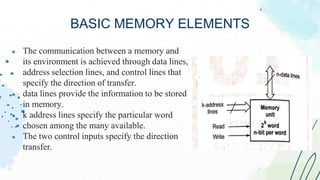
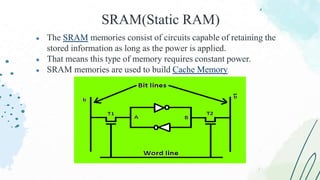
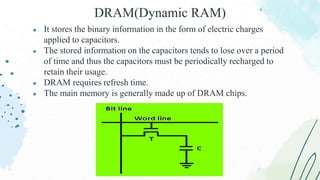
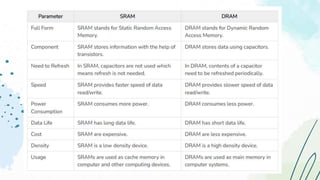
The document provides an overview of memory devices, detailing their structure, types, and functions. It explains the differences between volatile and non-volatile memory, with examples such as RAM, ROM, and various programmable memory types. Key concepts such as memory operations, data storage, and communication with external environments are also discussed.