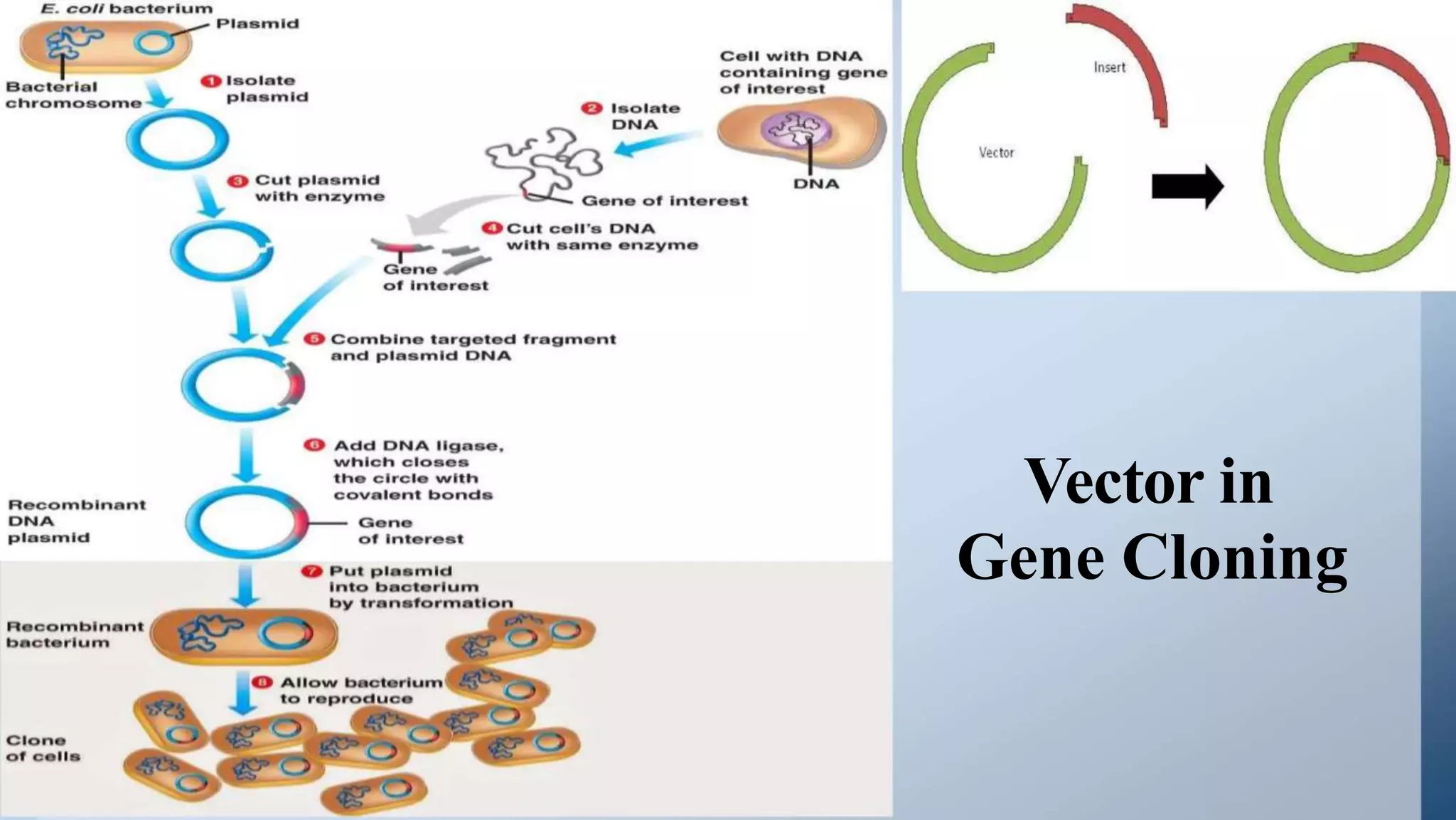
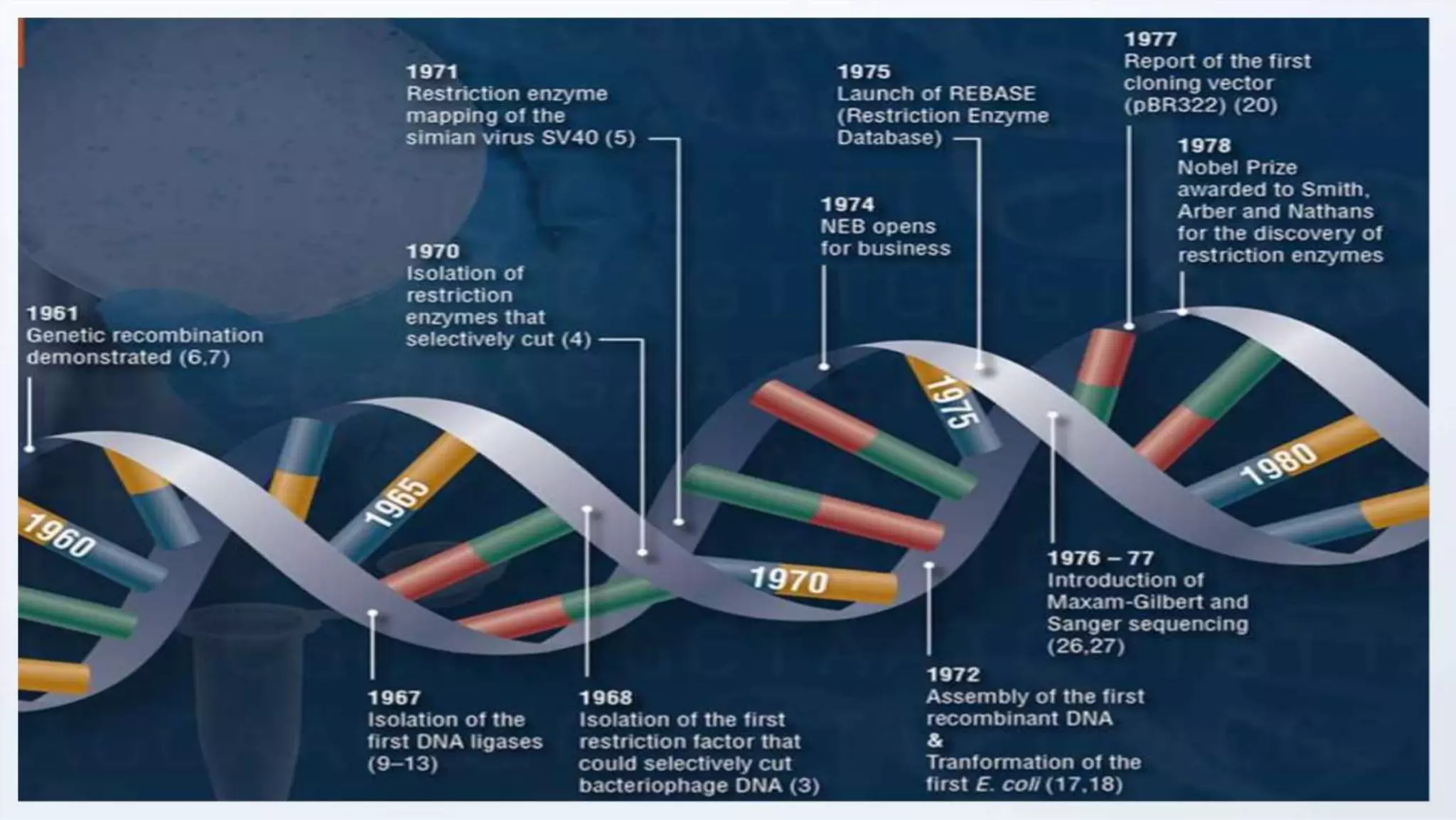
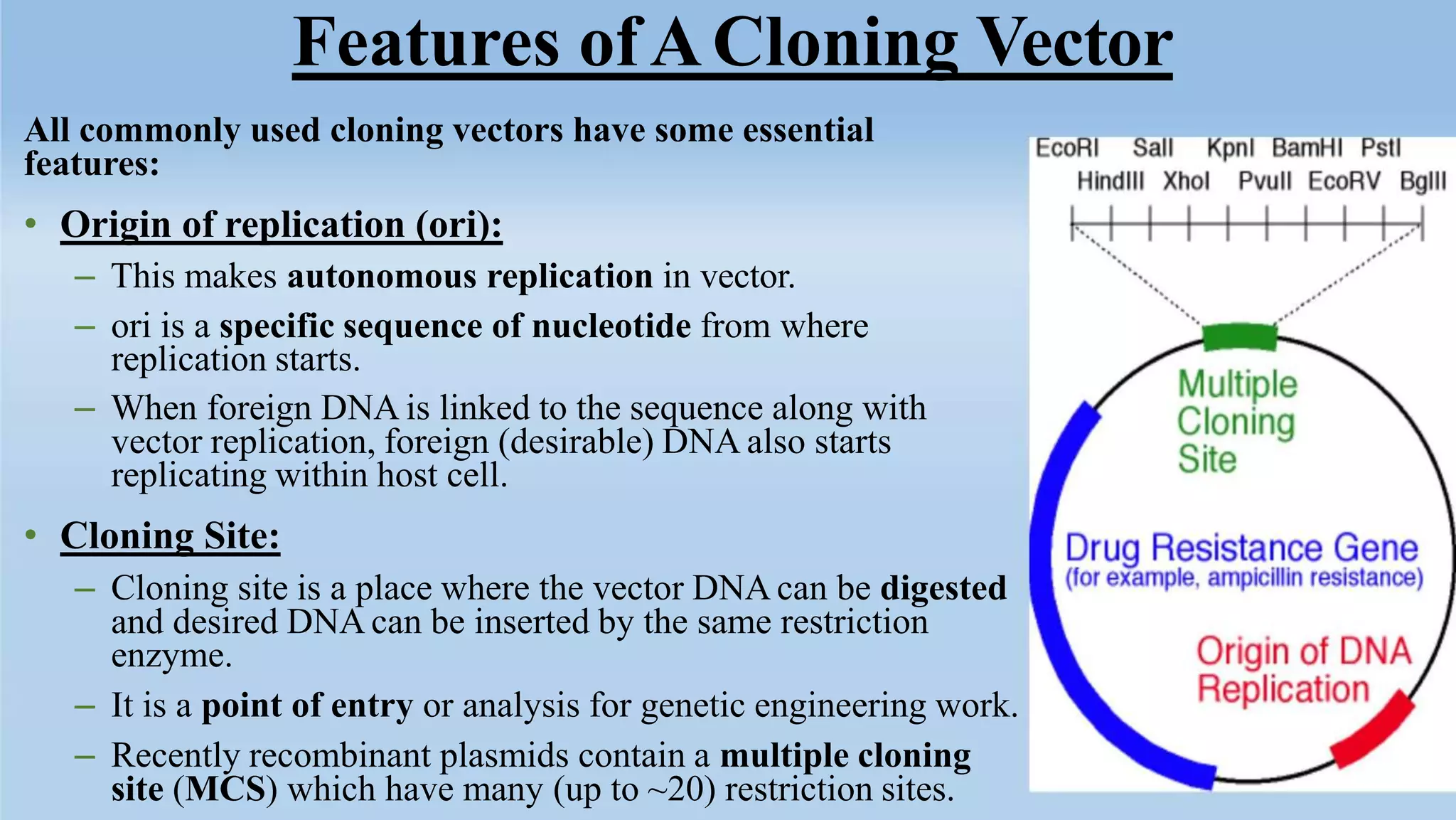
