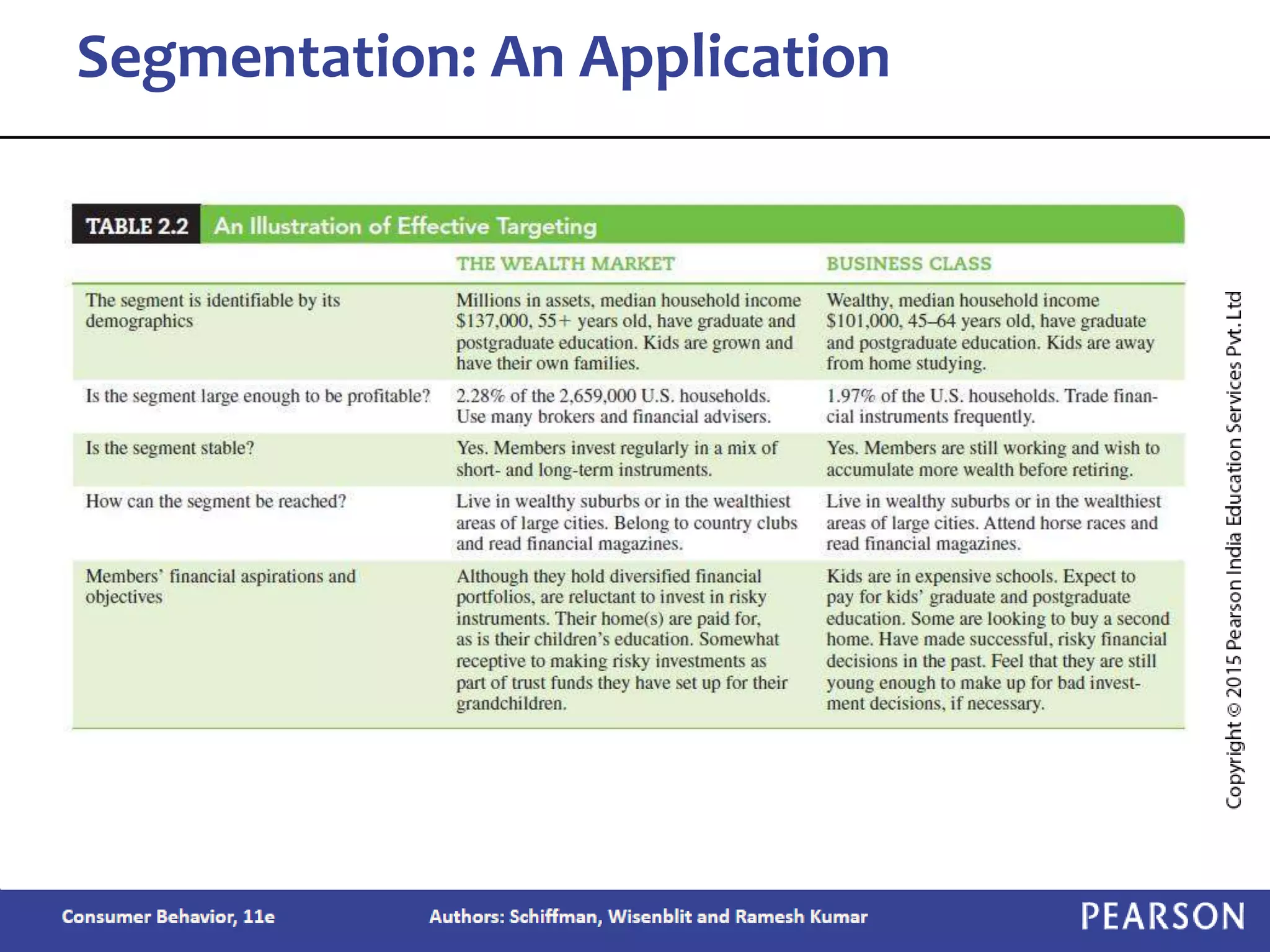
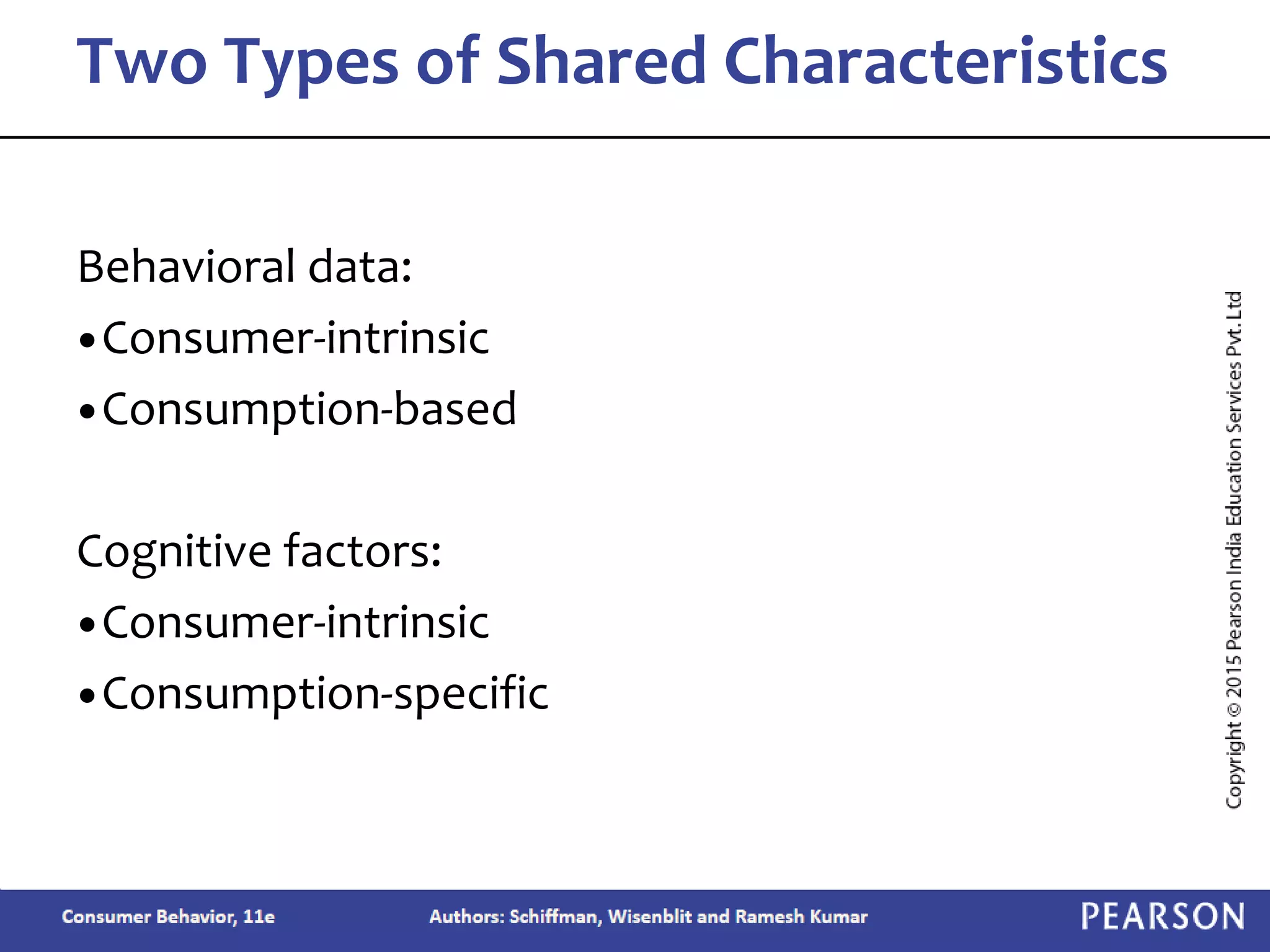
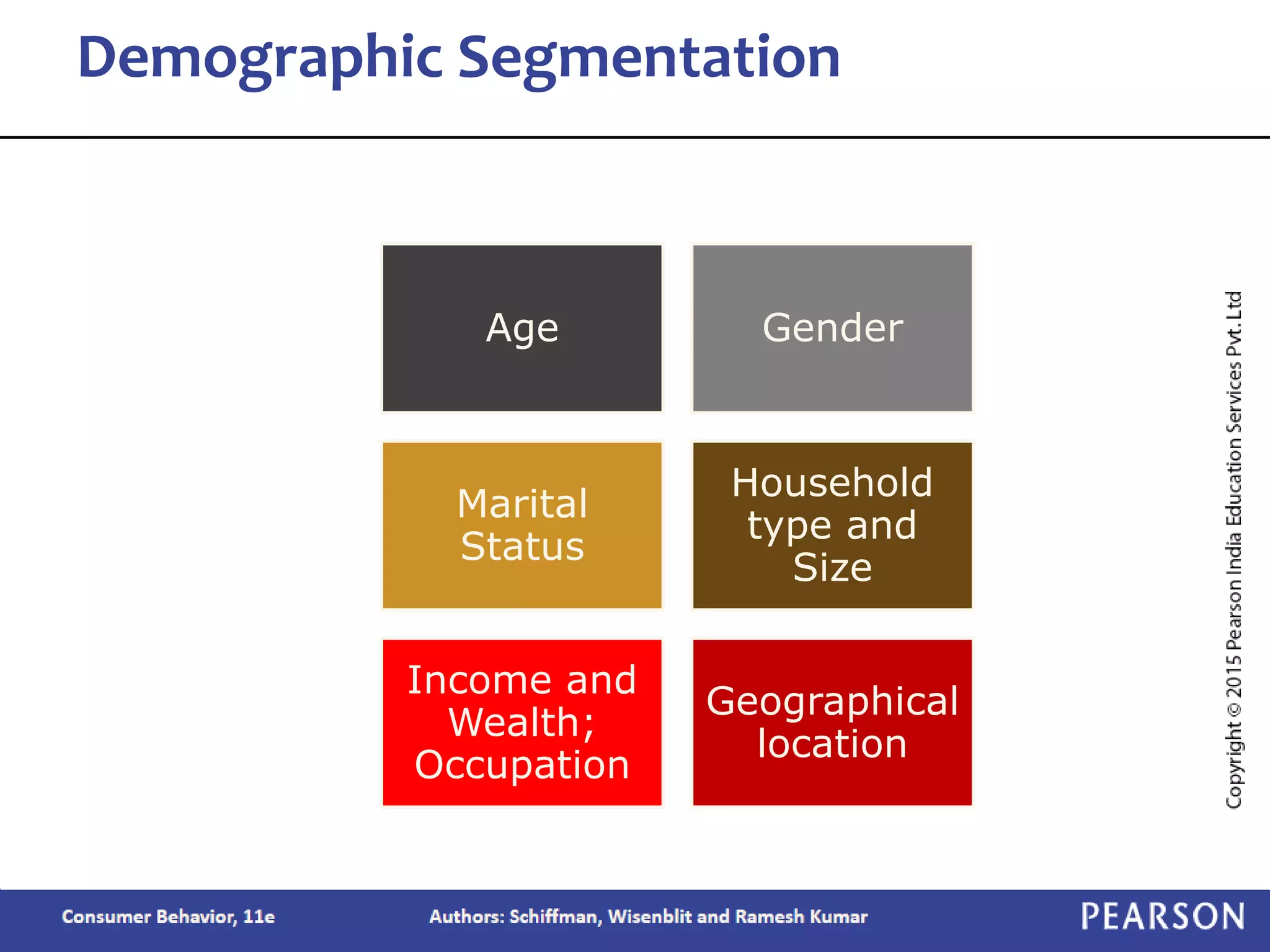
