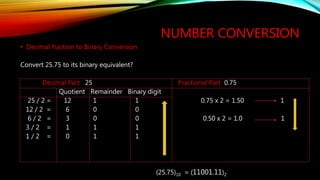
The document discusses computer memory structures and data storage units. It begins by defining basic memory units like bits, bytes and words. It then explains progressively larger units of data storage from kilobytes to yottabytes. The document also covers number systems, specifically decimal and binary. It provides examples of converting between binary, decimal and decimal fraction numbers. Conversions include binary to decimal, decimal to binary, and binary fraction to decimal fraction.