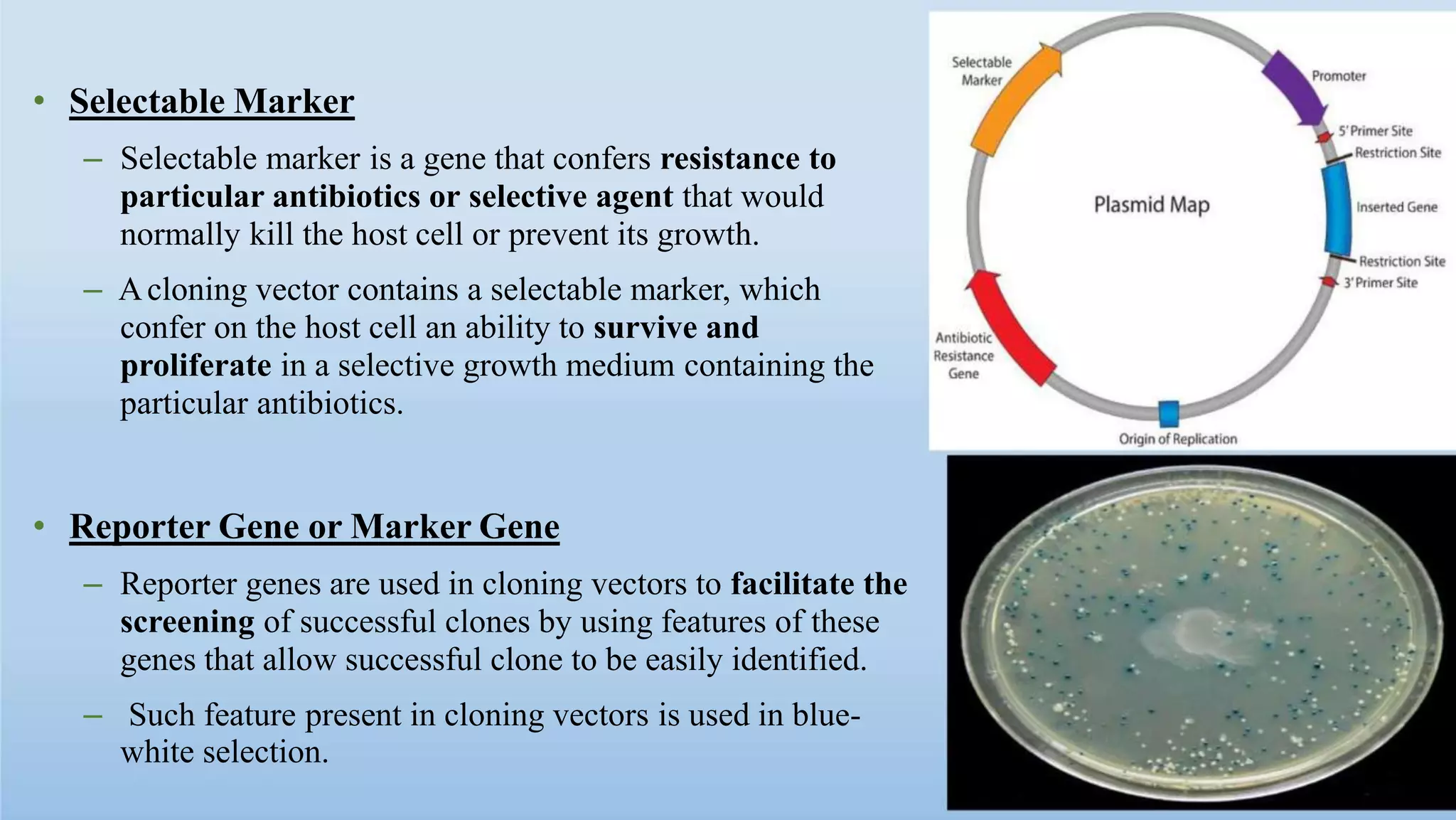
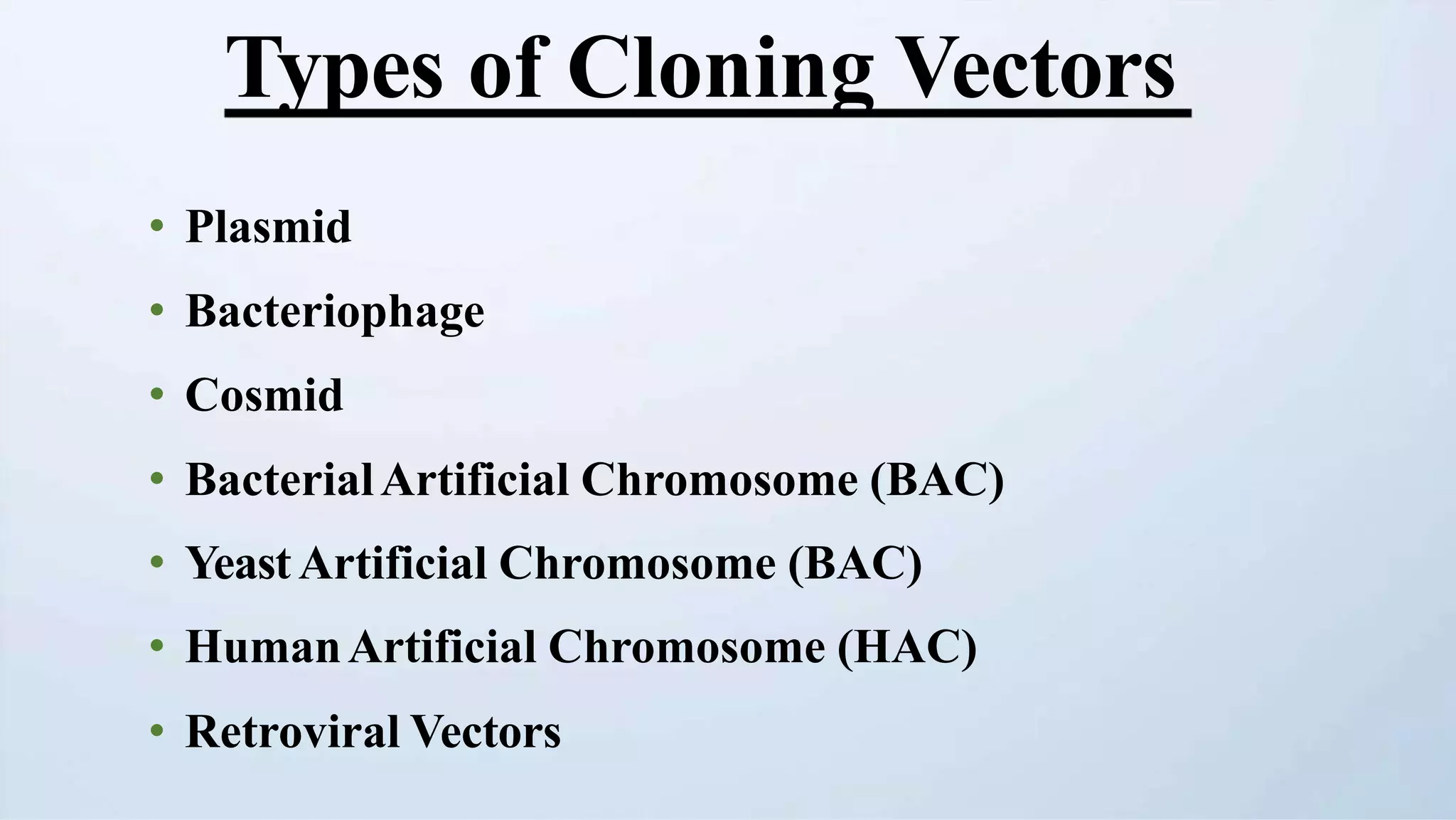
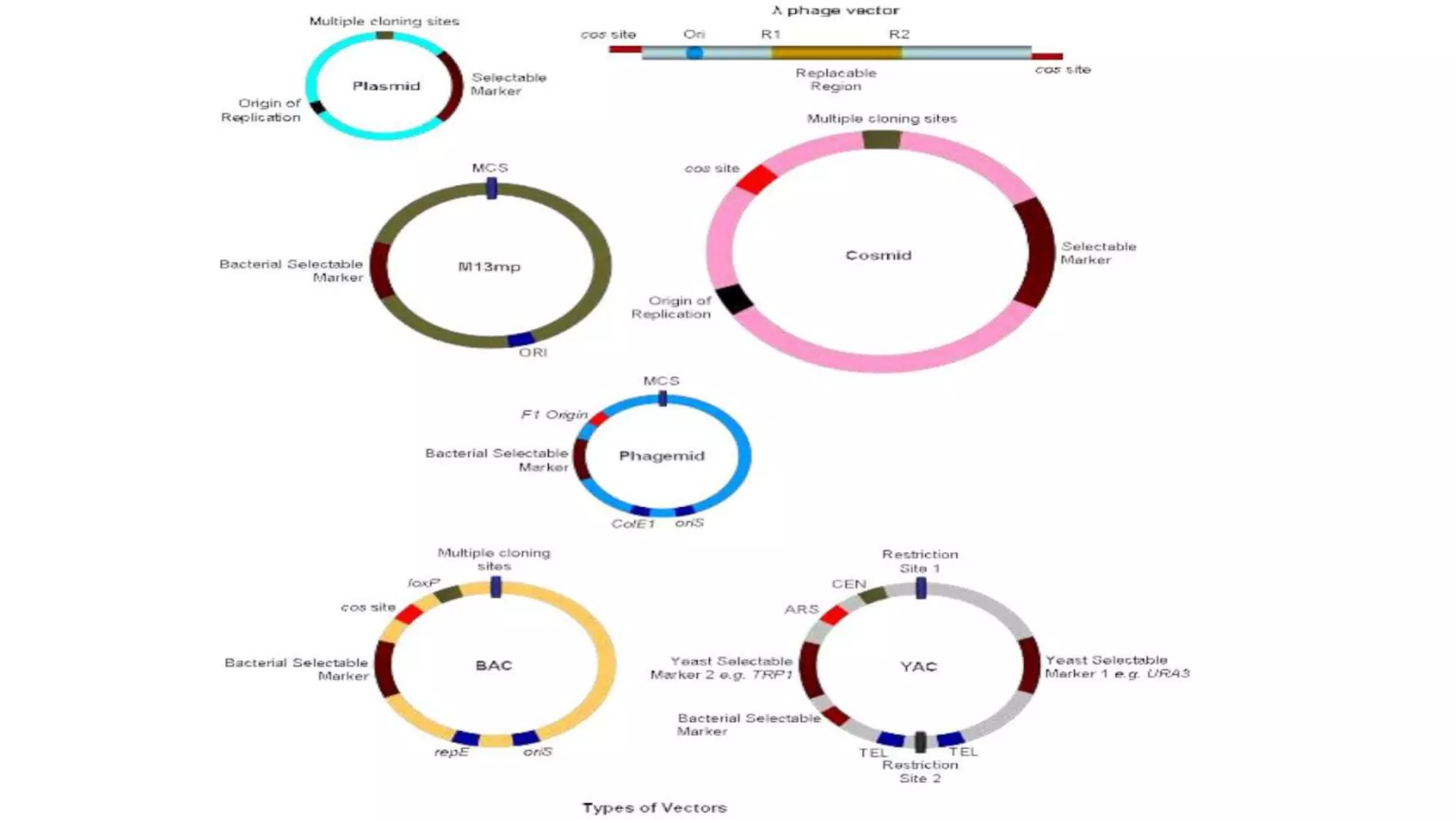
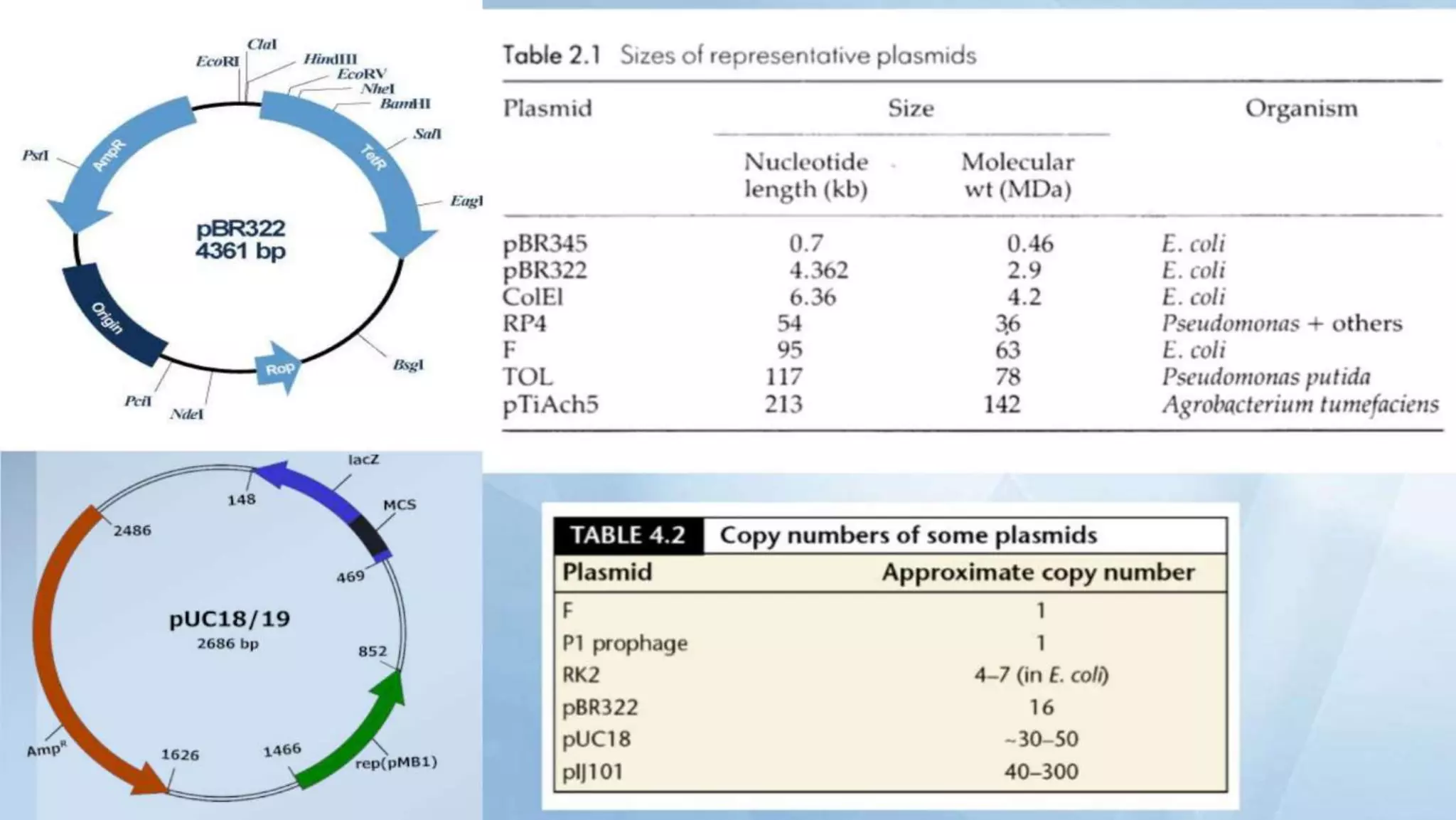