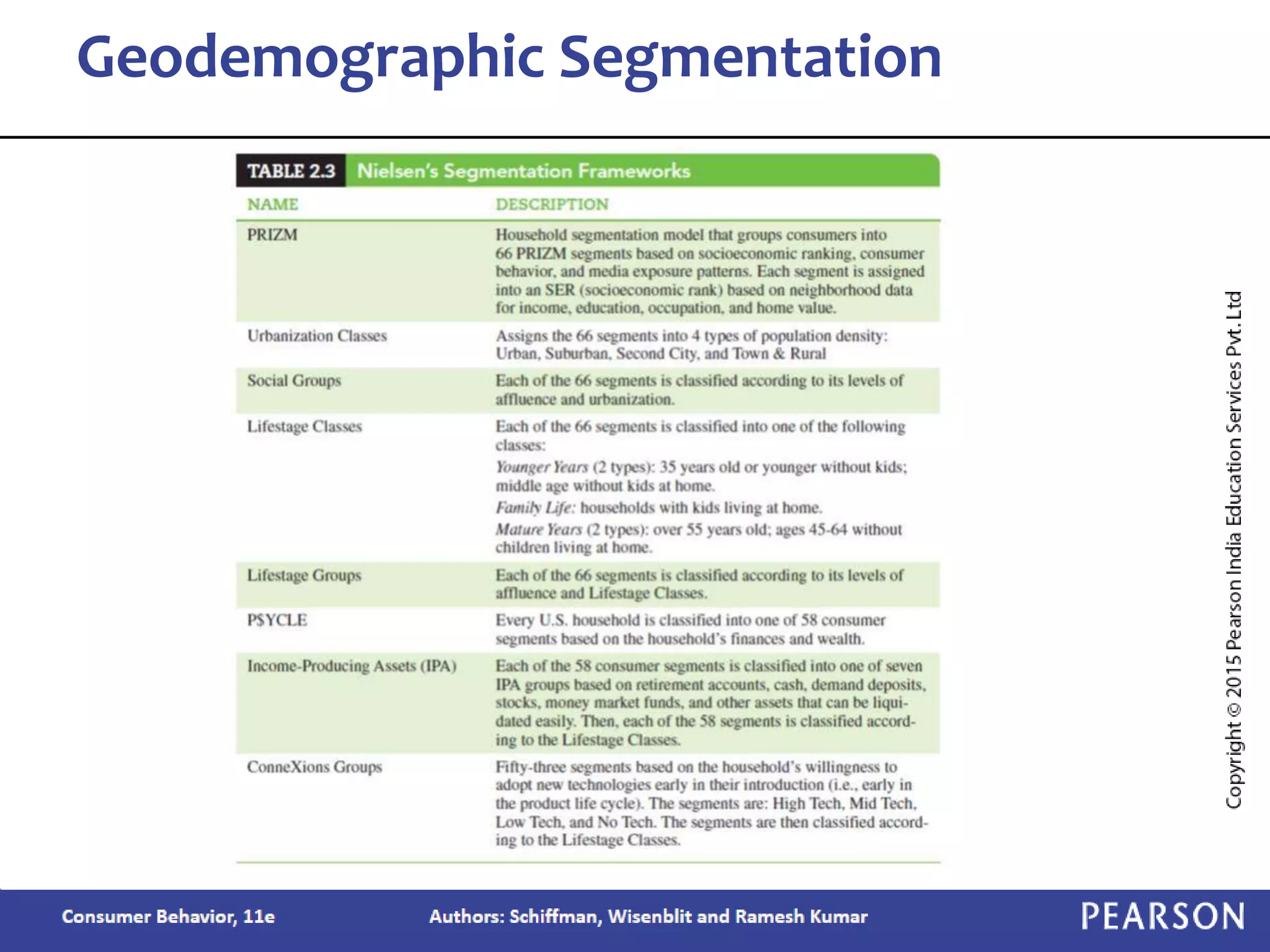
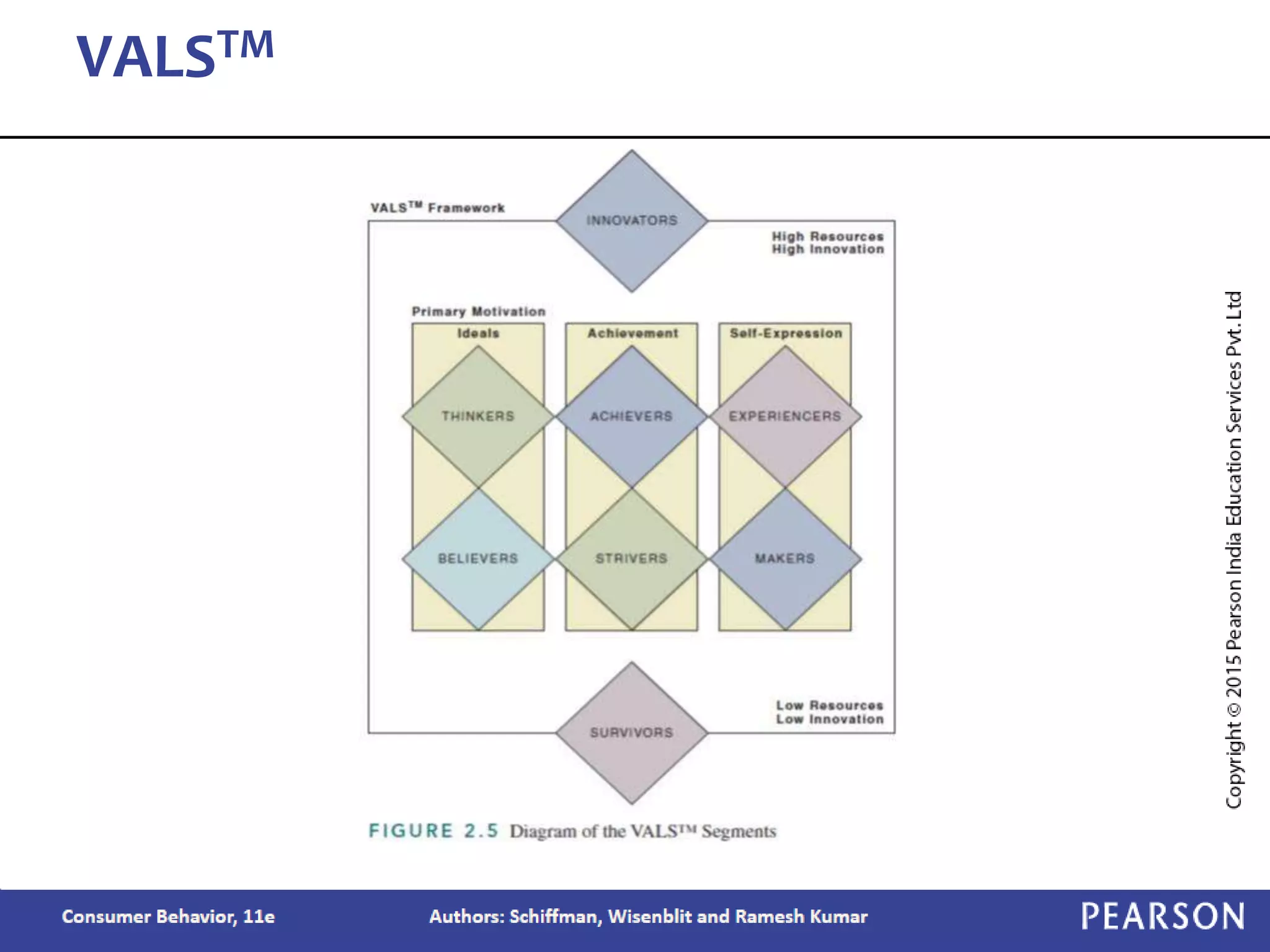
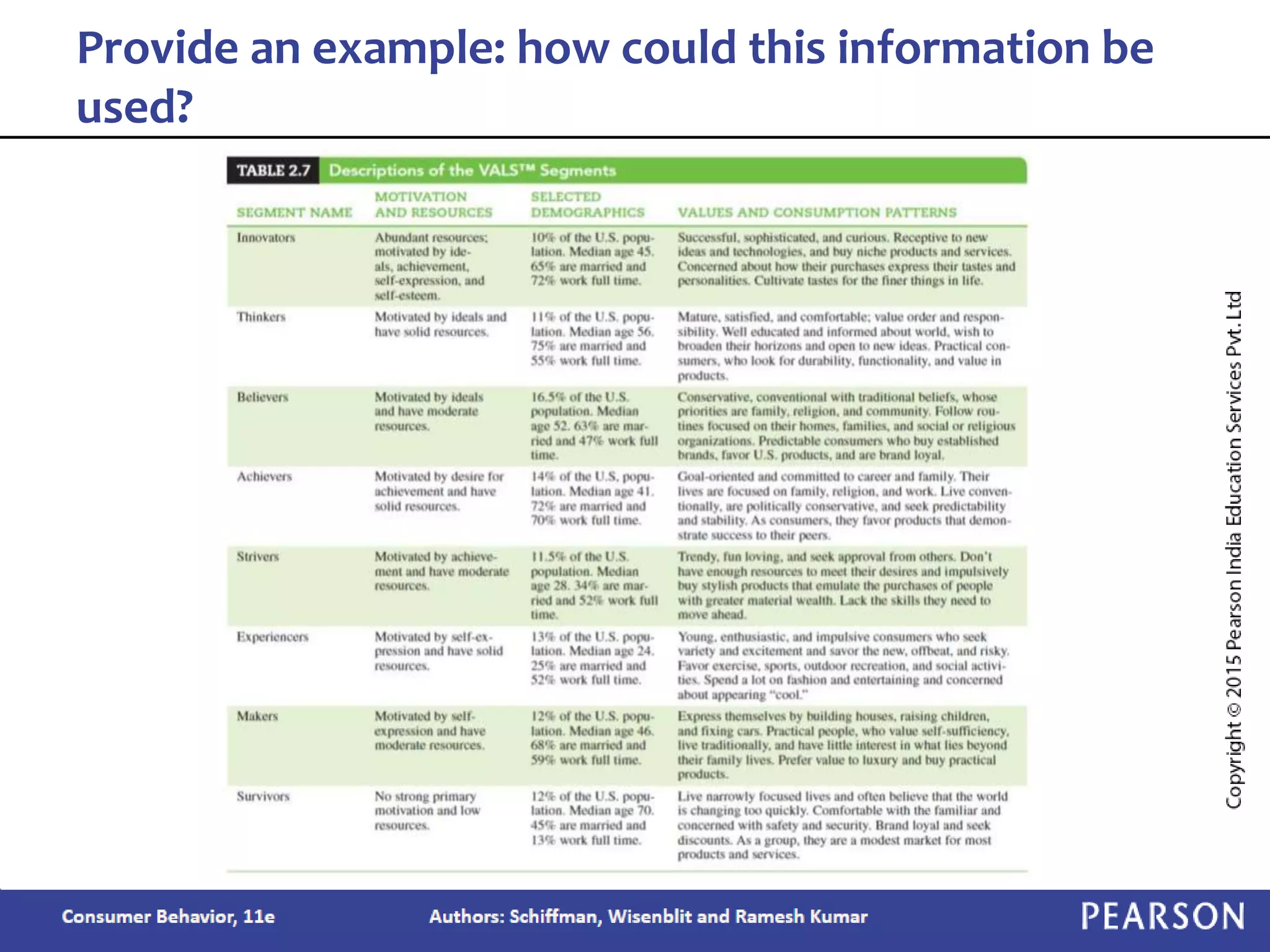
