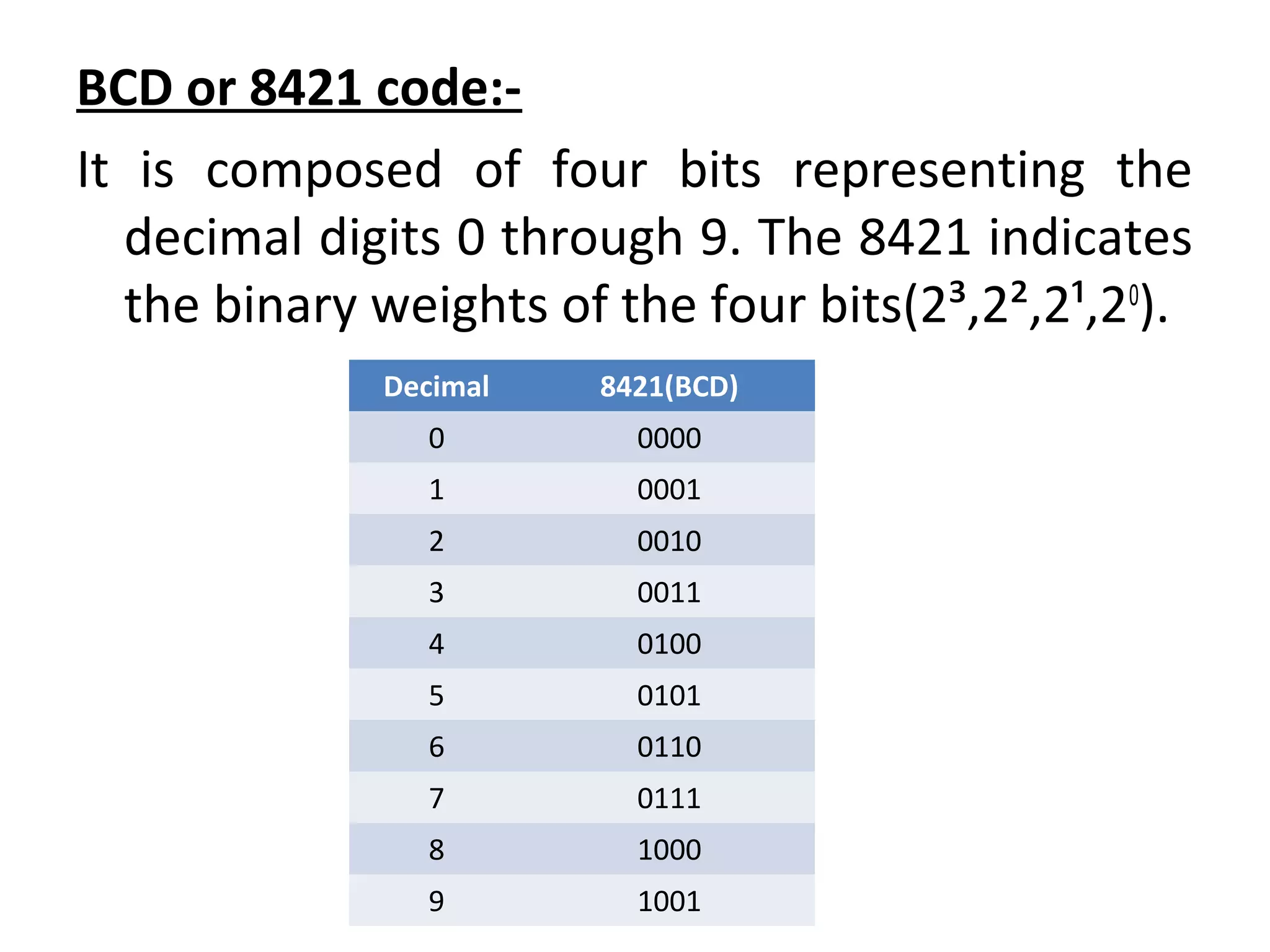
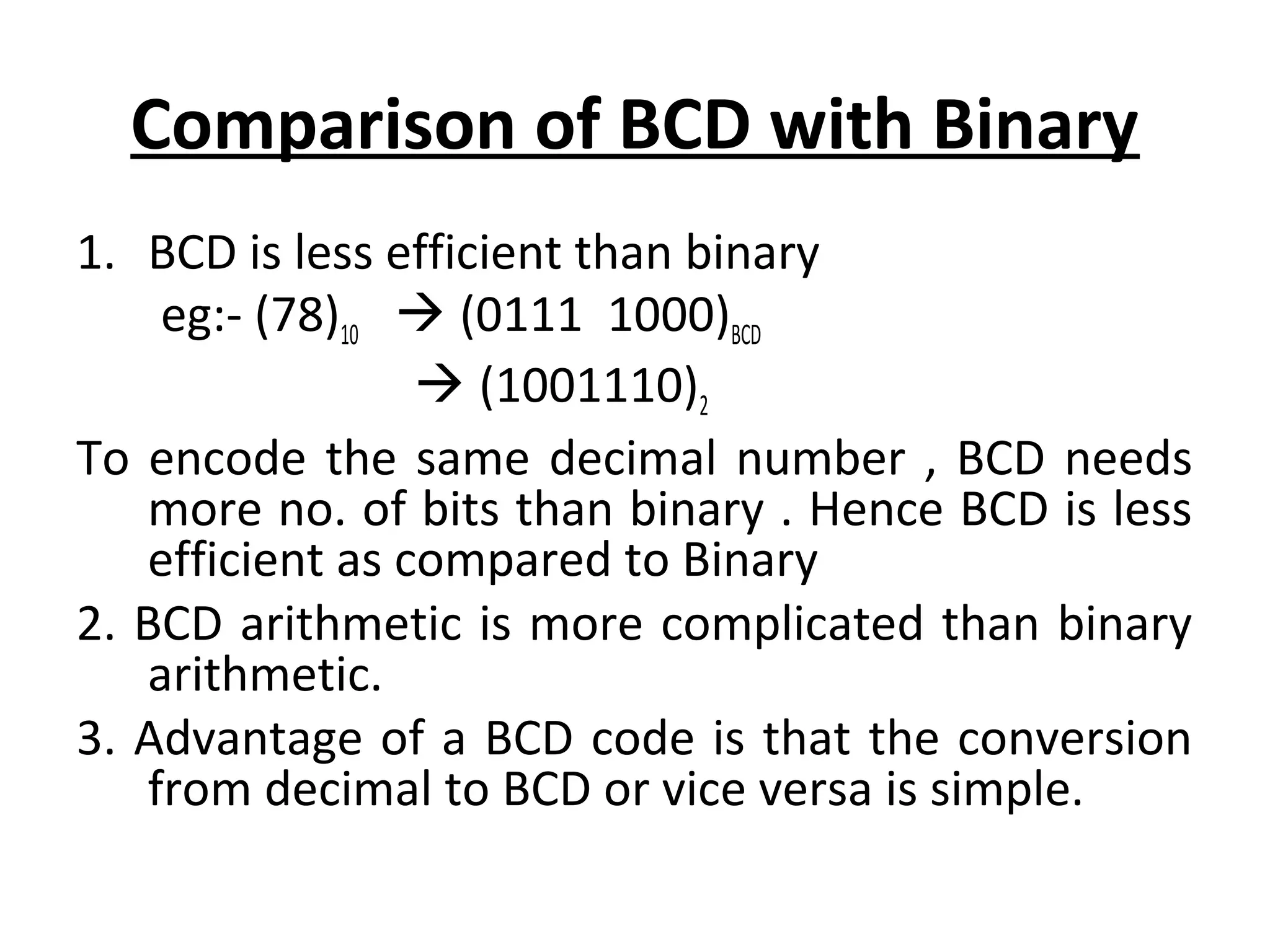
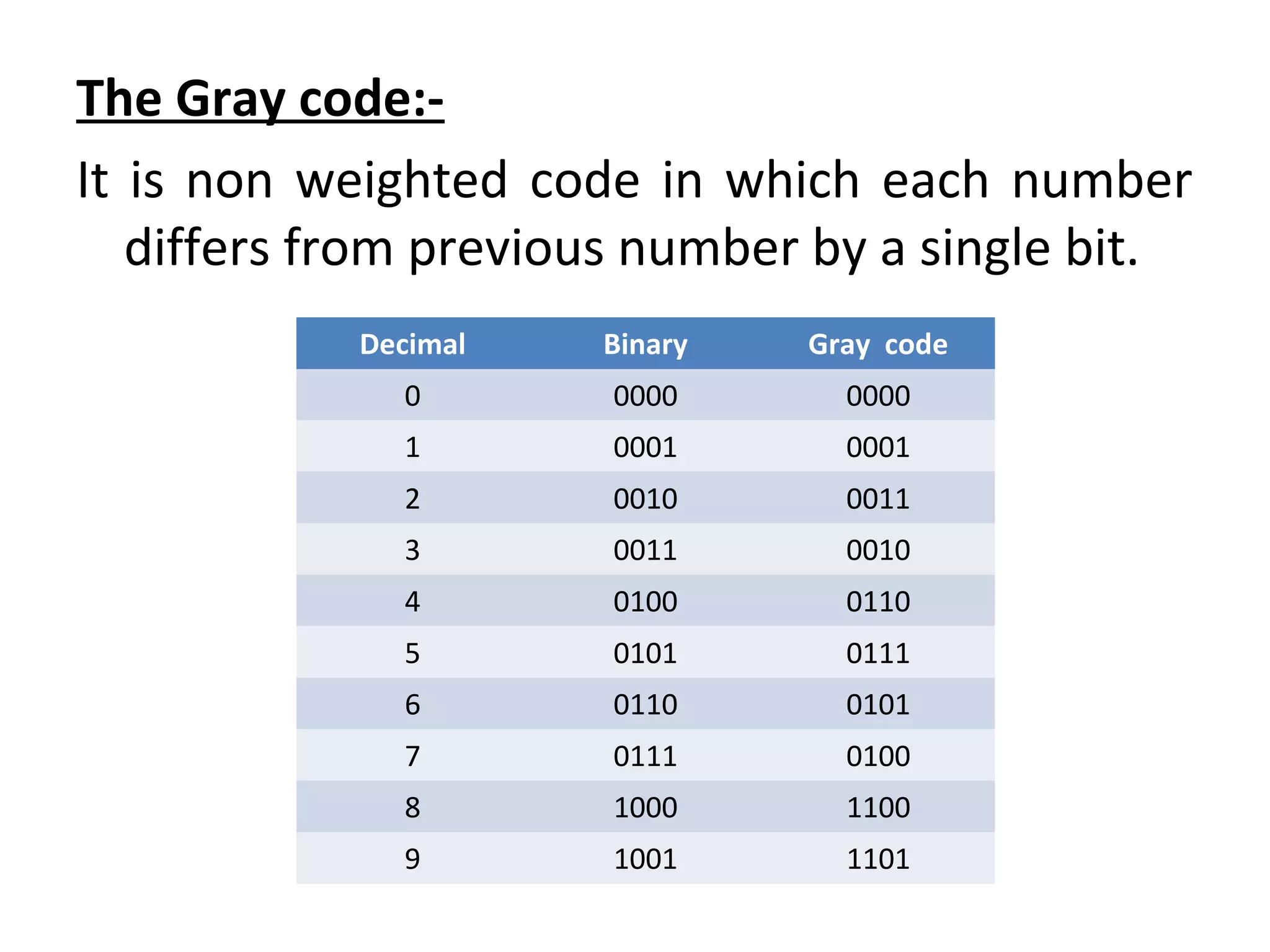
Weighted codes assign a positional weight or value to each digit, where the sum of the digit values multiplied by their weights represents the number. Non-weighted codes do not assign positional weights. BCD is a weighted 4-bit code that represents the decimal digits 0-9. It uses weights of 24, 23, 22, 21 from most to least significant bit. The Gray code is a non-weighted code where each number differs from the previous by one bit. Excess-3 code is a non-weighted 4-bit BCD code where 3 is added to each decimal digit before conversion to BCD.