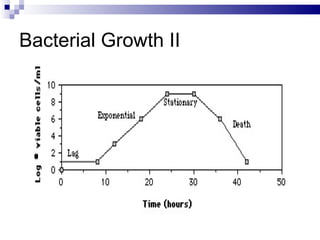
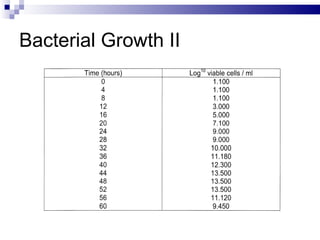
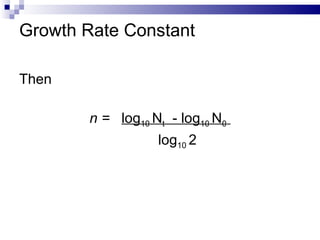
The document discusses diauxic growth and calculating growth rate constants in bacteria. It notes that during diauxic growth, bacteria will utilize carbon sources in a certain order and require a lag phase to produce enzymes for a secondary source. The growth curve shows two exponential phases separated by a lag phase. It also explains that the growth rate constant K represents the number of generations per hour and can be calculated using population measurements taken at two time points during exponential growth. An example calculation is provided.