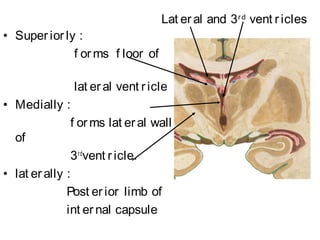
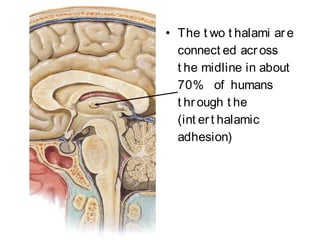
The document provides an overview of the diencephalon, which is the region of the brain between the cerebral hemispheres and below the thalamus. It describes the gross topography and borders of the diencephalon. The diencephalon includes the epithalamus, thalamus, metathalamus, subthalamus, and hypothalamus. Details are given on the structures and functions of these regions, including the thalamic nuclei and their connections. Clinical notes discuss lesions of the thalamus and how they can cause sensory loss or pain.