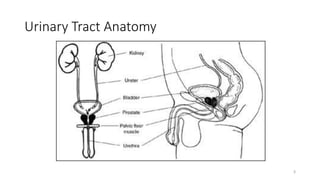
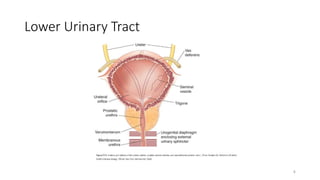
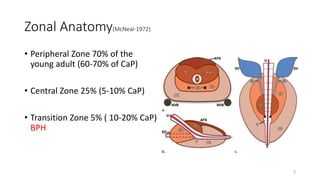
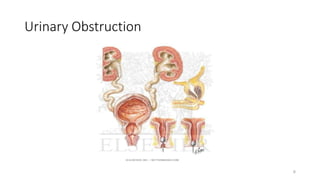
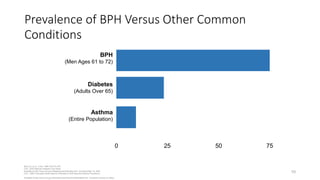
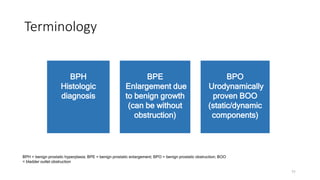
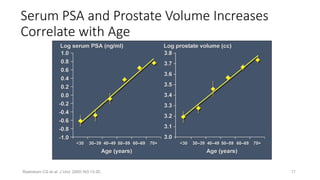
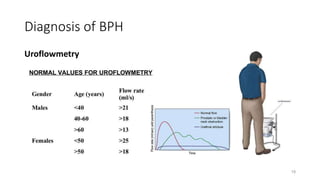
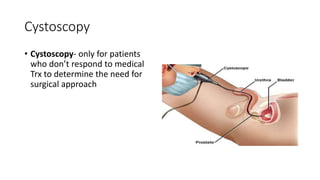
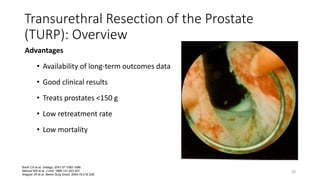
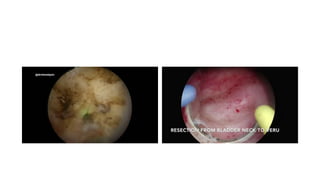
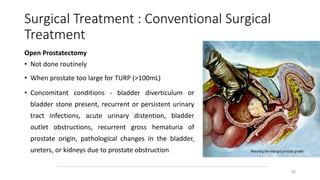
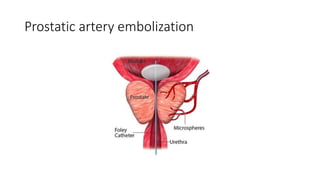
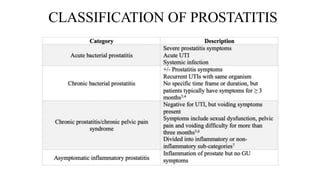
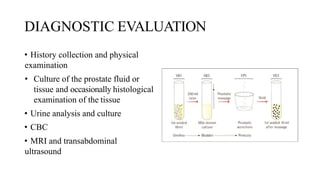
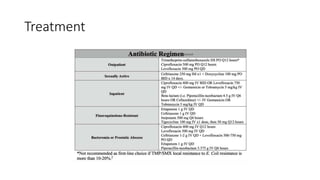
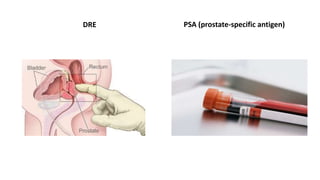
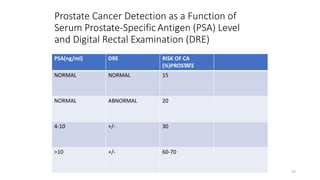
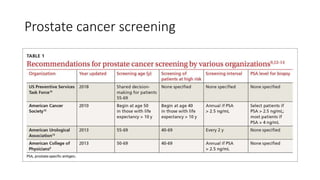
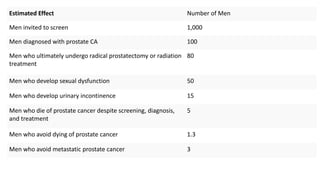
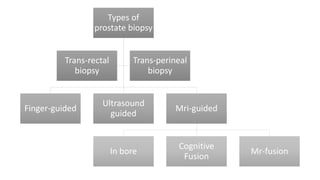
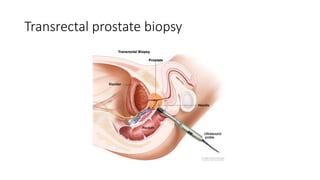
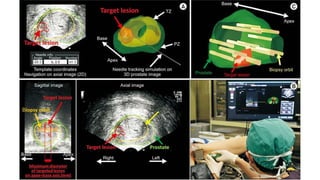
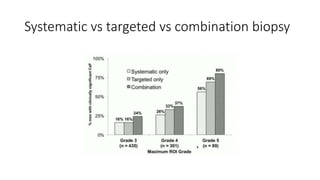
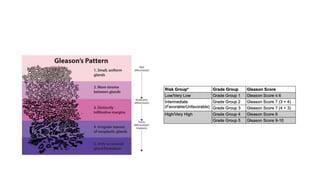
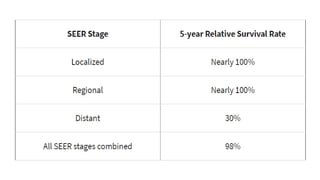