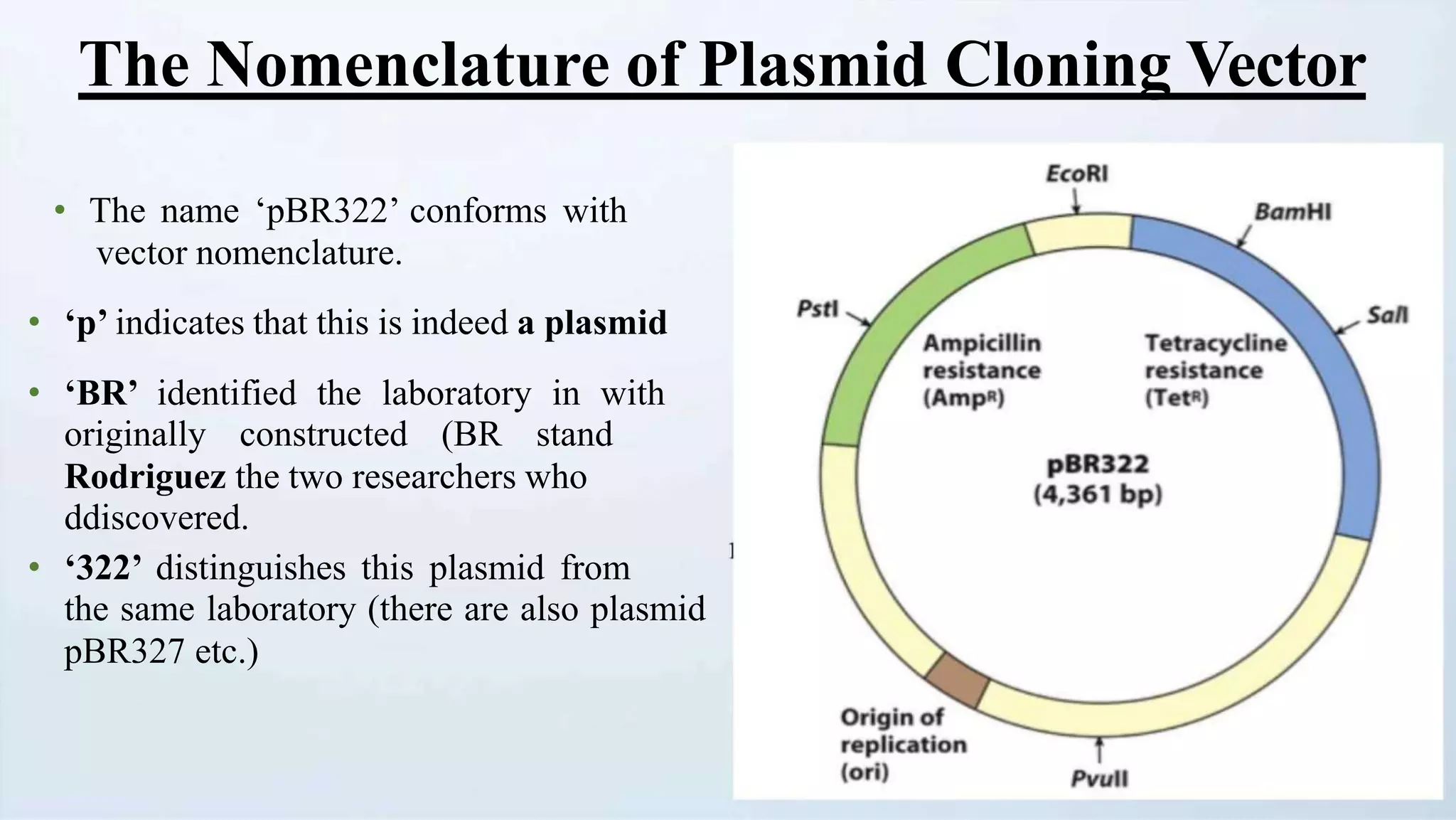
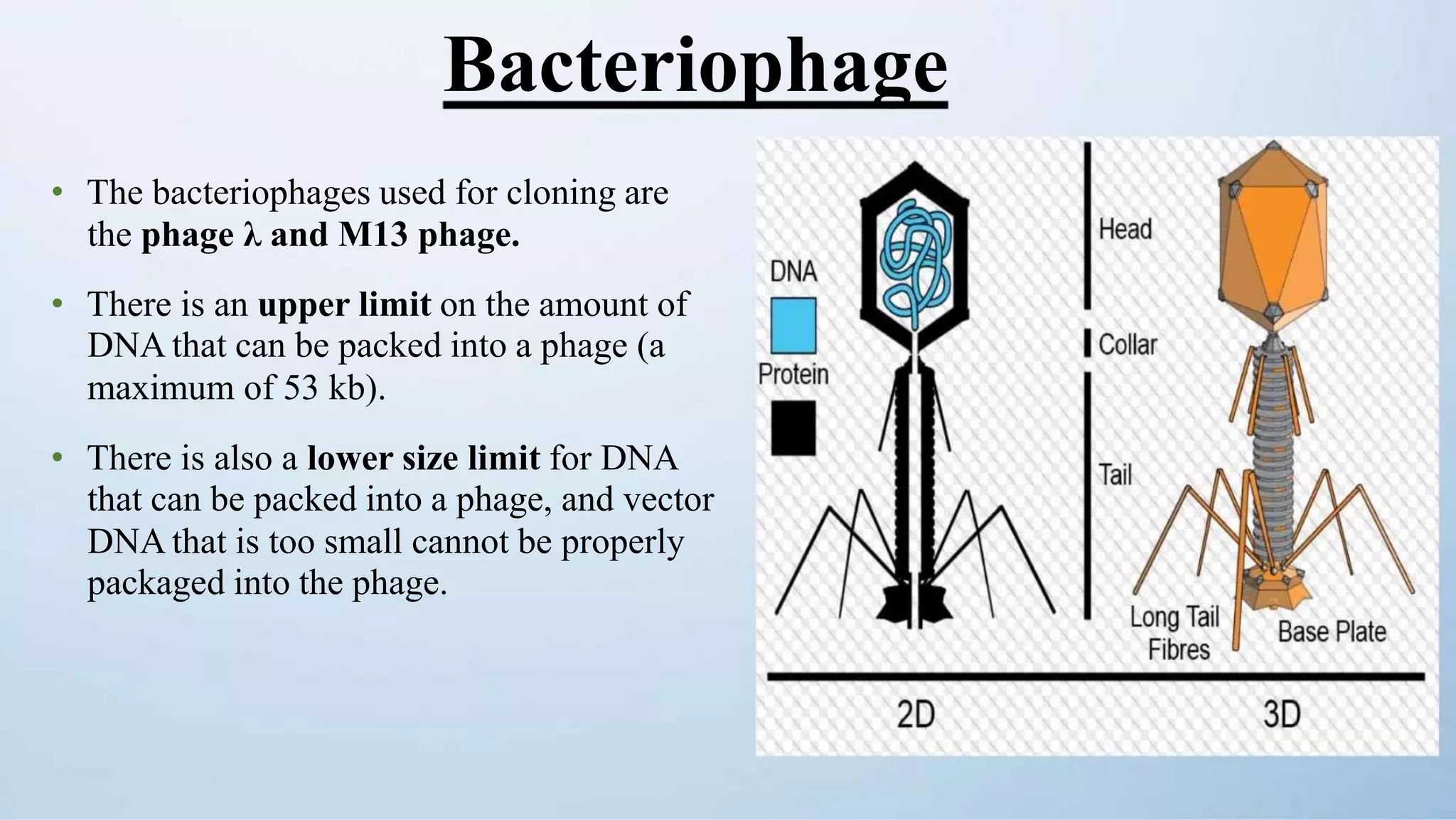
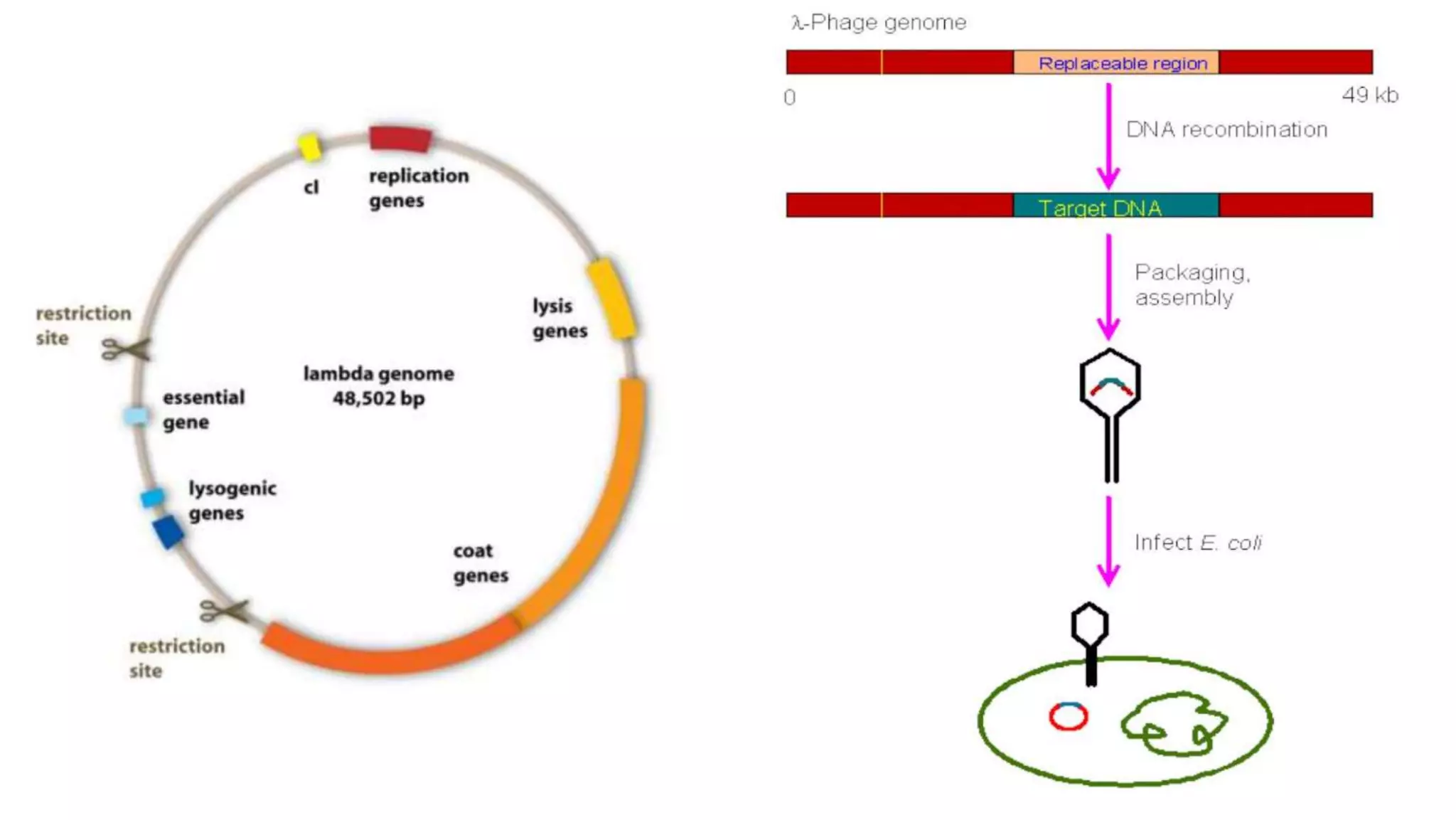