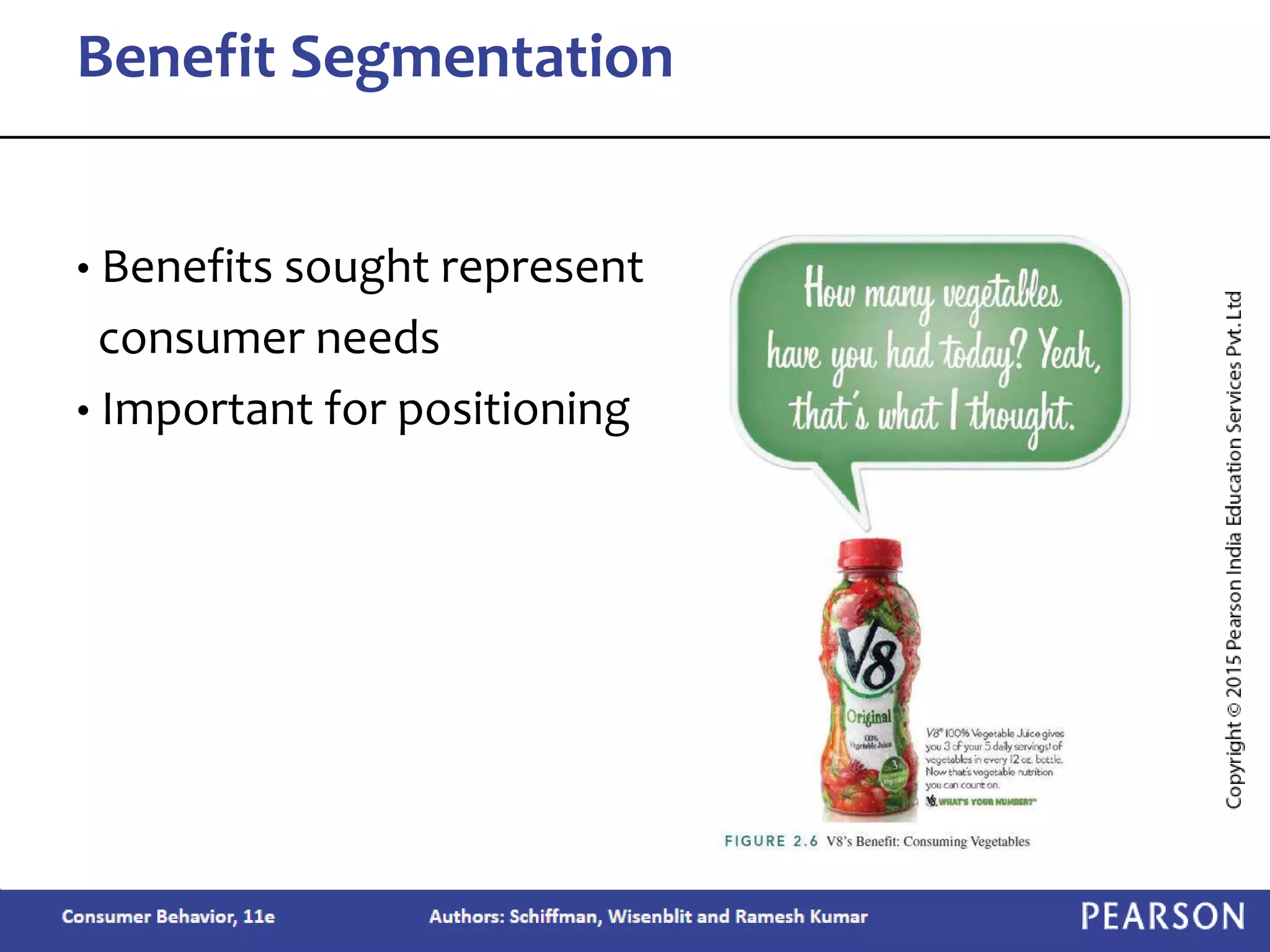
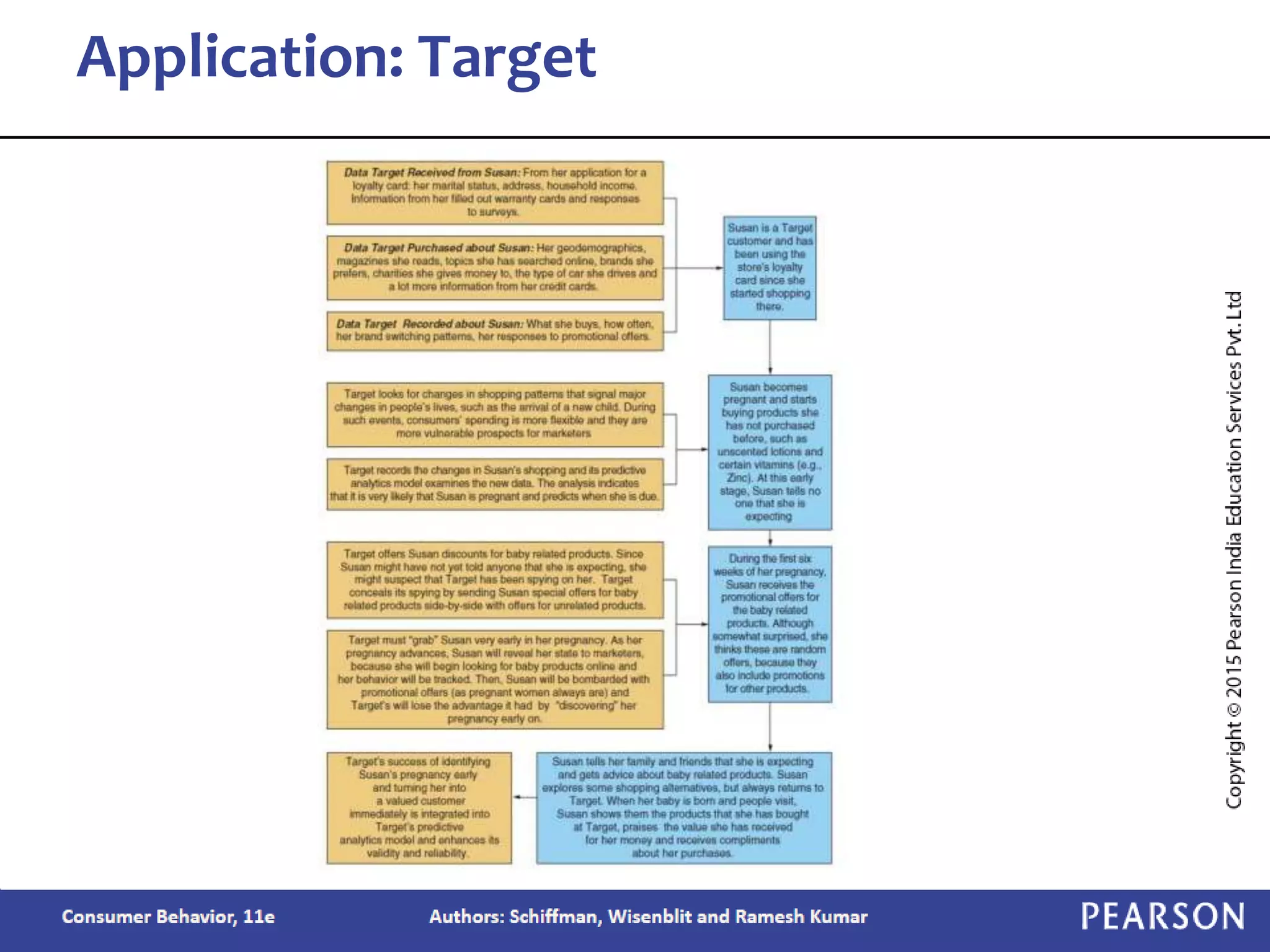
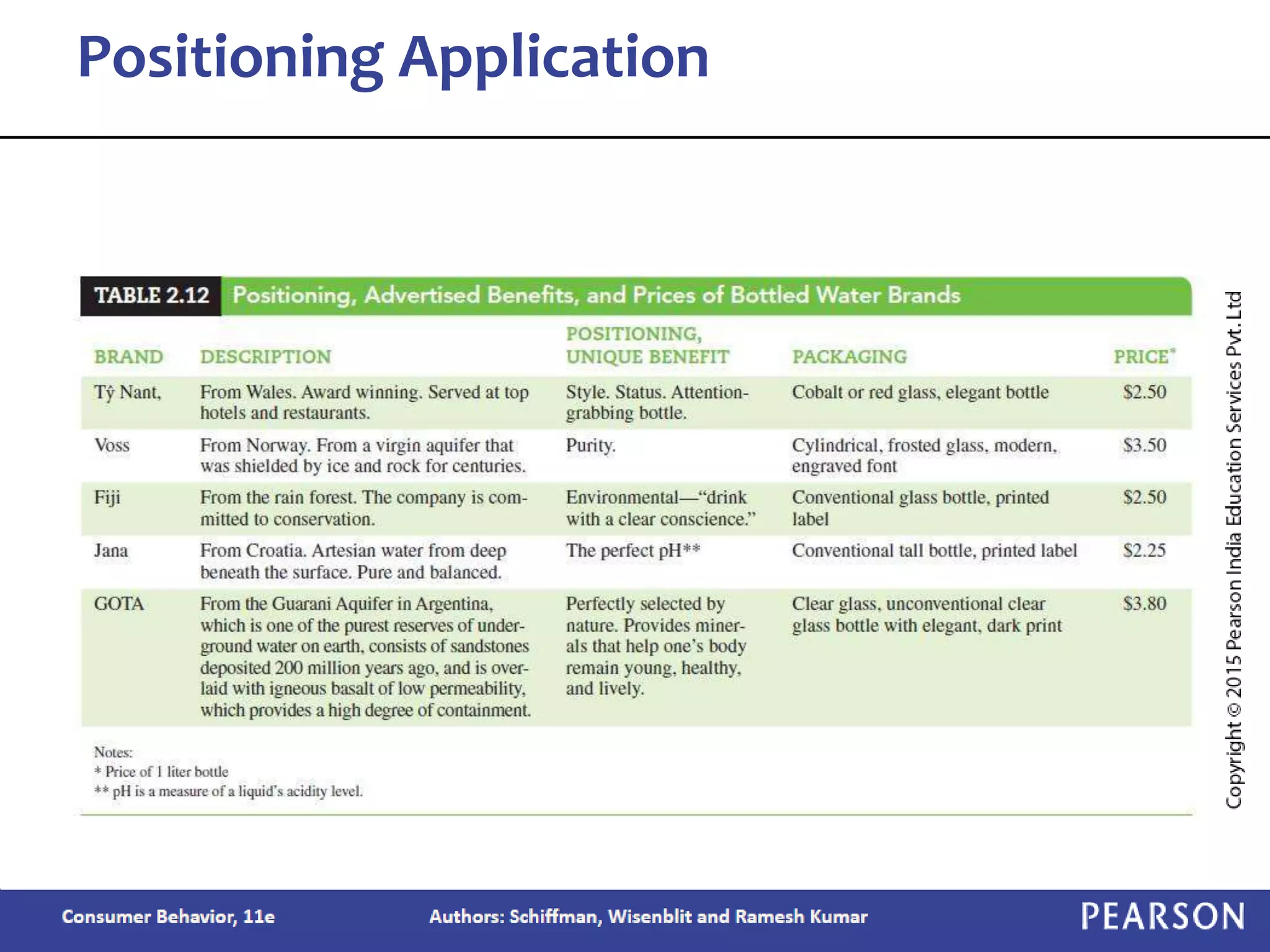
