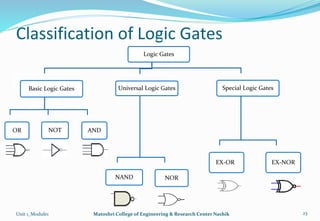
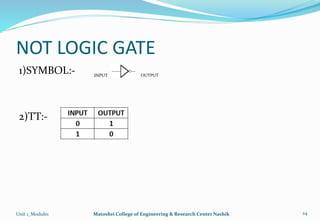
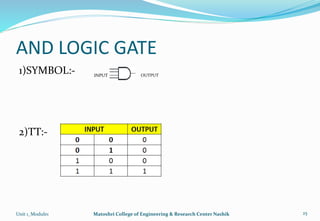
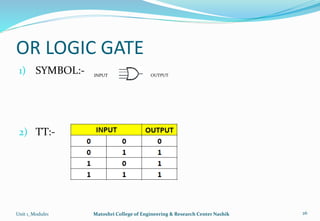
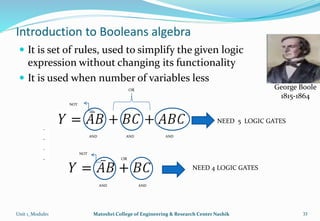
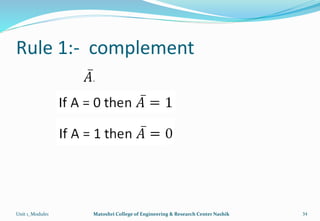
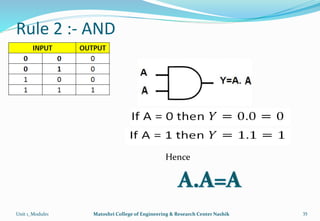
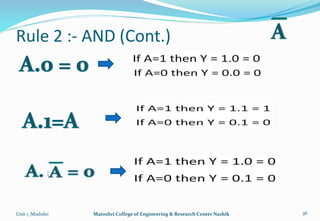
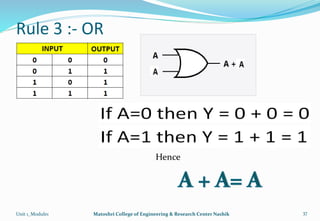
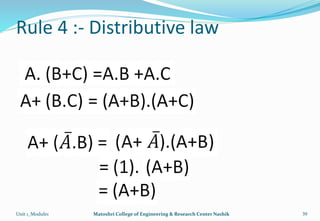
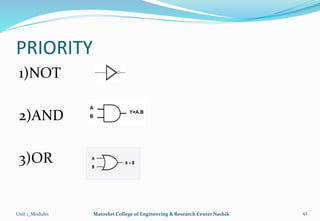
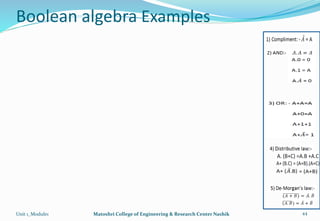
The document provides an overview of the Analog and Digital Electronics course taught at Matoshri College of Engineering & Research Centre. It includes information about the course's teaching scheme, examination scheme, objectives, and outcomes. The objectives are to design logical, sequential and combinational digital circuits using K-maps and to develop concepts related to operational amplifiers and rectifiers. The document also provides details of the topics to be covered in the first unit including Boolean algebra, K-maps, and the design of combinational circuits. It introduces concepts such as logic gates, number systems, and digital signals.

![203143: Analog And Digital Electronics
Teaching Scheme
Lecture : 03 Hrs/ Week
Practical : 02 Hrs/ Week
Credits
Th: 03
PR:01
Examination Scheme [Marks]
In Sem : 30 Marks
End Sem : 70 Marks
Practical : 50 Marks
Unit 1_Module1 Matoshri College of Engineering & Research Center Nashik 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1-210305050002/85/module1-Introduction-to-digital-electronics-2-320.jpg)