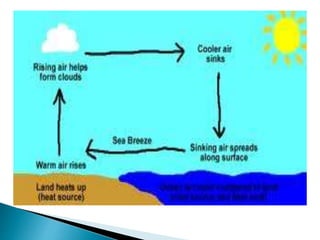
The document discusses different types of winds and factors that influence wind patterns. It explains that convection currents cause local winds like sea and land breezes as land and bodies of water heat and cool at different rates. Prevailing winds blow over long distances due to global wind patterns influenced by unequal heating from the sun and the Coriolis effect from the Earth's rotation. These winds are classified into belts and some regions experience seasonal monsoon winds as air pressures and temperatures shift between land and ocean areas.