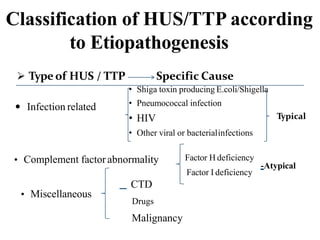
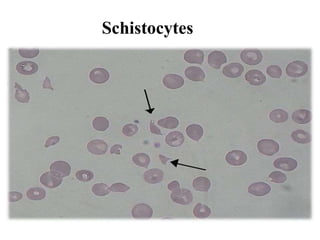
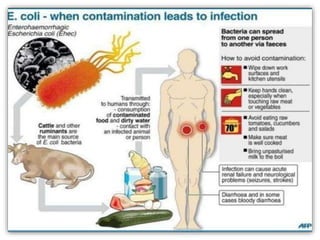
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease characterized by hemolytic anemia, low platelet count, and kidney failure. It is predominantly seen in children and can be typical (caused by E. coli or Shigella infection) or atypical (caused by complement abnormalities or other infections). Treatment involves supportive care, antibiotics for infections, and plasma therapy for complement abnormalities to replace deficient factors. With aggressive treatment, over 90% of patients survive the acute phase, though some may have long term kidney or other organ damage.