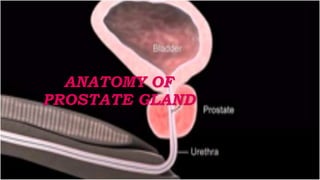
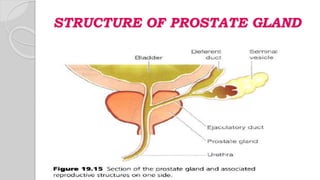
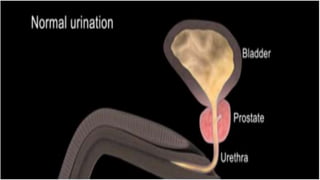
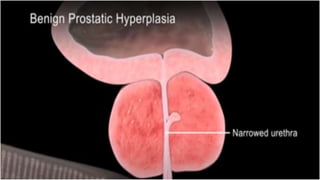
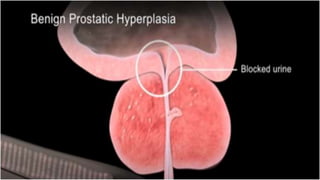
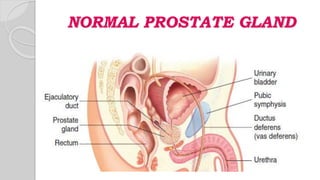
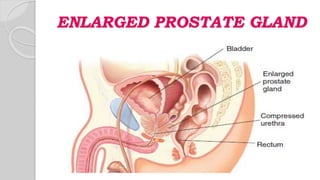
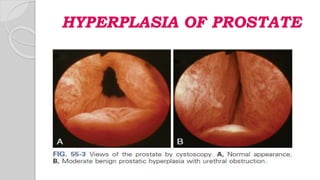
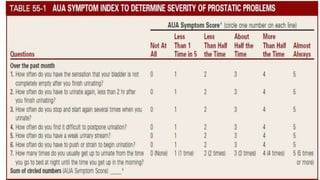
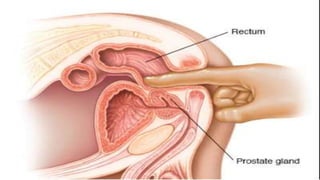
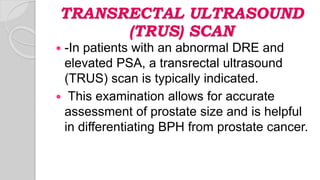
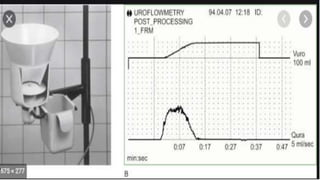
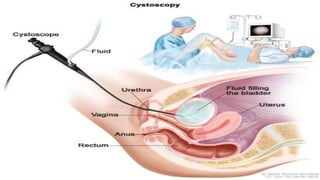
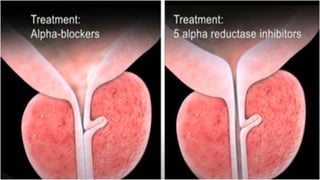
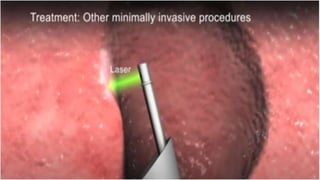
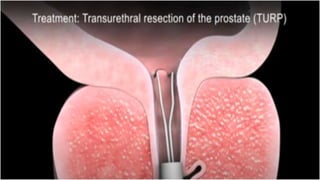
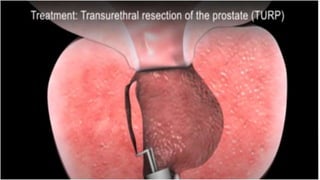
This document discusses benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as an enlarged prostate. It begins by covering the anatomy and physiology of the prostate gland. It then defines BPH, describes its causes including hormonal changes, and risk factors like aging and obesity. The document outlines the pathophysiology of BPH in which dihydrotestosterone stimulates prostate cell growth. It also covers the clinical manifestations of BPH including irritative and obstructive symptoms. Diagnostic tests and treatments are summarized, including drug therapies, minimally invasive procedures like TUMT and TUNA, and laser prostatectomy.






















































































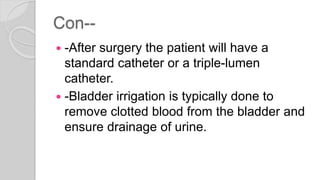













![Con--
- If bladder spasms develop, check the
catheter for clots.
-If present, remove the clots by irrigation so
that urine can flow freely.
-Belladonna and opium suppositories or
other antispasmodics (e.g., oxybutynin
[Ditropan]), along with relaxation
techniques, are used to relieve the pain
and decrease spasm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bphnprostatetectomy-210529082338/85/Benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-BPH-119-320.jpg)













![Con--
(4) observing for signs and symptoms of
urinary tract and wound infection;
(5) preventing constipation;
(6) avoiding heavy lifting (more than 10 lb
[4.5 kg]); and
(7) refraining from driving or intercourse
after surgery as directed by the physician.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bphnprostatetectomy-210529082338/85/Benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-BPH-133-320.jpg)