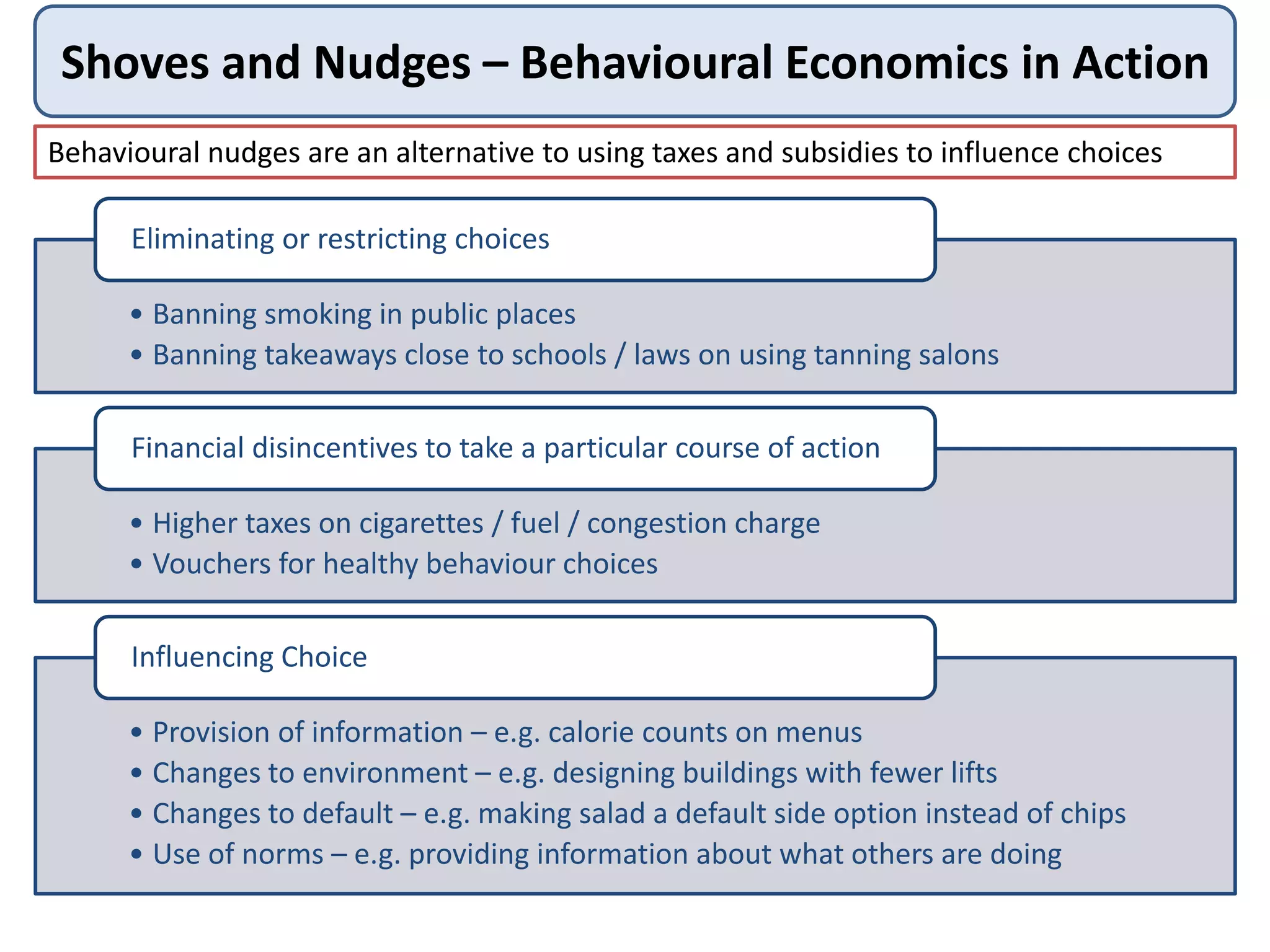
This document introduces concepts from behavioural economics, including bounded rationality and heuristics. It discusses how social, emotional, and psychological factors can influence economic decisions in non-rational ways. Examples are given of how choice architecture, defaults, framing, and other cognitive biases shape choices. Behavioural economics aims to design "nudges" through subtle changes that guide people towards making beneficial decisions. However, some argue that nudging risks excessive paternalism or underestimating consumer rationality.