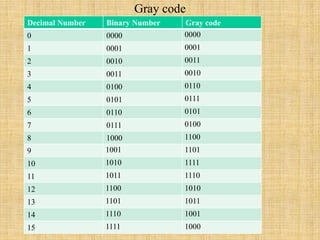
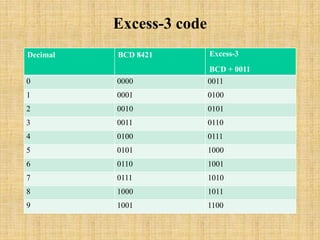
The document provides an introduction to various computer codes and number systems used in digital computing, including BCD, EBCDIC, ASCII, Gray code, Excess-3 code, and Unicode. Each code is explained with its purpose, structure, and application, highlighting their significance in representing data and character encoding. Unicode is emphasized as a universal standard capable of encoding up to 1 million characters across multiple languages.