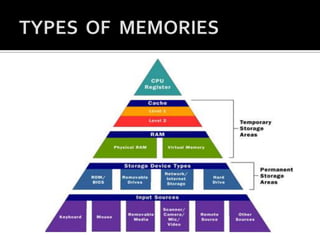
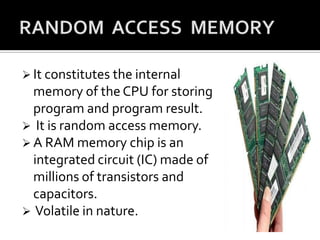
This document discusses the different types of computer memory. It describes cache memory as a buffer between the CPU and main memory that is less than 512 KB in size. It stores frequently used data and programs. Main memory, also called primary memory, is semiconductor memory that holds the data and instructions currently being processed; it is volatile and includes RAM and ROM. RAM is random access memory that constitutes the CPU's internal memory, while ROM is read-only memory that permanently stores its contents. Secondary memory, also called external memory, is non-volatile storage like hard disks and USB drives that permanently store data and are slower than primary memory.