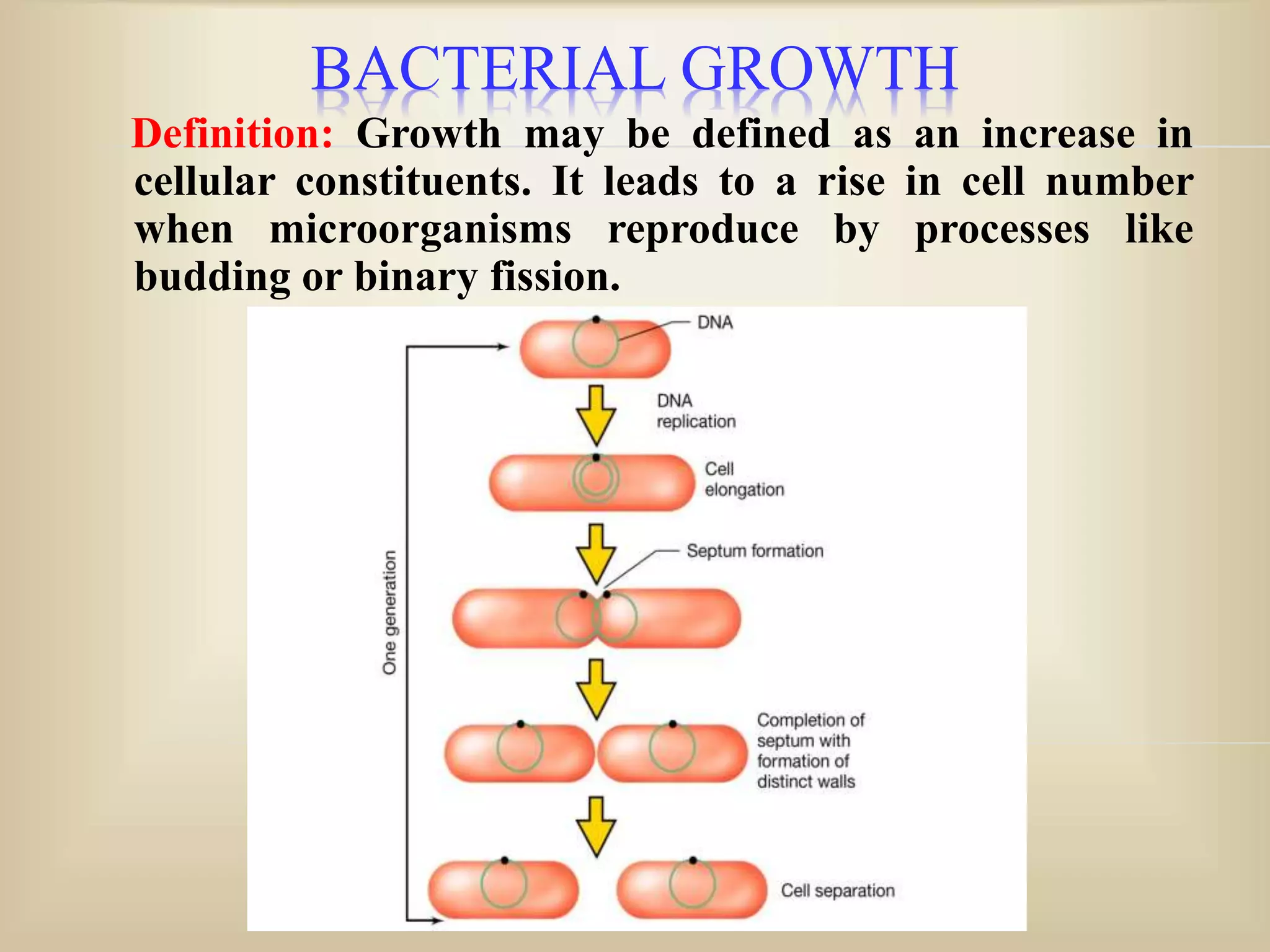
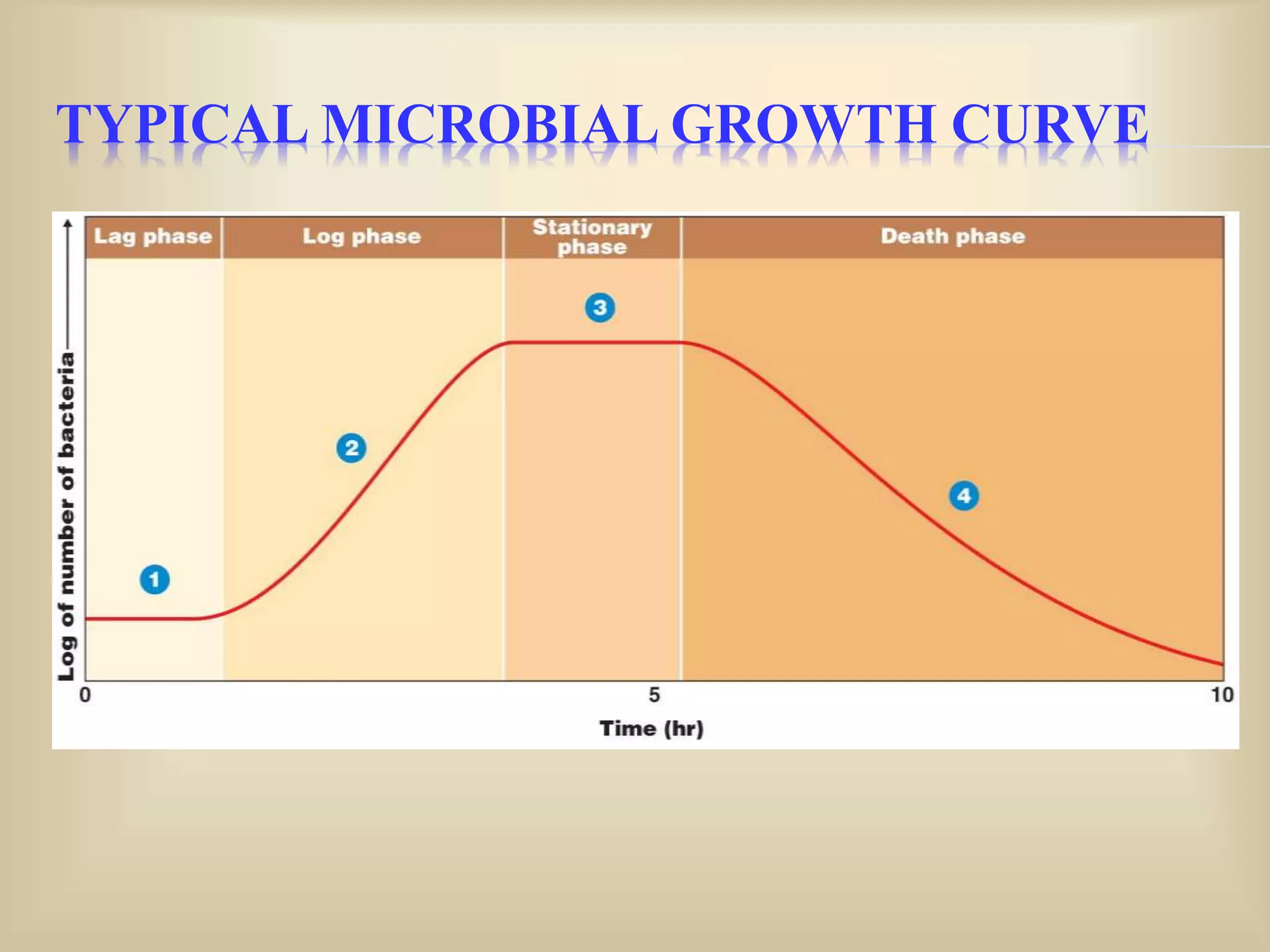
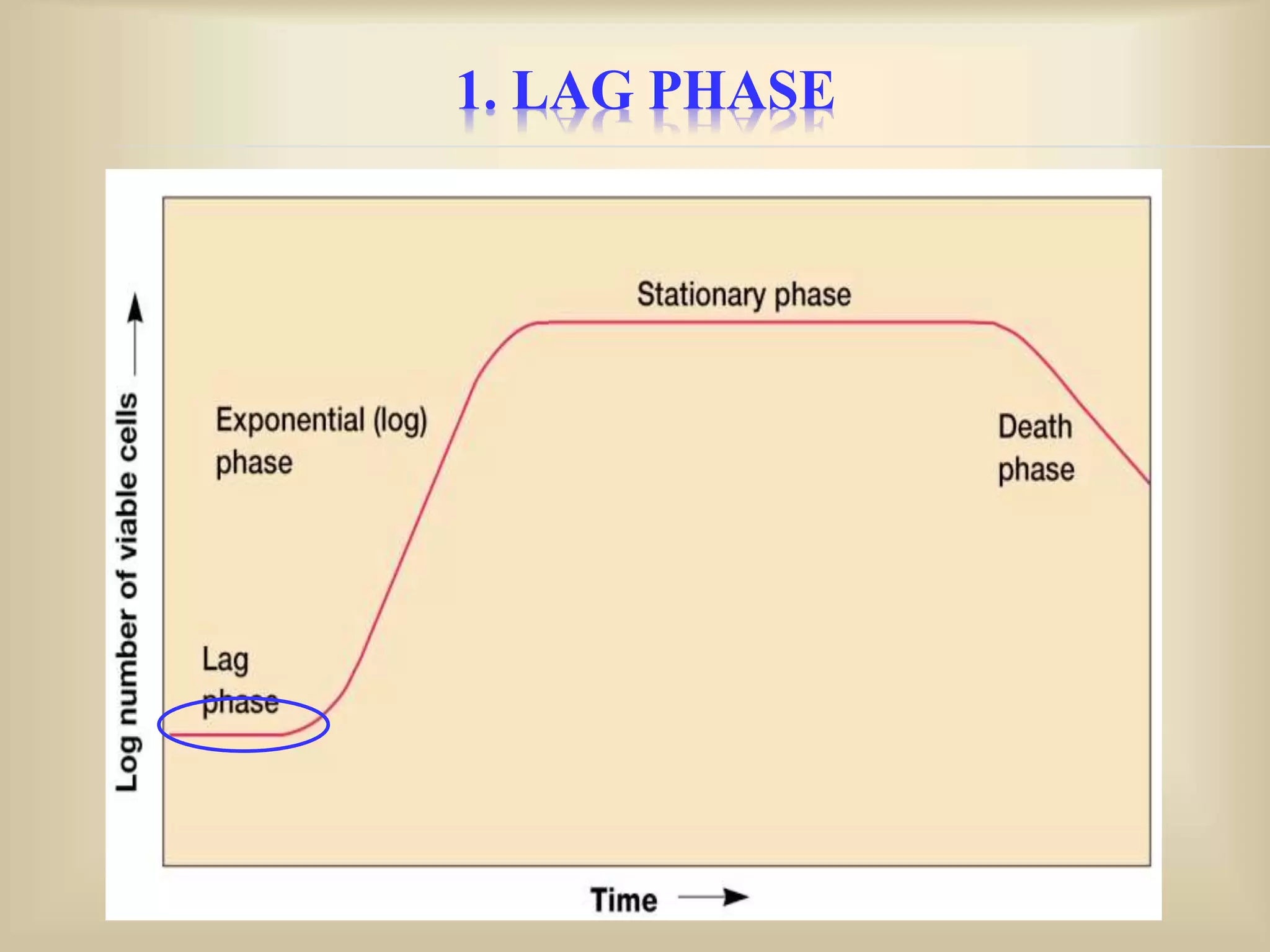
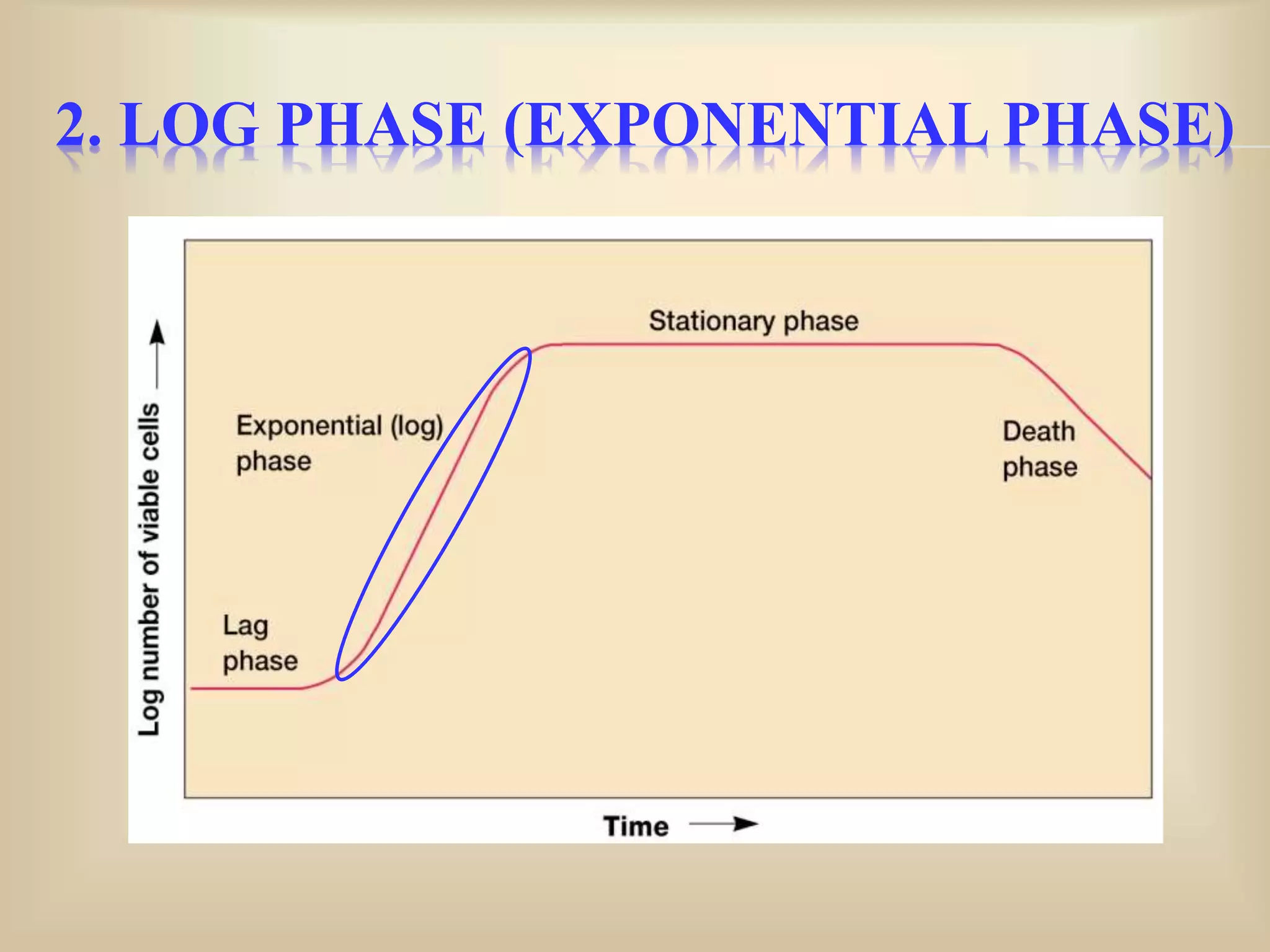
The document discusses bacterial growth curves. It explains that bacterial growth is defined as an increase in cellular constituents that can result in increased cell number or size. The growth of bacteria reproducing by binary fission can be plotted on a curve with four phases: 1) Lag phase where cells adapt to new conditions, 2) Log or exponential phase where growth is maximal, 3) Stationary phase where growth balances with death due to nutrient depletion or waste accumulation, and 4) Death phase where cells begin dying off. The generation time, growth rate, and growth curve mathematics are also explained.