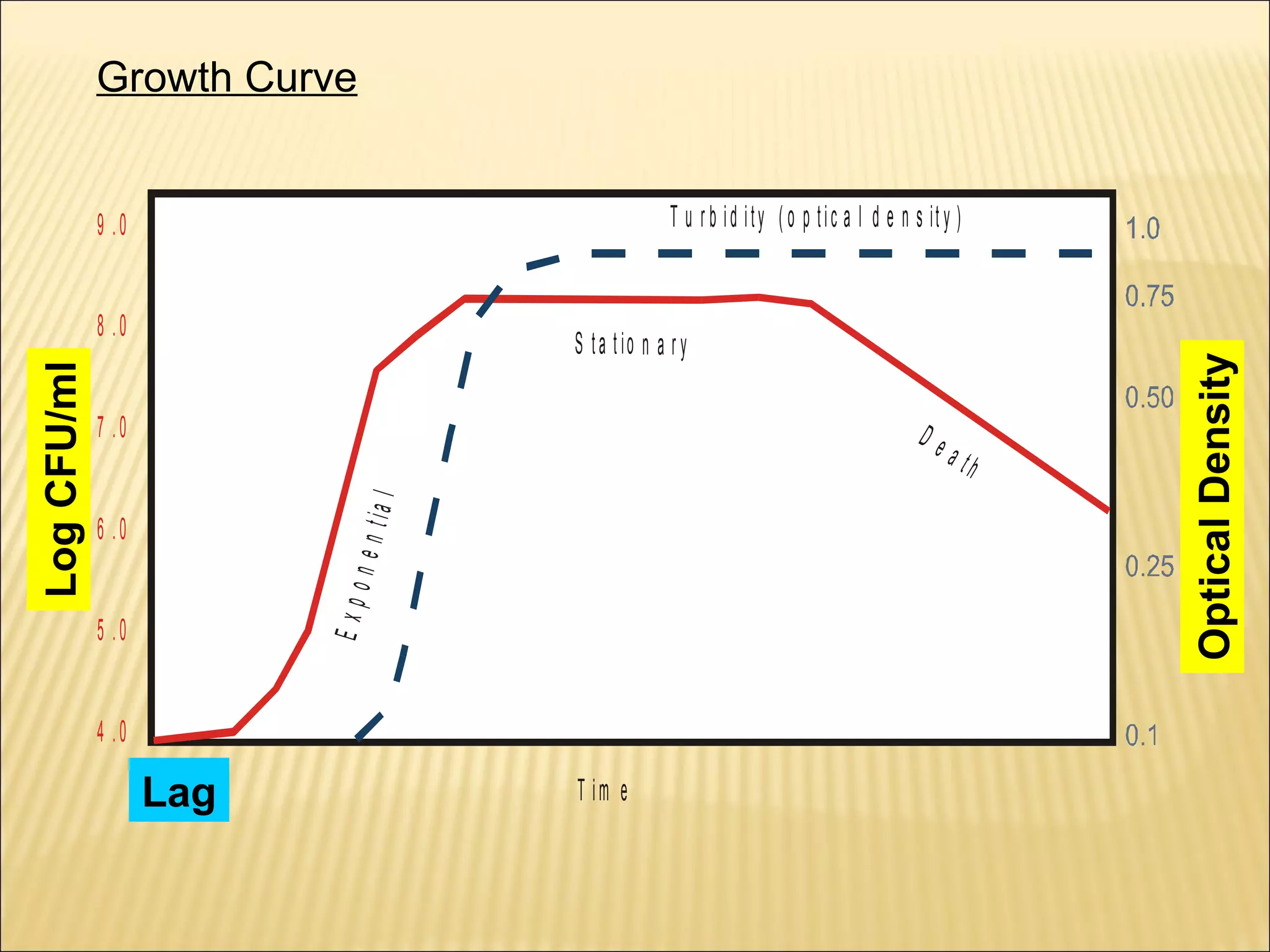
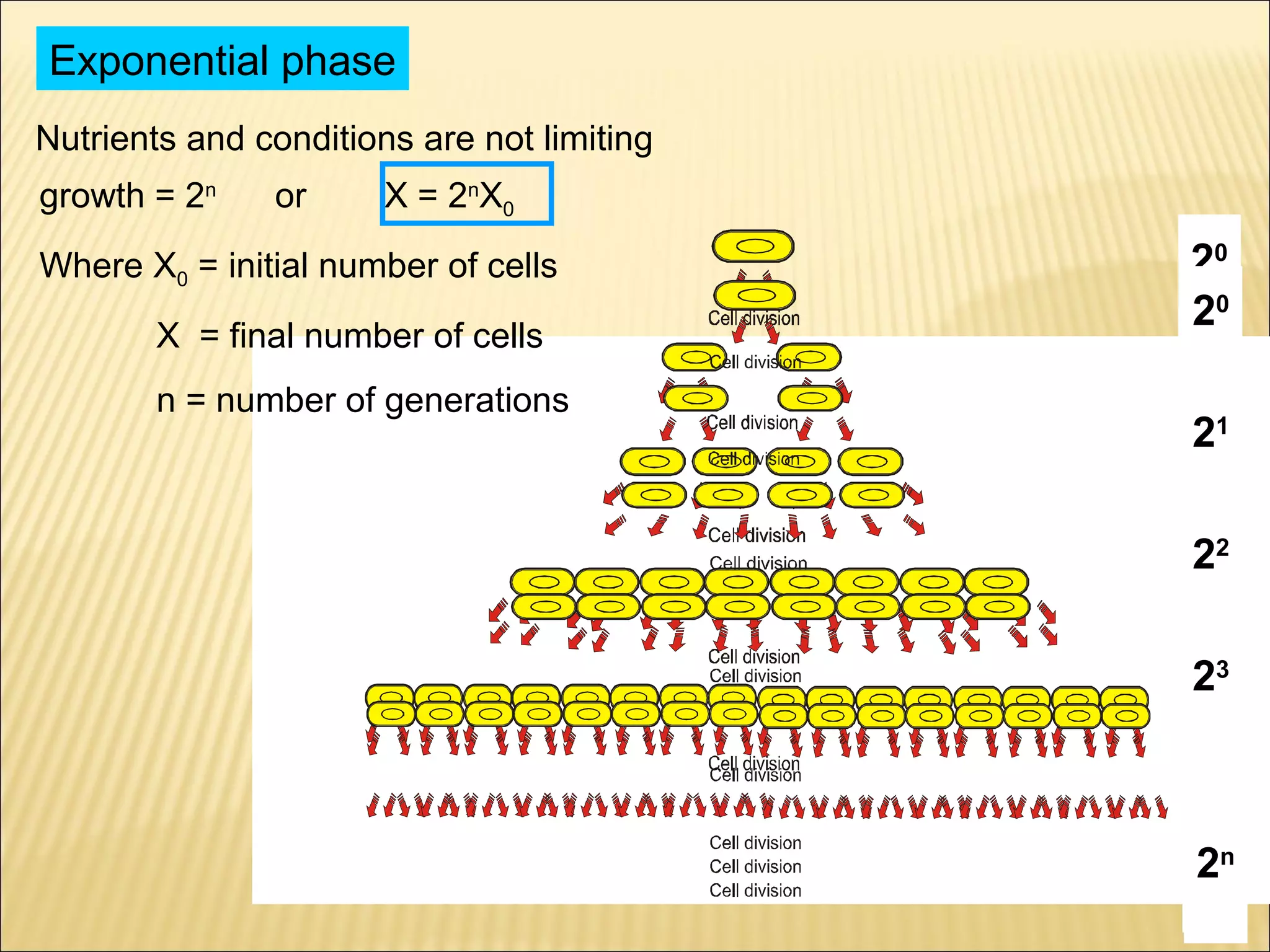
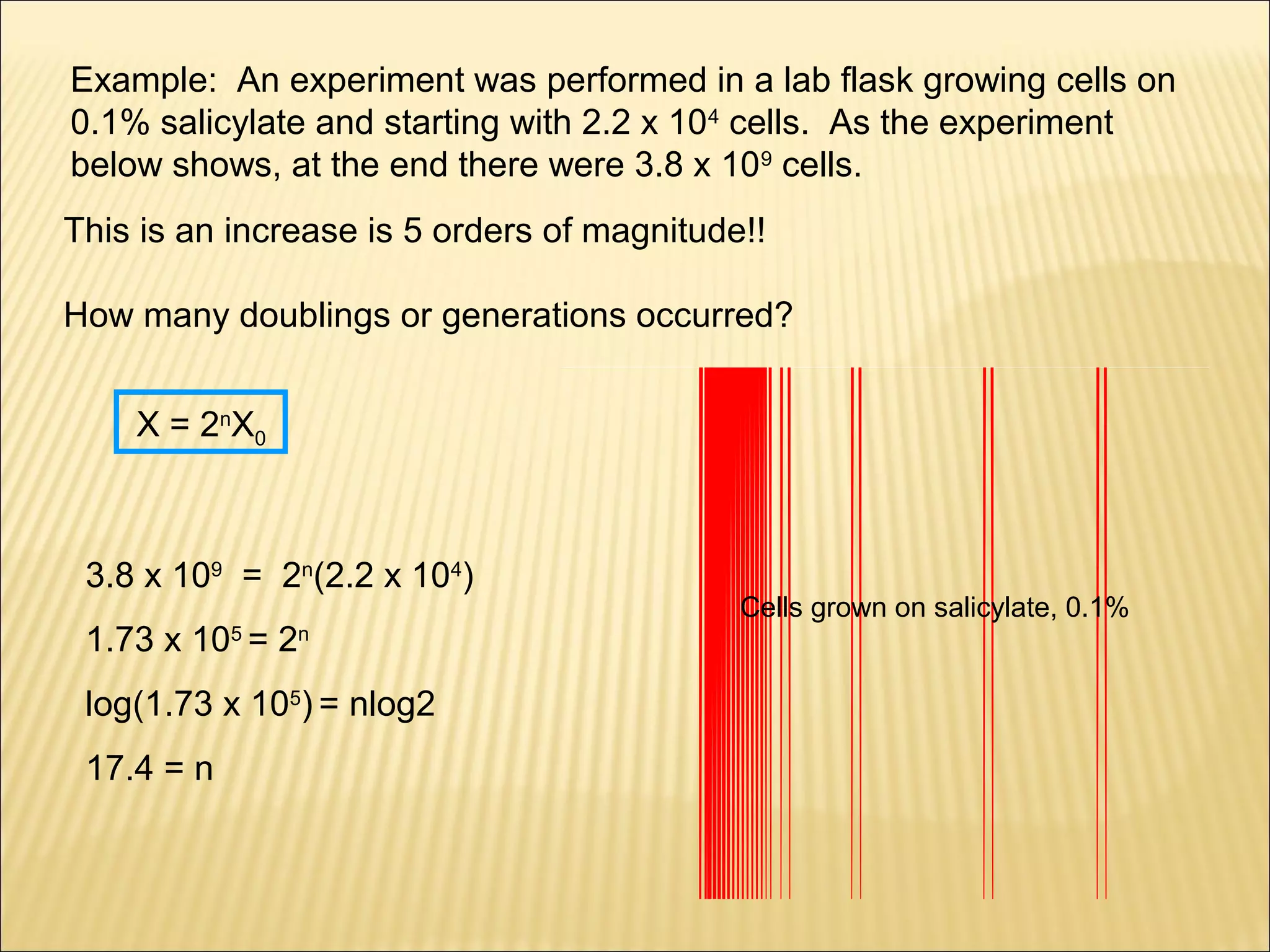