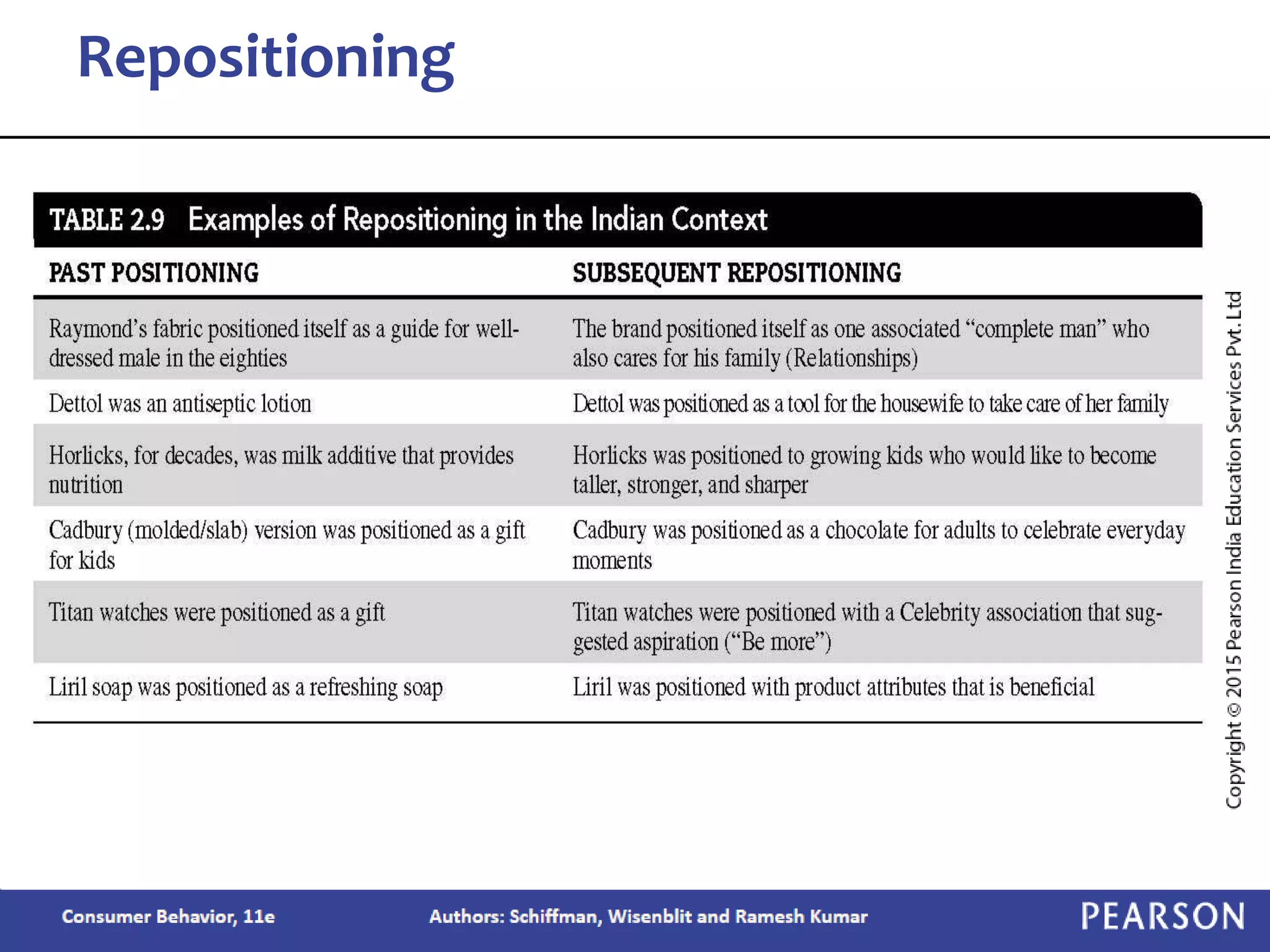
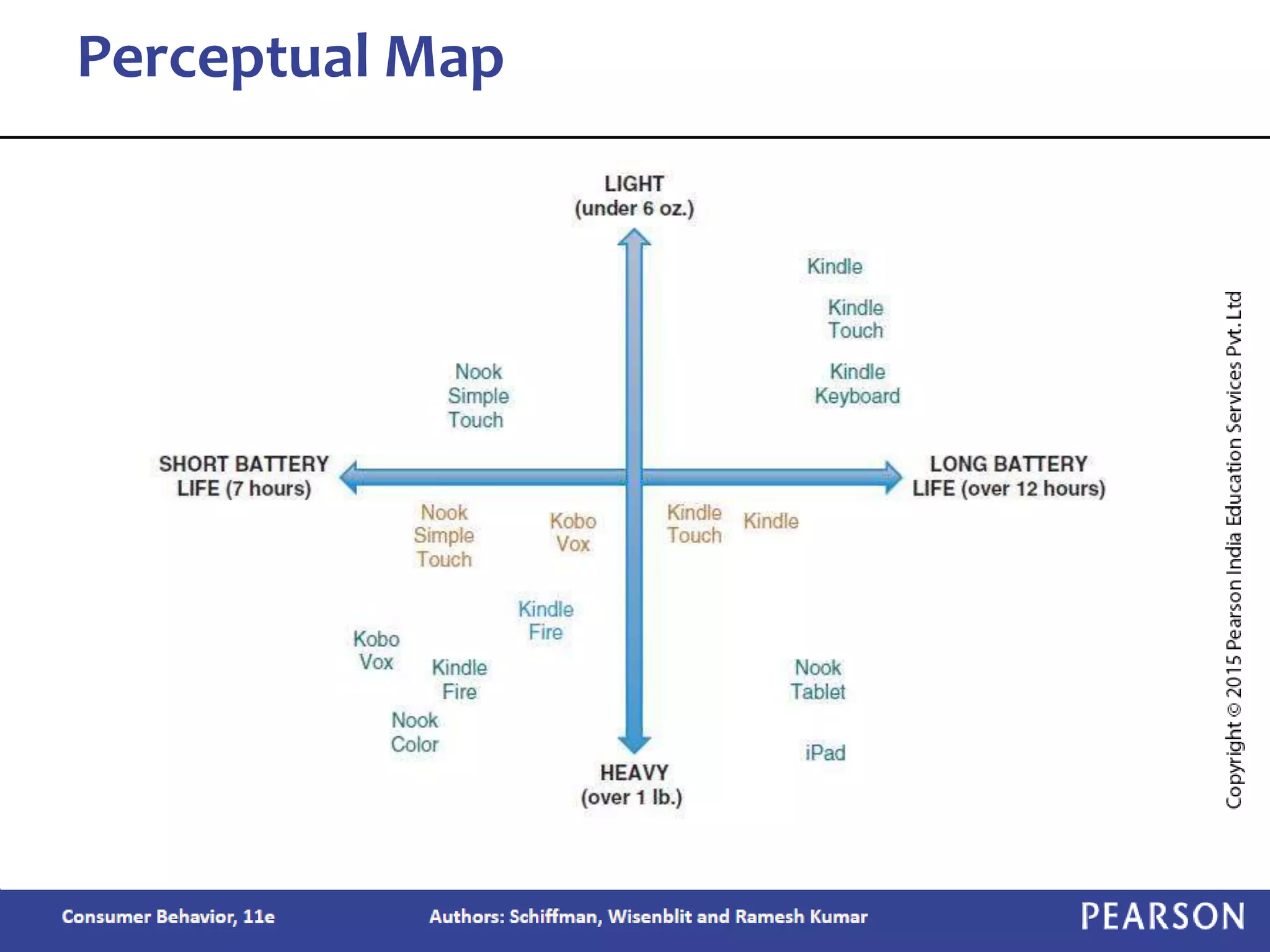
Chapter 2 outlines the learning objectives related to market segmentation, targeting, and positioning, emphasizing the importance of selecting effective target markets based on various segmentation bases such as demographics and psychographics. It discusses behavioral targeting in today's marketing and how personalized offers are used to engage consumers effectively. The chapter also details the positioning process that companies employ to create a distinct image of their products in consumers' minds.