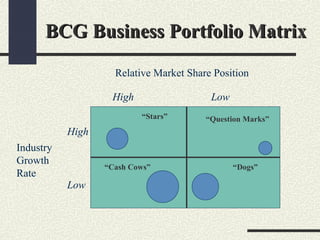
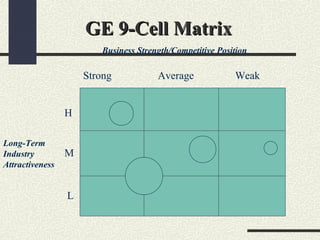
This document provides an overview and comparison of the BCG Growth-Share Matrix and GE 9-Cell Matrix portfolio analysis tools. The BCG Matrix uses industry growth rate and relative market share to categorize businesses into Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs. It encourages viewing a firm as a collection of cash flows but oversimplifies some factors. The GE 9-Cell Matrix adds long-term industry attractiveness and business strength as dimensions, allowing intermediate rankings. It suggests investment priorities but provides no specific strategy guidance. Both tools have limitations around being static rather than dynamic analyses.