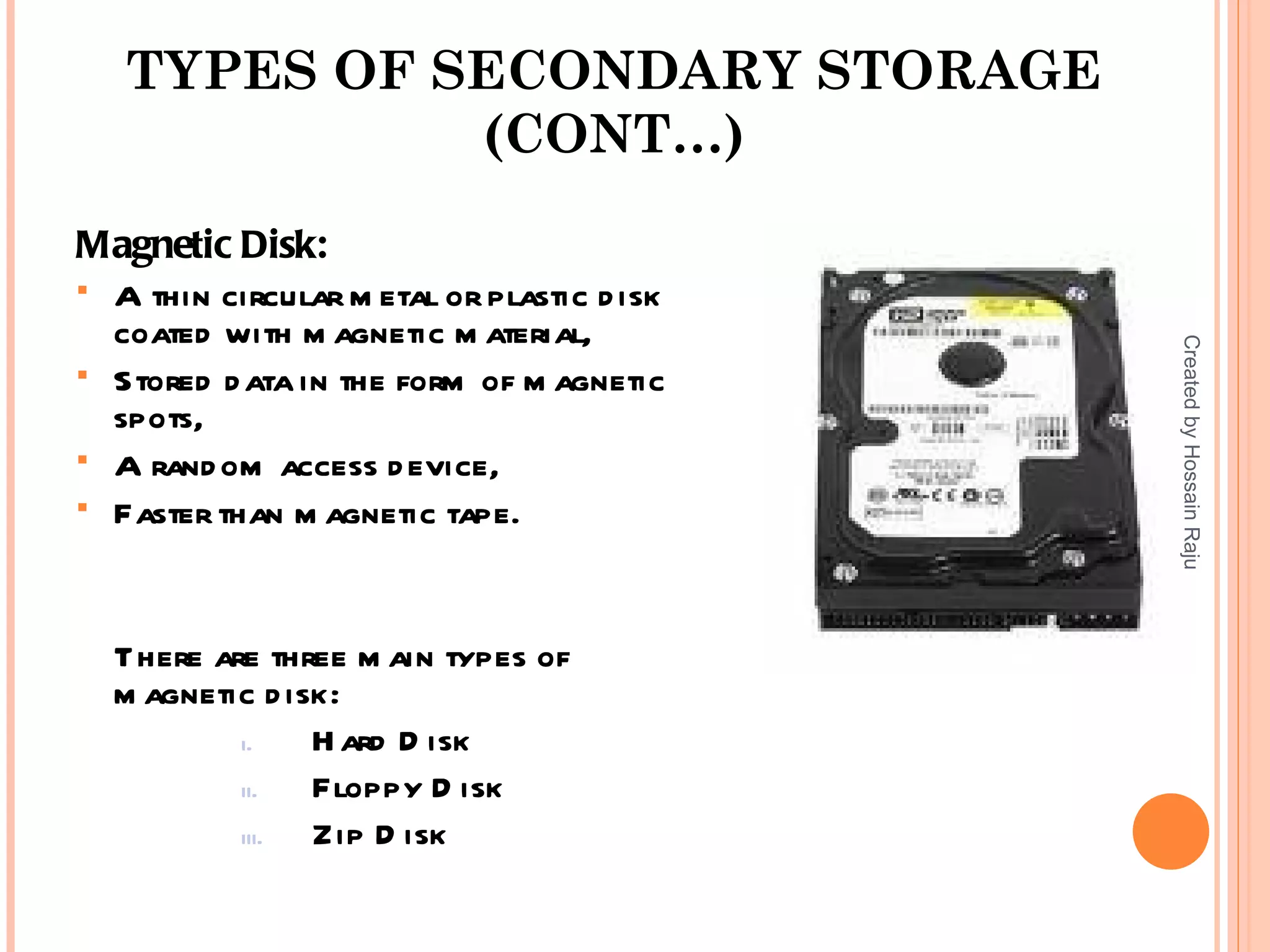
The document provides an overview of secondary storage, including its advantages and disadvantages. It discusses the evolution of secondary storage devices and the main types, which include magnetic tape, magnetic disks like hard disks and floppy disks, and optical disks like CDs, DVDs, and their variations. Secondary storage is used to overcome limitations of primary storage and provide virtually unlimited storage capacity to store large volumes of data permanently or for backup purposes.