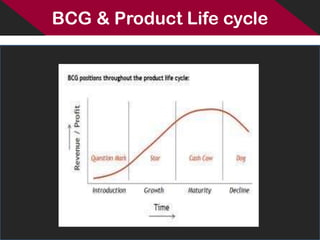
The BCG matrix is a portfolio analysis tool developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the early 1970s. It uses a 2x2 grid to classify businesses based on their market share and market growth. Businesses fall into one of four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. Stars have high market share and growth, cash cows have high share but low growth, question marks have low share but high growth, and dogs have low share and growth. The matrix is used to analyze how much investment each business requires and its potential to become more profitable. However, it also has limitations as market share and growth alone do not determine profitability and the categories can be too simplistic.