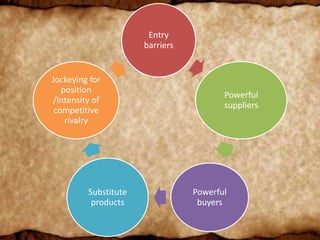
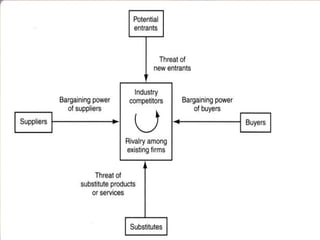
The document discusses Porter's five forces model as it applies to the apparel industry. It analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability of the industry by looking at the barriers to entry, power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors. The summary is:
[1] The apparel industry has high barriers to entry due to economies of scale, significant capital requirements, and intense competition from established brands.
[2] Suppliers have bargaining power when materials are unique or undifferentiated, while buyers wield power in bulk purchases or when many supplier options exist.
[3] Substitute brands pose a threat if switching costs are low based on quality or status.