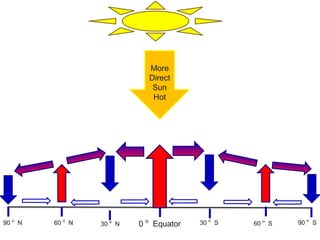
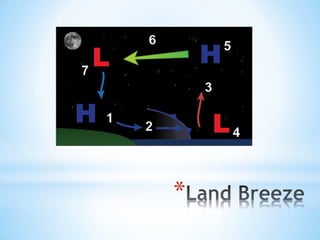
The document discusses various atmospheric phenomena including:
1) Jet streams, which are fast winds in the upper atmosphere between air masses of different temperatures.
2) El Niño, which causes unusual weather patterns globally due to higher ocean temperatures off South America.
3) Ocean currents like the Gulf Stream that influence climate by transporting heat across oceans.