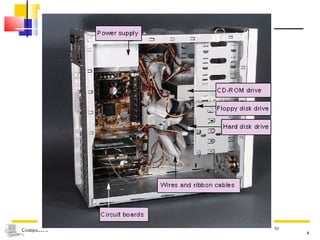
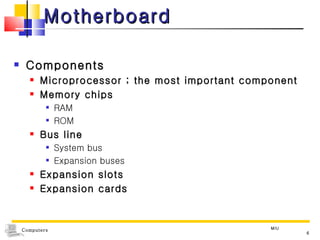
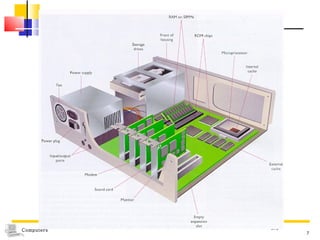
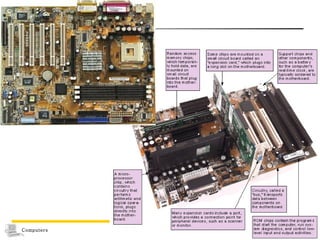
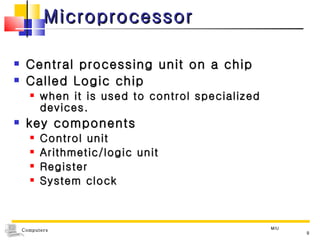
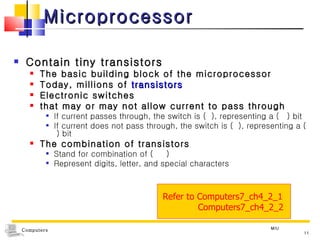
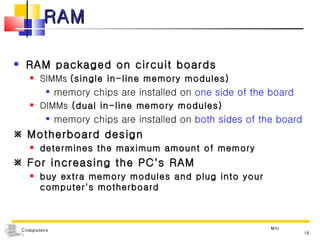
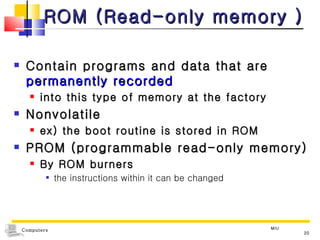
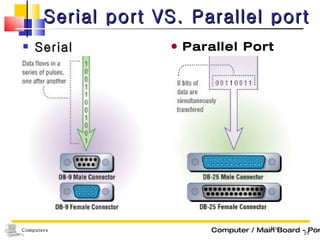
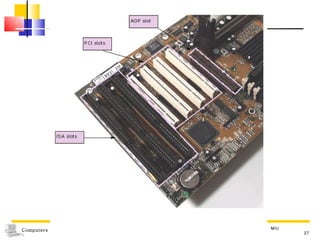
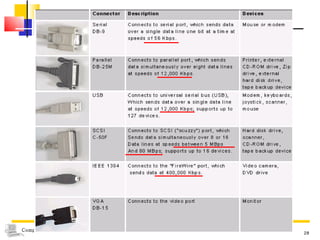
The document discusses the key components that make up a computer system unit. It describes the central processing unit, memory components like RAM and ROM, the motherboard, buses that transfer data, expansion cards and ports that connect peripheral devices. The system unit houses the electronic components and motherboard that organize the computer's activities.