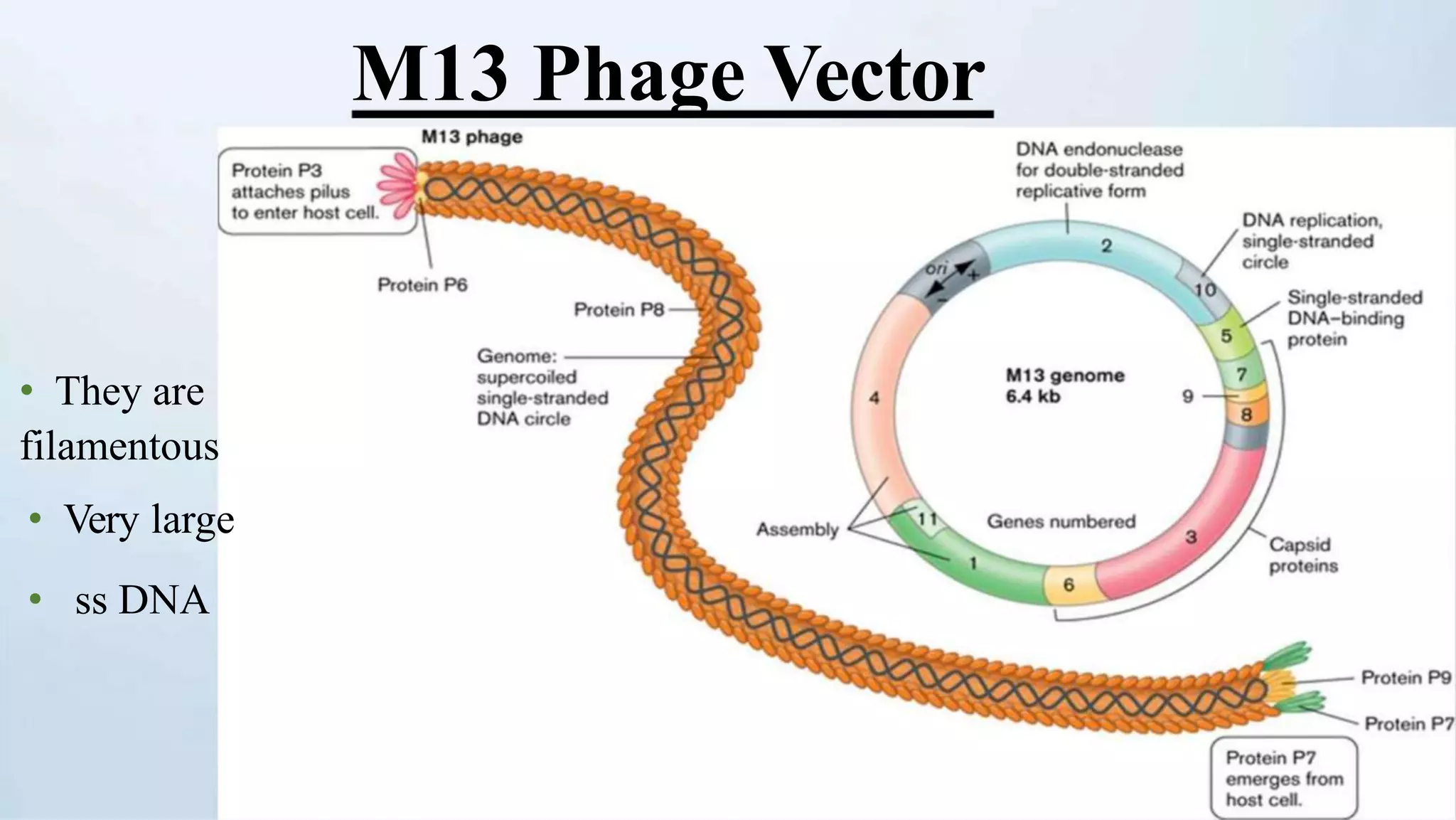
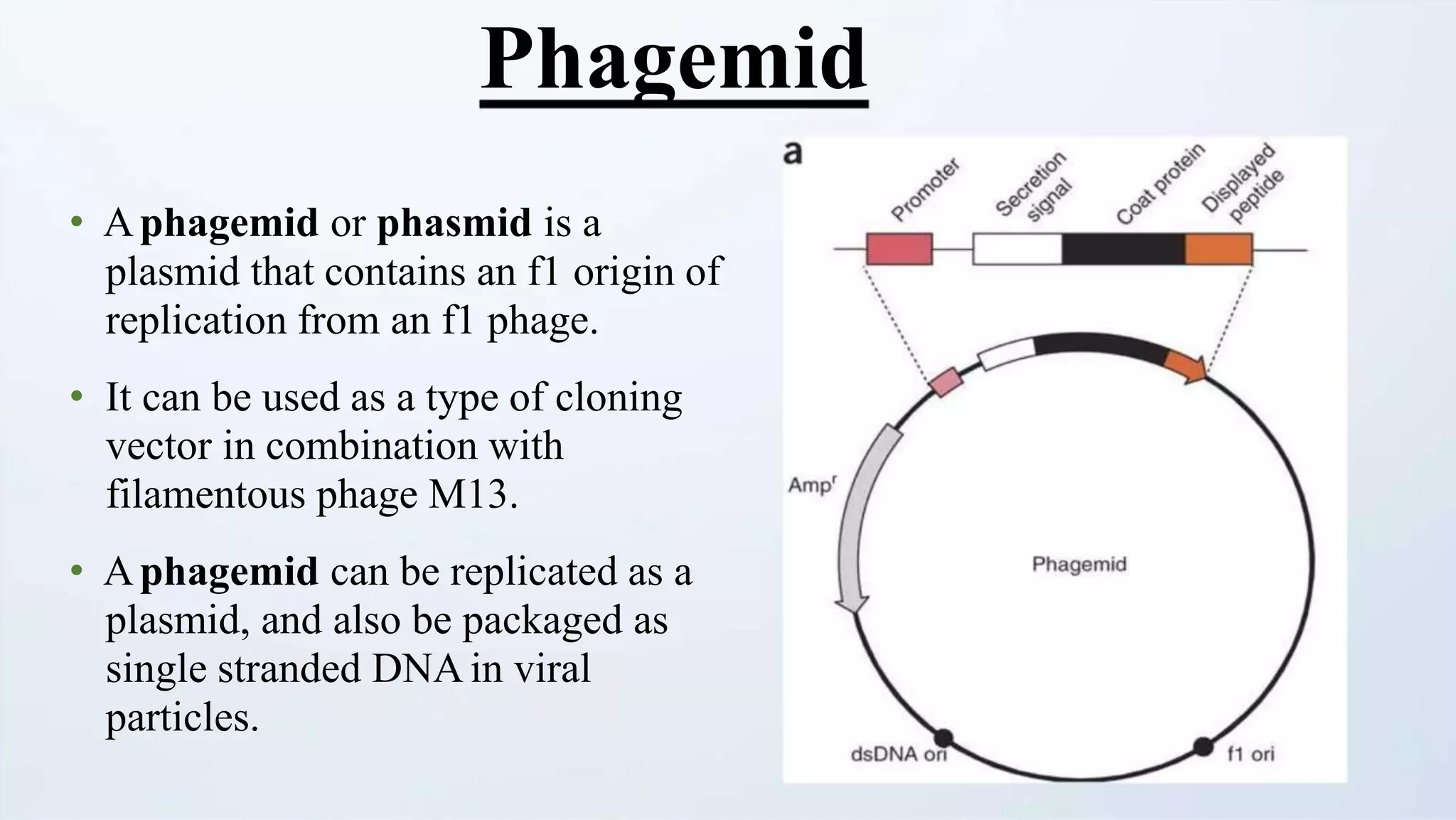
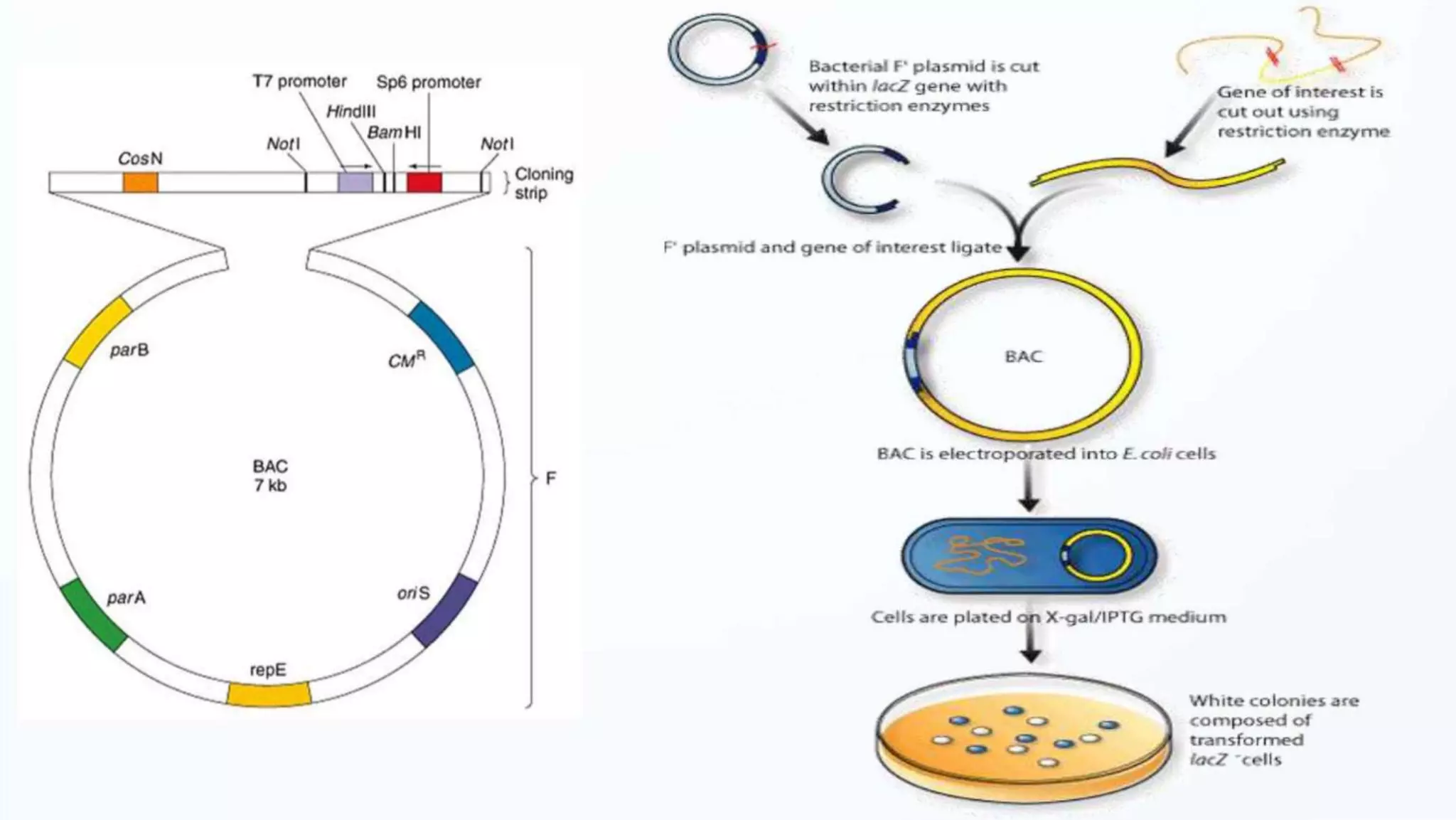
