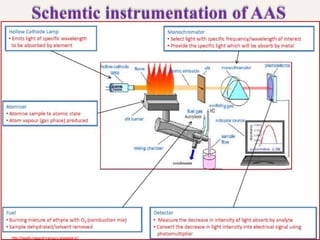
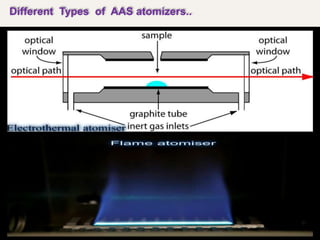
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a technique used to determine the concentration of elements in a sample. It works by vaporizing the sample and passing it through a flame where it absorbs light from a lamp emitting a characteristic wavelength for the element. The amount of light absorbed is measured and corresponds to the concentration of the element in the original sample. AAS can be used to detect over 70 different elements and has applications in fields like pharmacology, toxicology, and food analysis. Modern AAS instruments have components like lamps, atomizers, monochromators, detectors, and readouts to precisely measure the light absorption of vaporized sample elements.