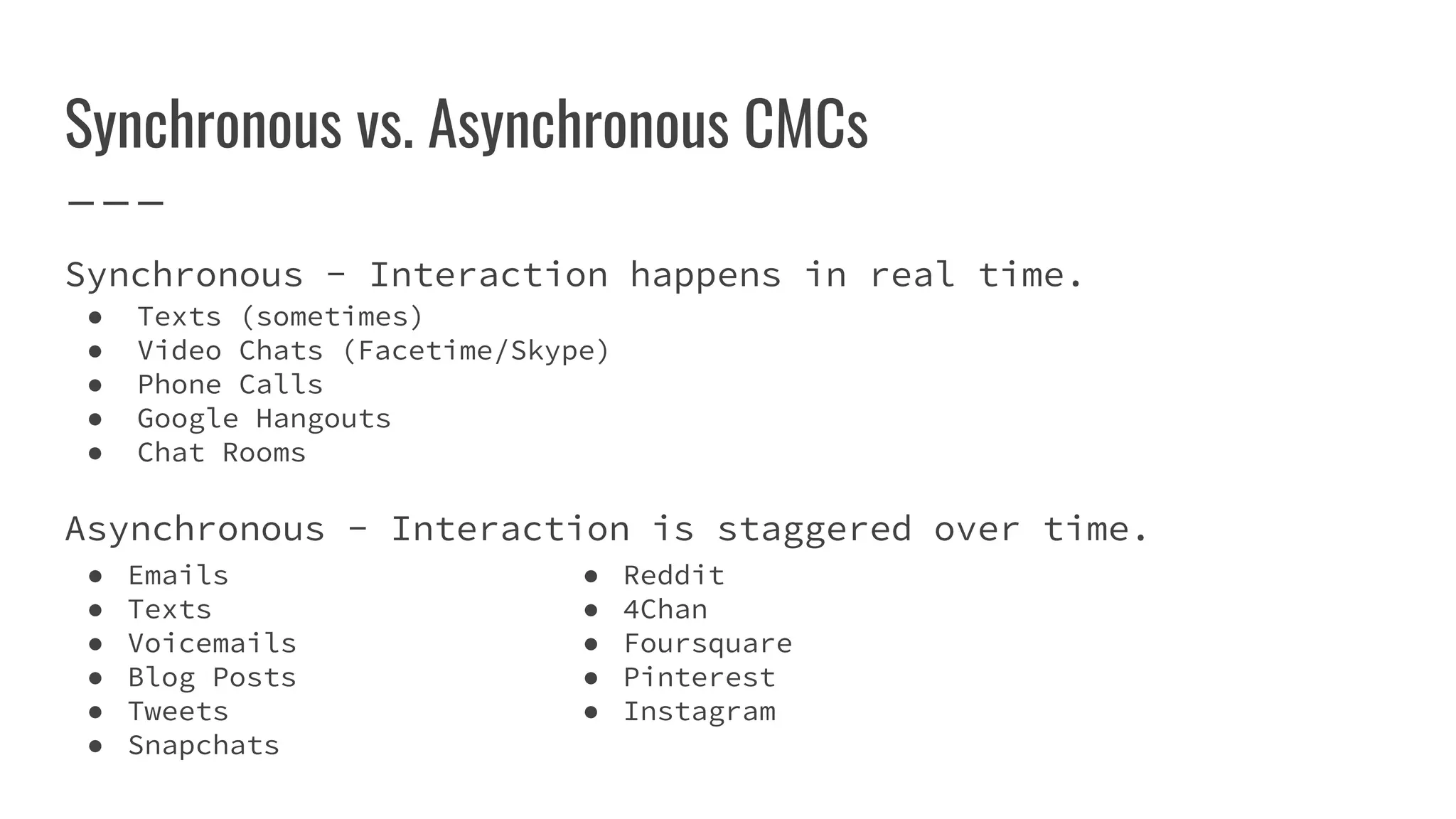
Computer-mediated communication (CMC) refers to human communication through digital devices like smartphones, computers, and tablets. CMC involves a sender composing a message and encoding it into a digital format to transmit through a medium to a receiver. It can be synchronous, with real-time interaction, or asynchronous with staggered interaction over time. CMC differs from face-to-face communication in that it lacks non-verbal cues and has a permanent record, and led to the development of emoticons and acronyms to convey tone. Social media further changed CMC by incorporating images, hashtags for indexing posts, and combining different media into messages.