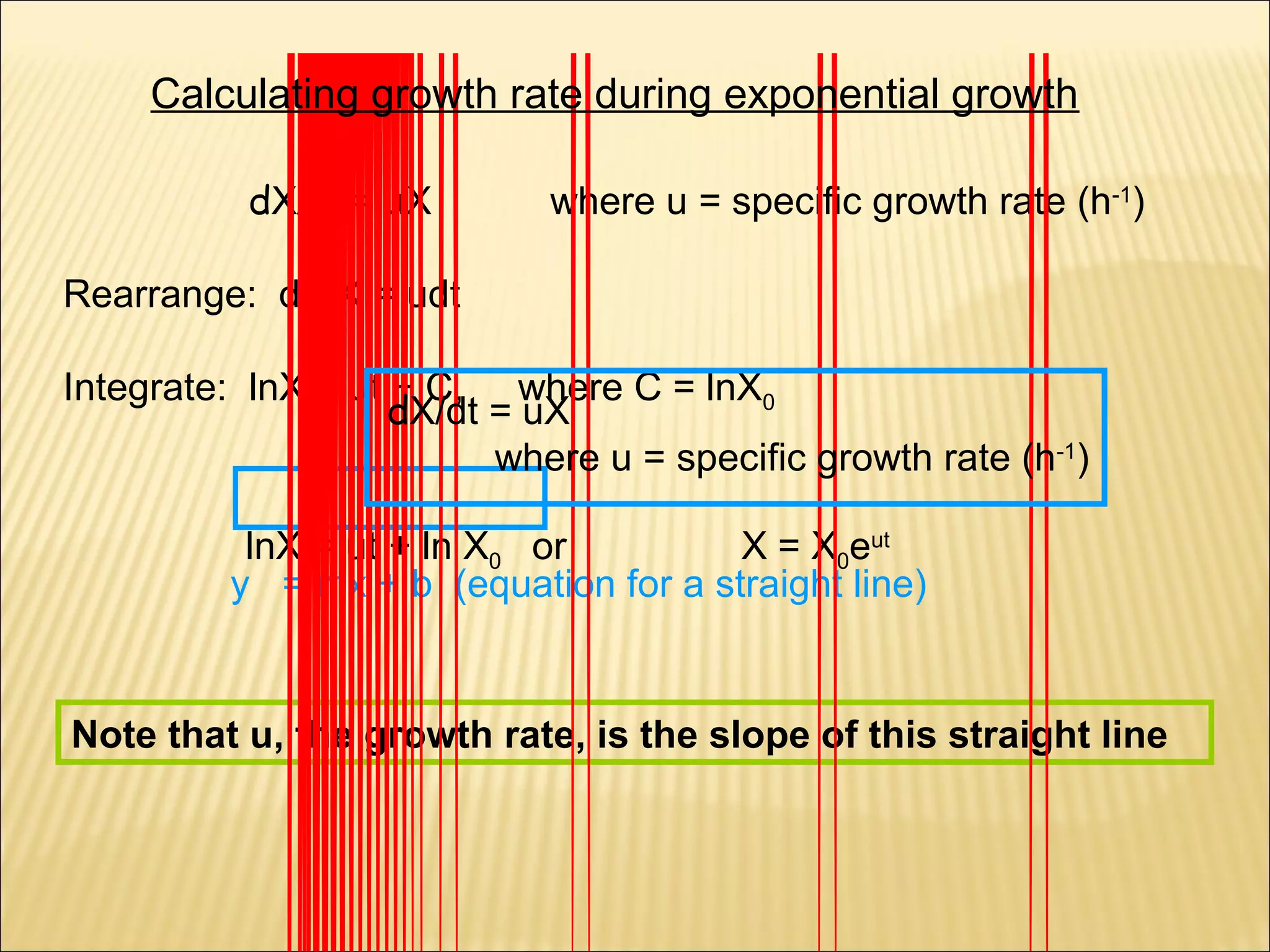
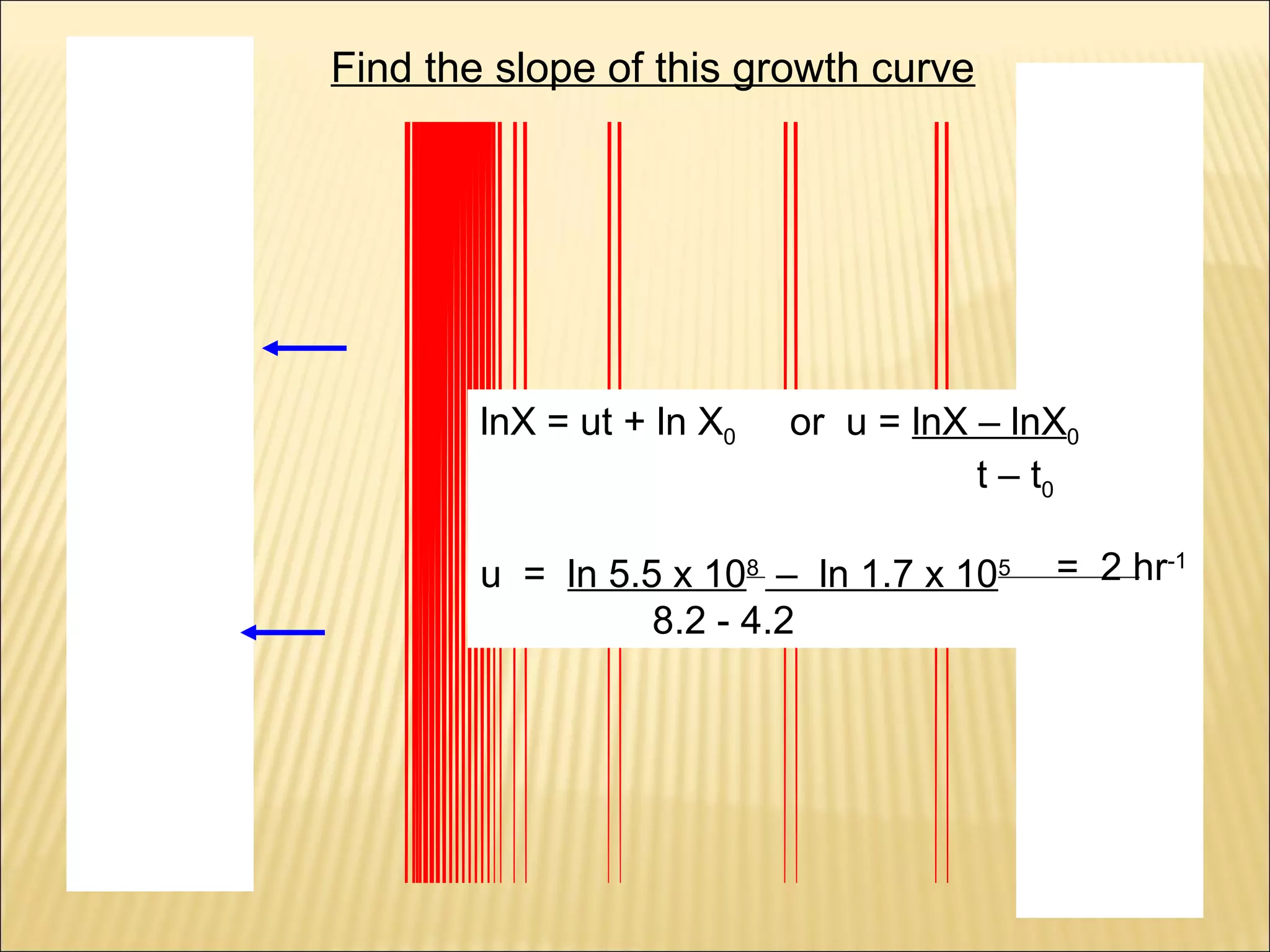
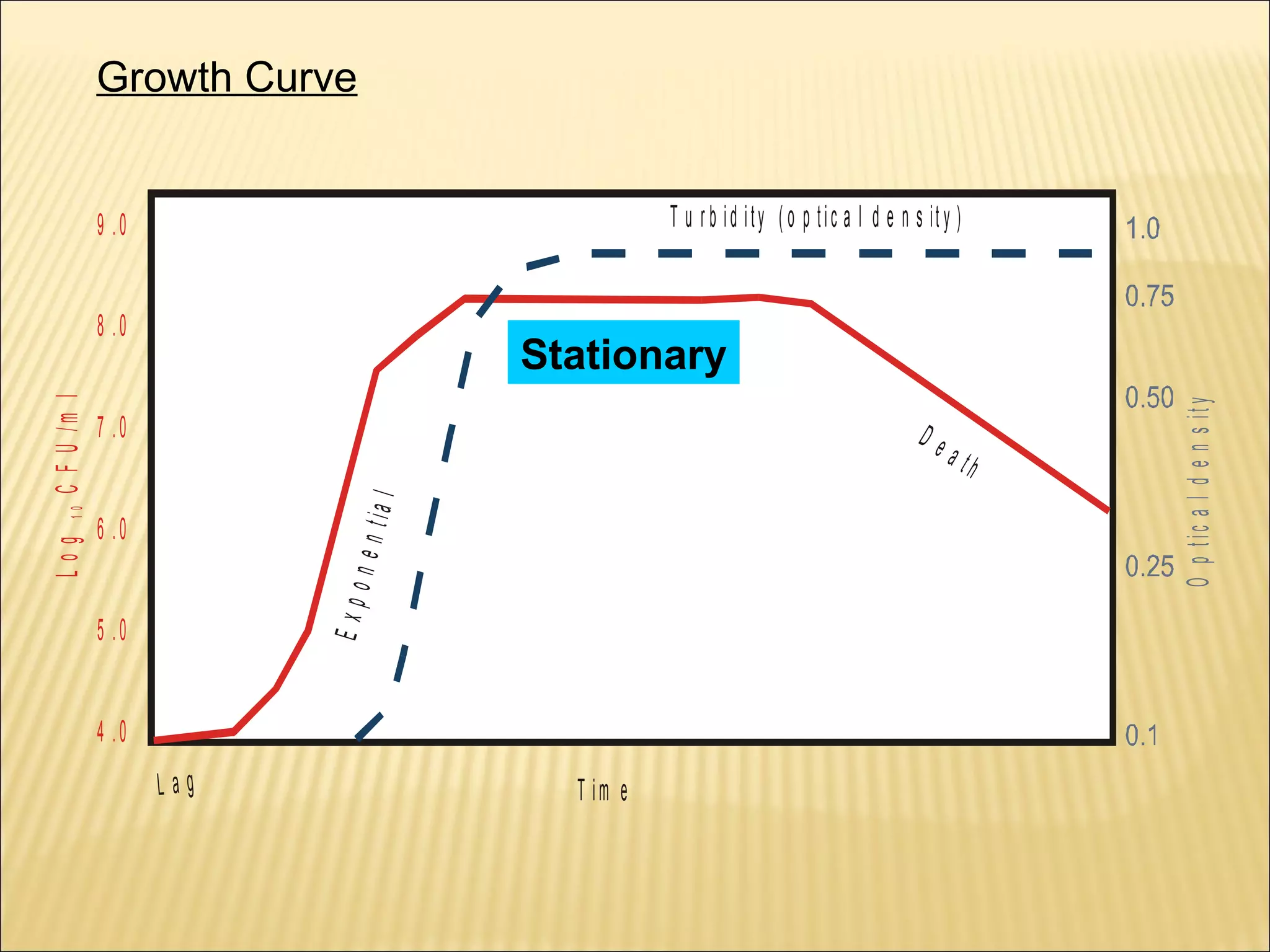
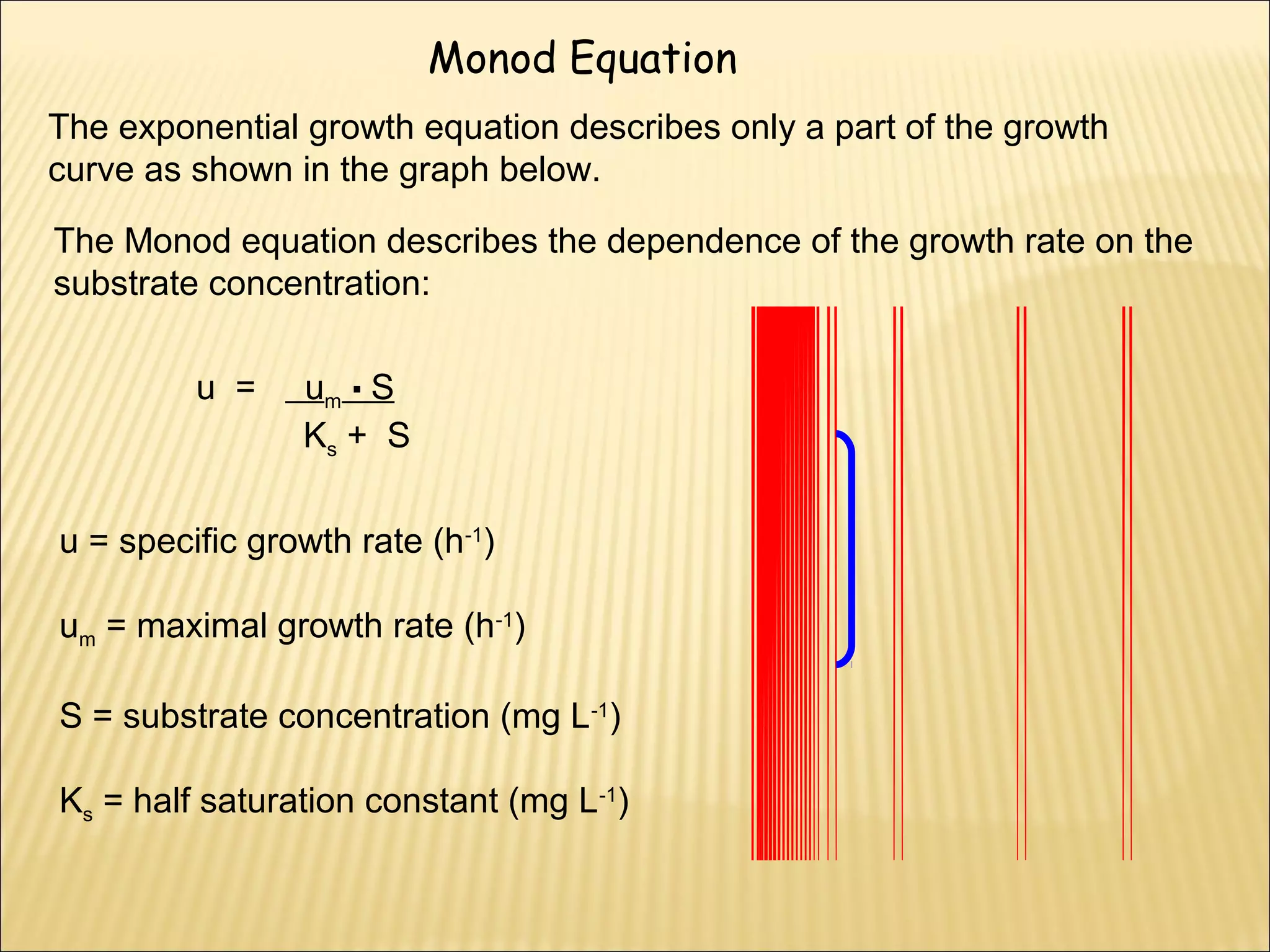
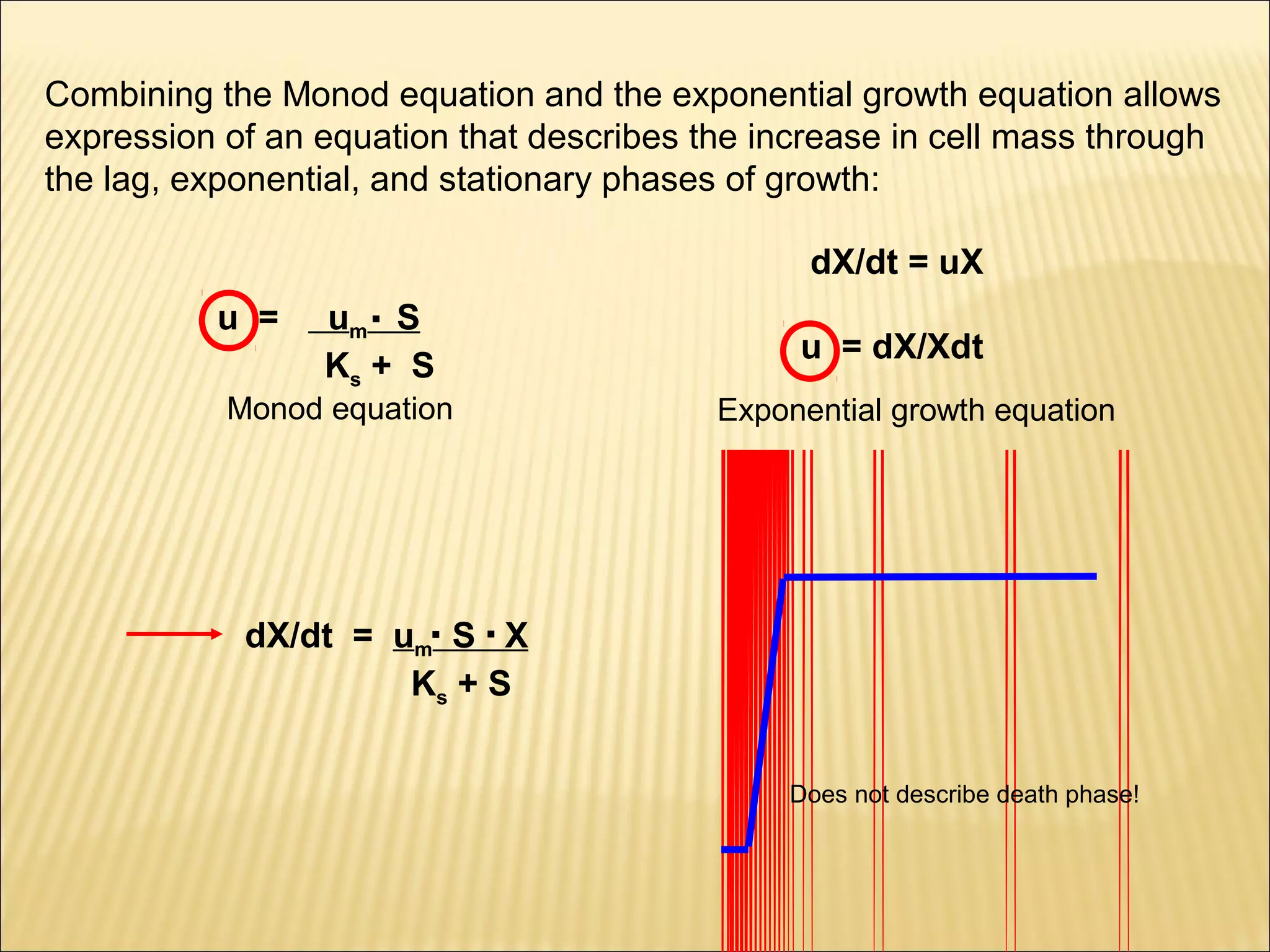
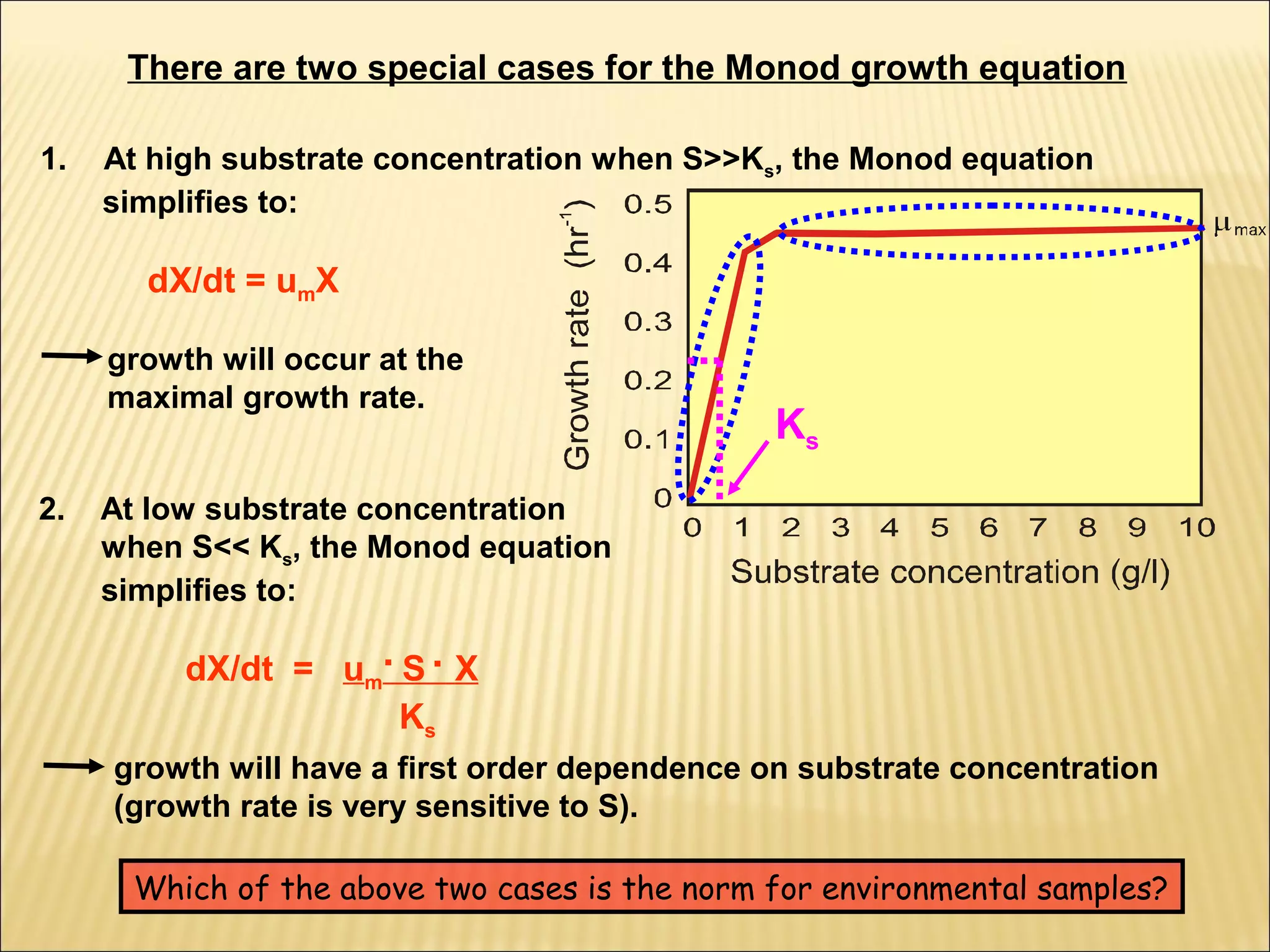
