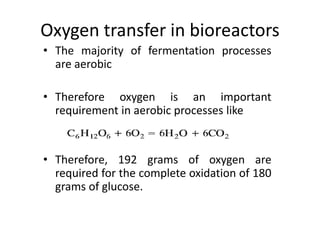
Oxygen transfer is an important factor in aerobic fermentation processes. Dissolved oxygen must be maintained above the critical level for the microorganism being used, typically through aeration and agitation of the fermentation broth. The specific oxygen uptake rate of microorganisms increases with increasing dissolved oxygen concentration up to the critical level, above which no further increases in oxygen uptake occur. Maintaining dissolved oxygen concentrations greater than the critical level maximizes biomass production by meeting the microorganism's maximum oxygen demand.