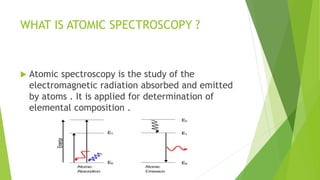
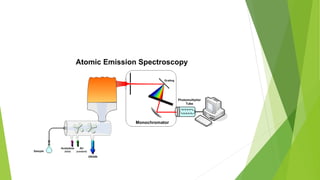
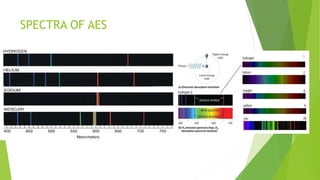
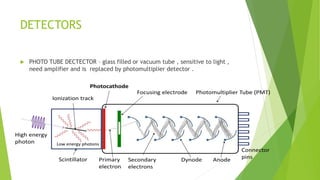
Atomic emission spectroscopy is a technique that uses the intensity of light emitted from atoms excited by a heat source to determine the quantity of elements in a sample. The sample is converted to free atoms using a flame or electrothermal atomizer, then excited. A monochromator is used to selectively monitor the emission lines, and a detector measures the light intensity. This intensity is proportional to the number of atoms present. The technique can be used to identify and determine trace amounts of metals in samples like alloys and oils.