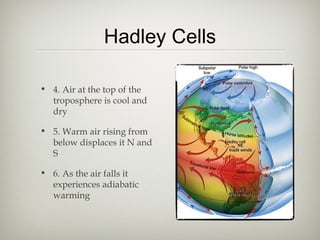
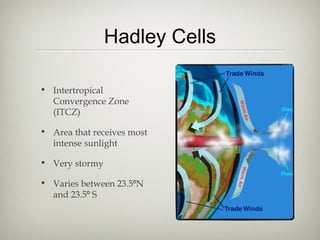
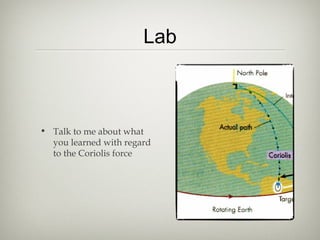
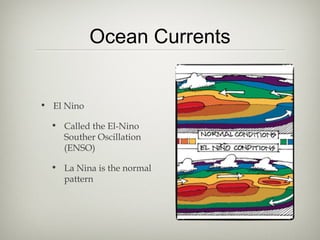
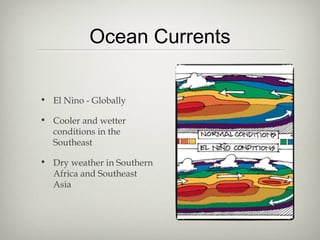
The document discusses an ecology lesson that includes activities on biomes and ocean currents, with students setting bait cards and sticky traps to sample different habitats, as well as assignments on the Pacific garbage patch and a group project on biomes due next week, with a test on chapters 4 and 5 on climate, atmosphere, and biomes.