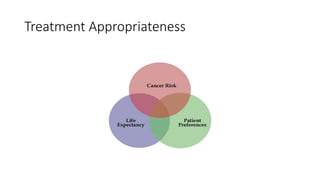
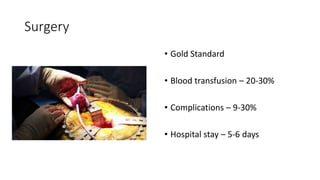
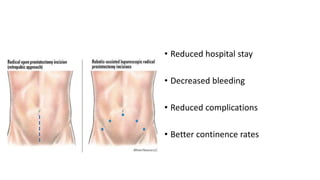
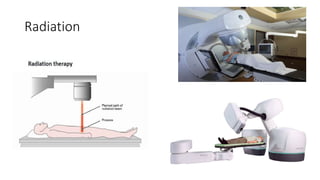
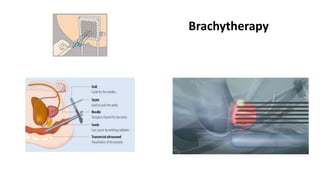
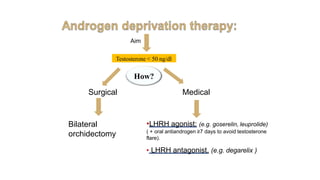
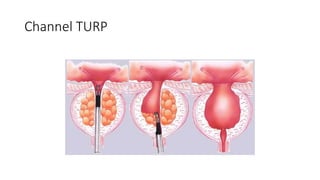
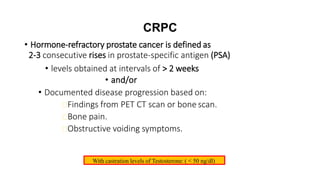
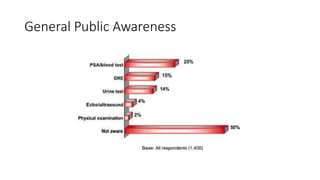
Prostate diseases are common among aging men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that leads to urinary symptoms. BPH prevalence increases with age, affecting 20% of men aged 41-50 and over 80% of men aged 81-90. Treatment options for BPH include lifestyle changes, watchful waiting, medical therapy with alpha blockers or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, and surgical procedures like TURP. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men. Screening includes a PSA test and digital rectal exam. Treatment depends on cancer risk and may include active surveillance, surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy.