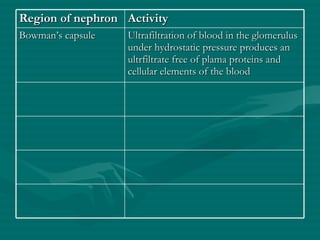
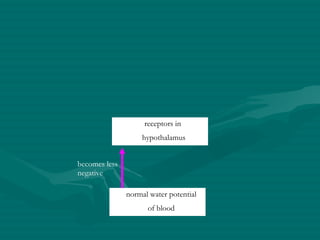
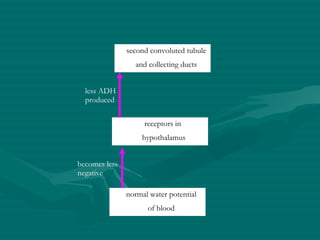
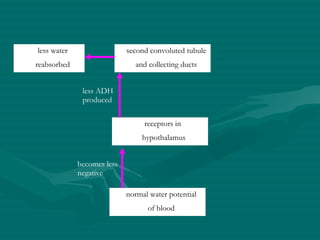
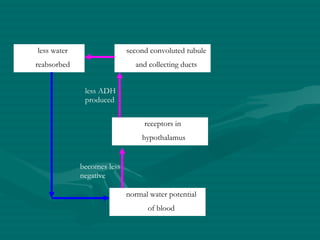
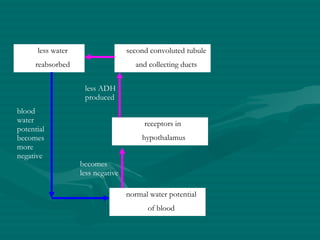
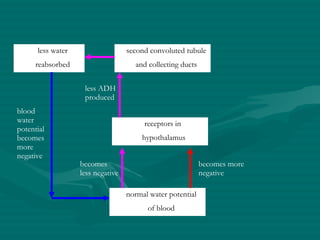
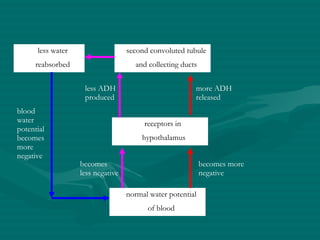
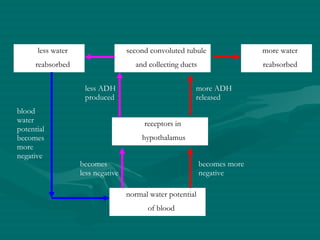
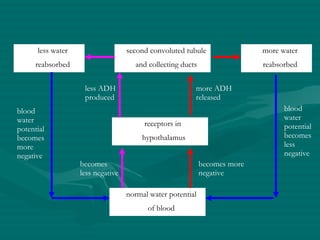
The document summarizes the kidney's role in controlling urine volume and concentration. It describes how the nephron filters blood to form an ultrafiltrate, reabsorbs necessary solutes and water along different regions of the nephron, and secretes wastes. The second convoluted tubule and collecting duct reabsorb additional water under control of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which increases their permeability. When blood concentration rises, ADH release increases water reabsorption to concentrate urine, and when it falls ADH decreases to produce dilute urine.