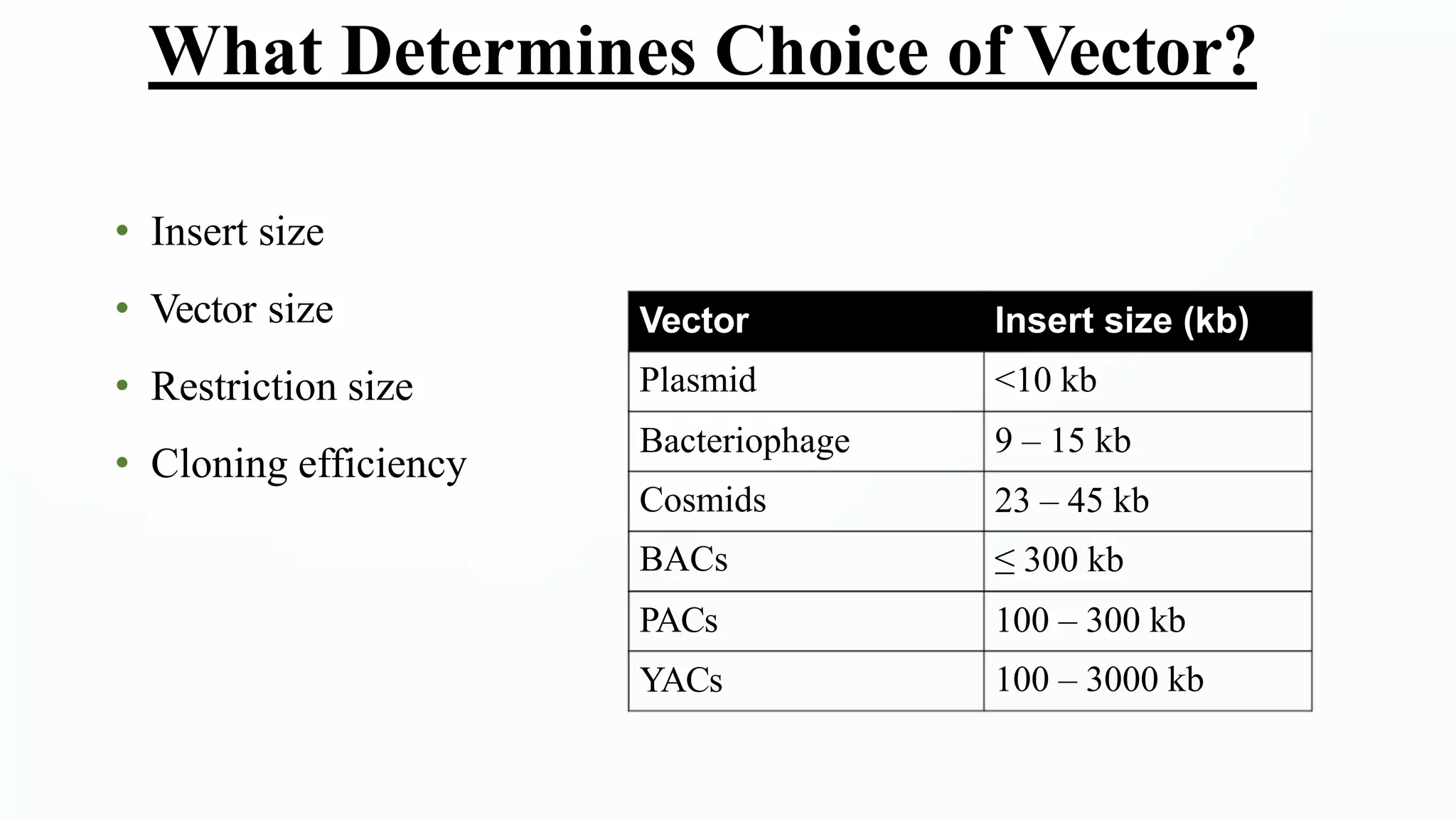
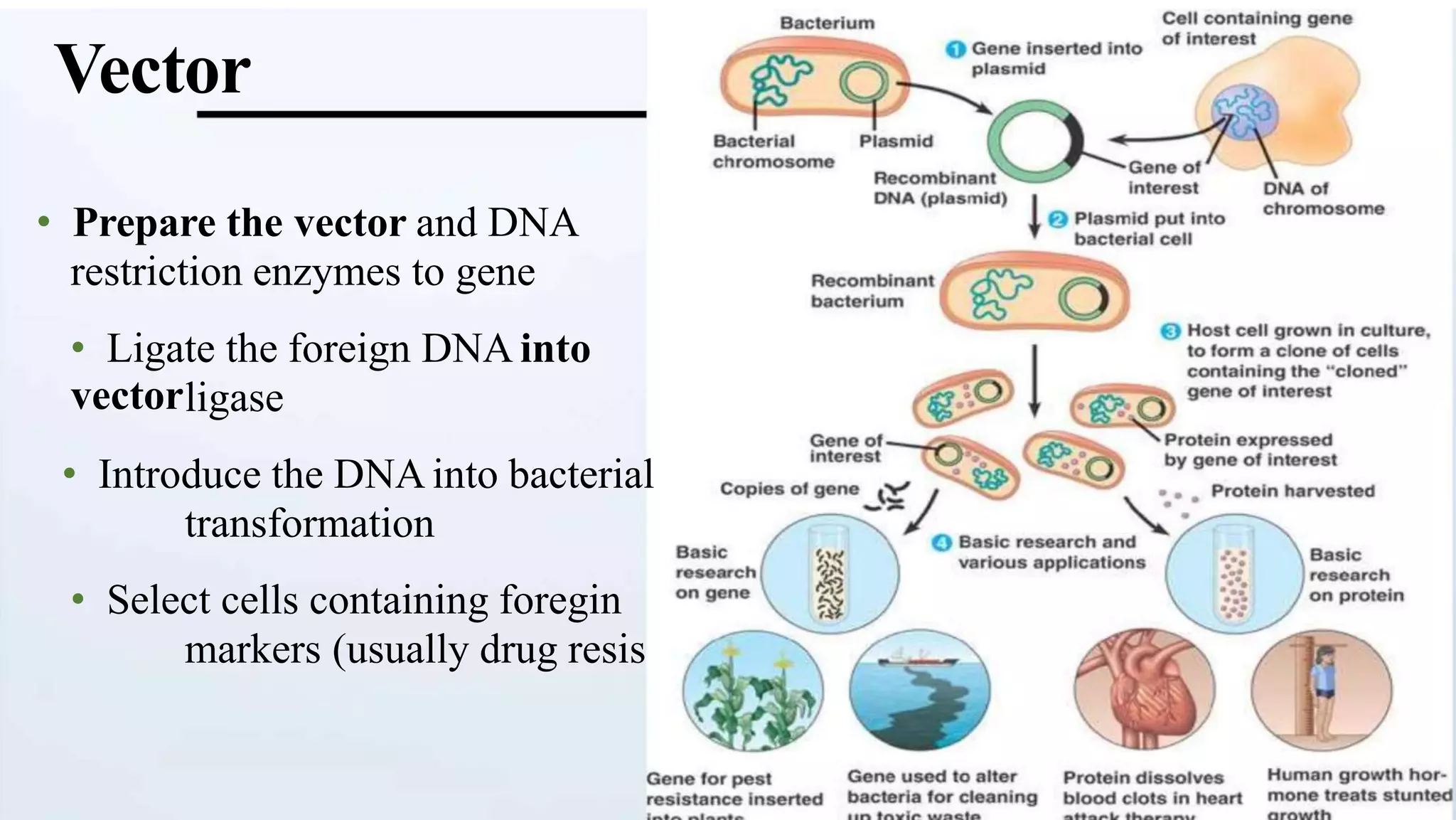
Cloning vectors are small DNA molecules that can accept foreign DNA inserts and replicate within a host cell. They contain features like an origin of replication, antibiotic resistance genes, and restriction enzyme cleavage sites. Common vector types include plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. The choice of vector depends on factors like the size of the DNA insert and the intended use. Vectors allow amplification and manipulation of cloned DNA fragments.