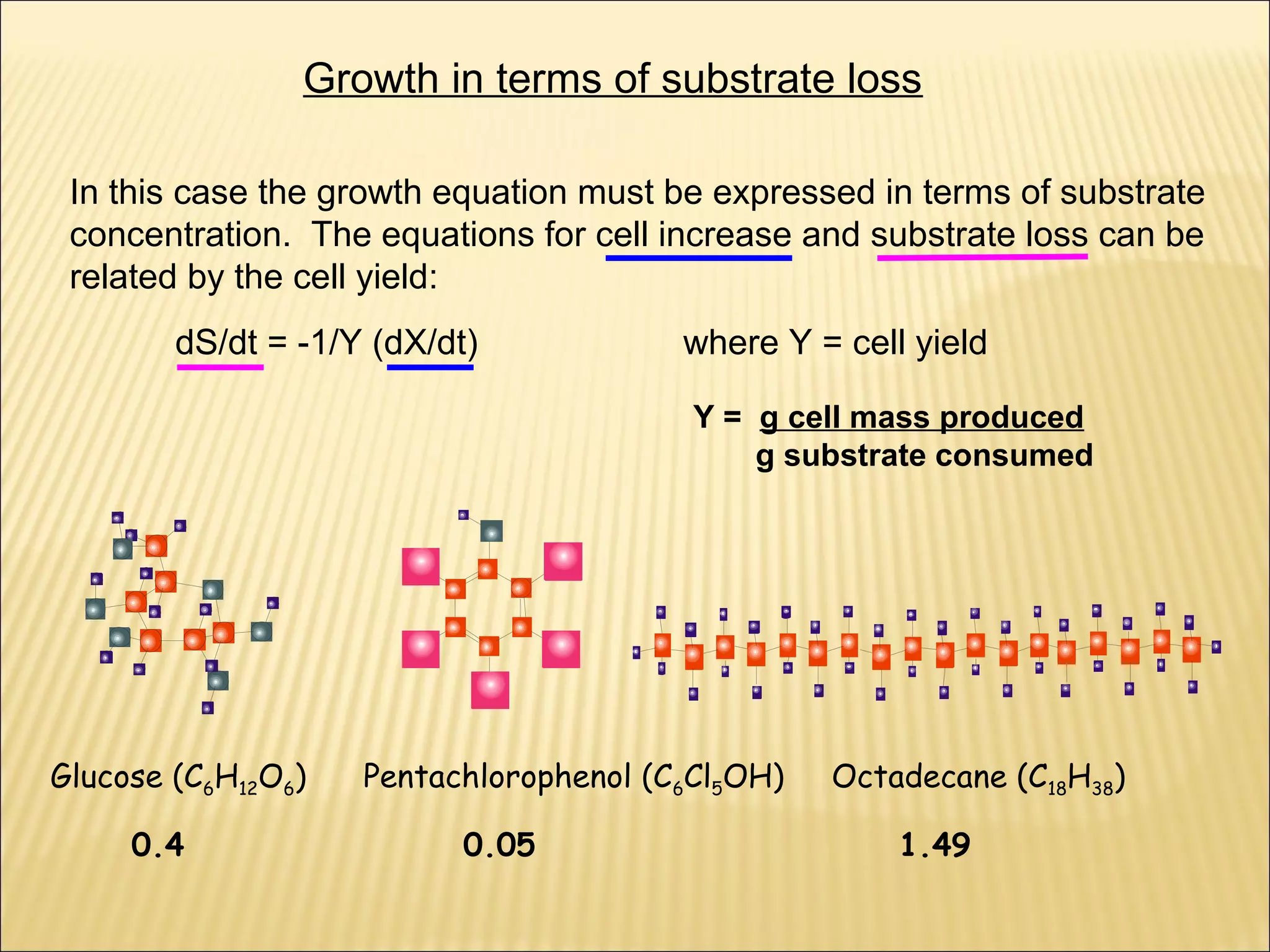
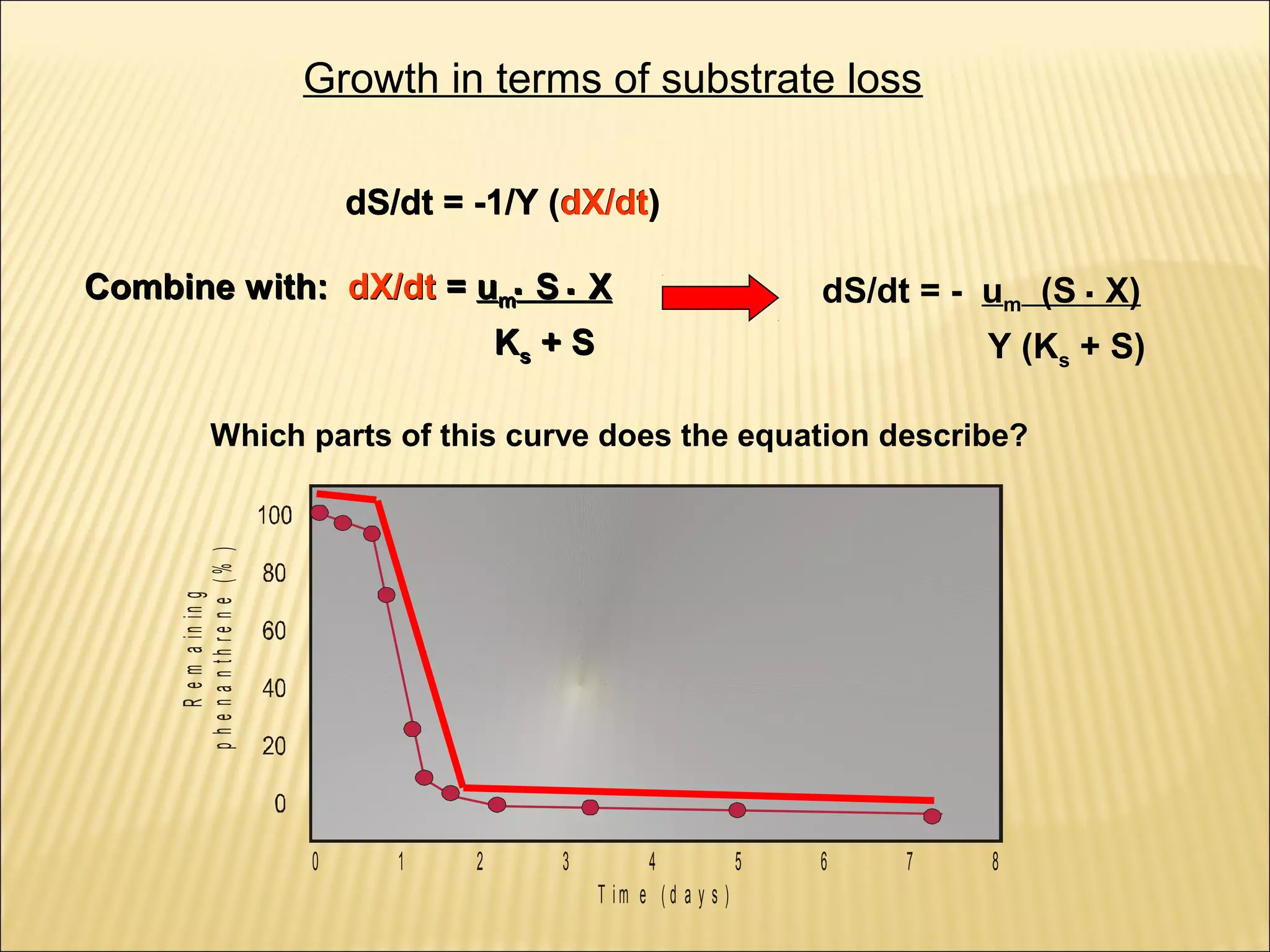
This document outlines the objectives and key concepts of bacterial growth. It discusses the fastest and slowest known doubling times for bacteria under different conditions. It also explains the different phases of a bacterial growth curve (lag, exponential, stationary, death), including the mathematical equations that describe each phase. Additionally, it covers factors that influence growth rates like temperature, substrates, and environmental conditions. The Monod equation is presented which models bacterial growth in relation to substrate concentration.