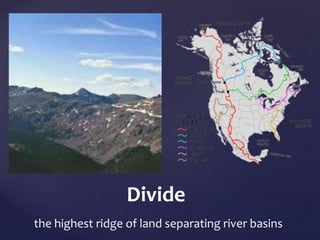
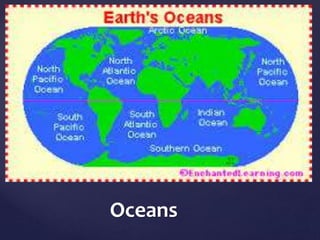
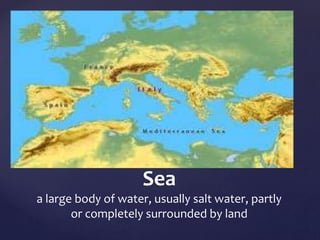
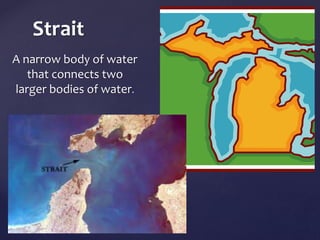
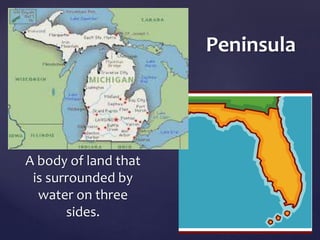
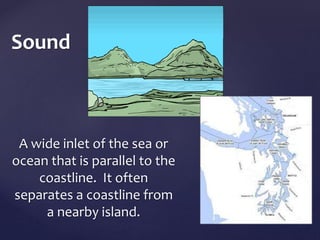
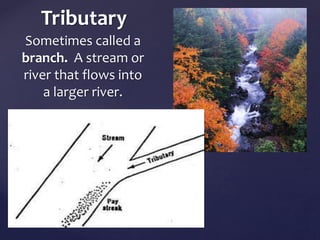
This document defines and describes various types of landforms and regions. It discusses mountains such as fault mountains and fold mountains that are formed by tectonic plate movement. It also covers plains, grasslands, deserts, forests, wetlands and bodies of water including rivers, lakes, seas and oceans. Regions described include prairies, savannas, tundra, and different forest biomes.