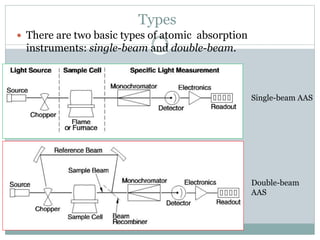
Atomic absorption spectrometry is a technique used to determine the concentration of chemical elements in solution. It works by vaporizing the elements in a flame or graphite furnace and measuring how much light of a specific wavelength is absorbed, which indicates the concentration. Key components of an atomic absorption spectrometer include a light source, atomizer such as a flame or furnace, monochromator, detector, and display. Flame atomic absorption is used for higher concentrations while graphite furnace atomic absorption can detect trace levels. Potential interferences must also be considered and addressed.