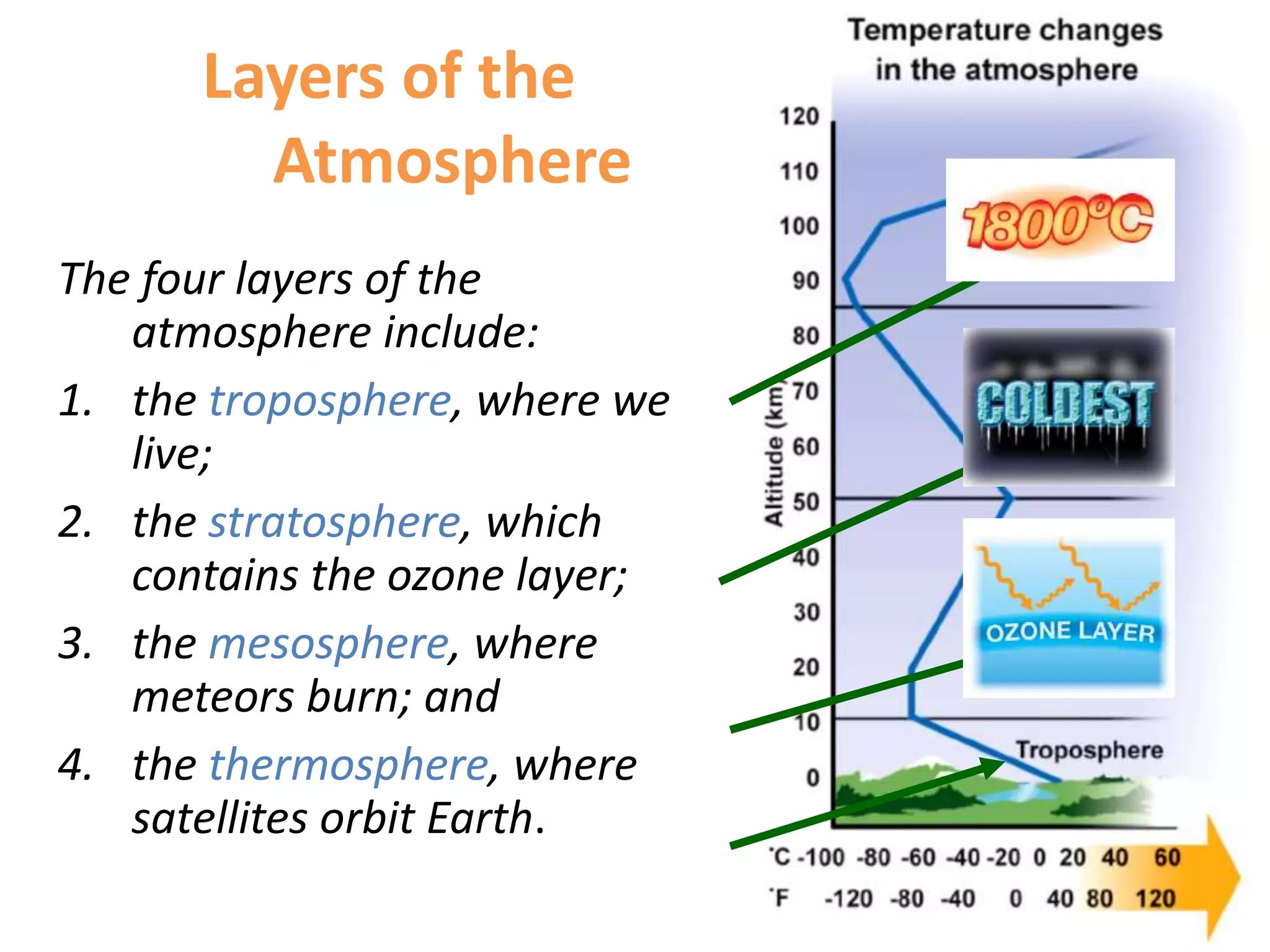
Earth's atmosphere is a layer of gases that absorbs solar energy, protects life, and burns meteoroids. It consists of four layers: the troposphere (where weather occurs), stratosphere (containing the ozone layer), mesosphere (where meteors burn), and thermosphere (home to satellites). The atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), along with trace amounts of other gases.