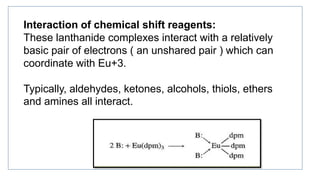
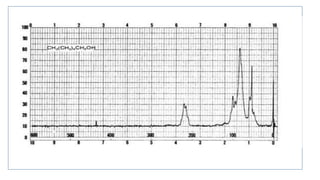
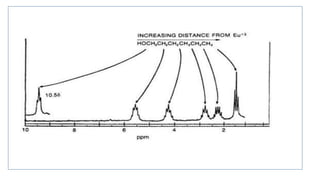
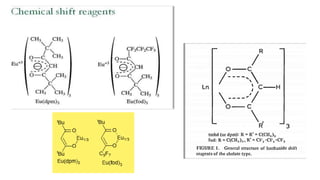
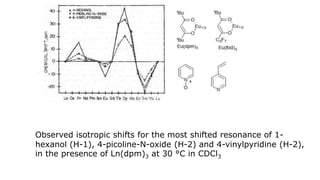
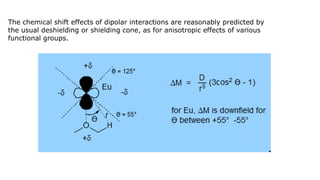
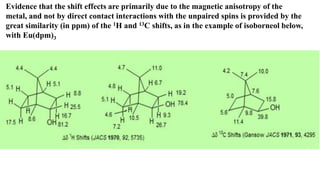
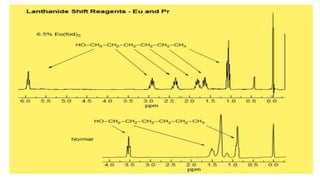
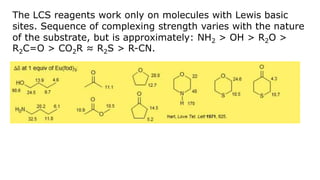
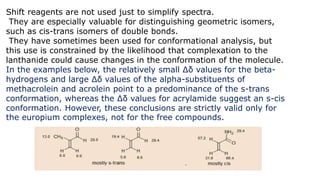
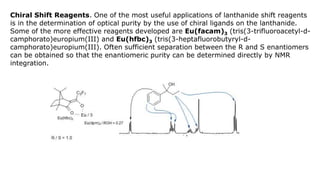
Lanthanide shift reagents are used in NMR spectroscopy to induce shifts in proton resonances. Europium complexes are commonly used shift reagents that cause downfield shifts, while cerium complexes cause upfield shifts. The amount of shift depends on the distance between the metal ion and protons, and the concentration of the shift reagent. Shift reagents simplify NMR spectra by resolving overlapping peaks and providing more detailed information about molecular structures. They are especially useful for distinguishing geometric isomers.