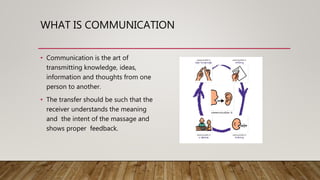
This document discusses various barriers to communication. It identifies physical, semantic/language, socio-psychological, organizational, and cross-cultural barriers. Physical barriers include large work areas, closed doors, and noise. Semantic barriers involve words with multiple meanings or pronunciations. Socio-psychological barriers stem from human psychology like inattention or status differences. Organizational barriers occur from message distortion between levels. Cross-cultural barriers involve differences in concepts of space, gestures, and traditions across cultures. The document provides recommendations to overcome these barriers through appropriate environments, simple language, active listening, understanding different cultures, and creating open communication channels.