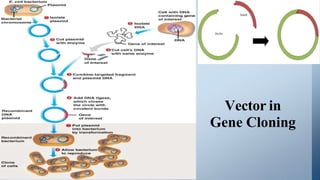
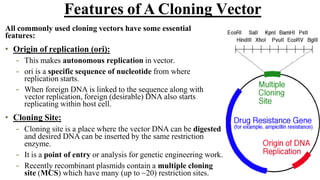
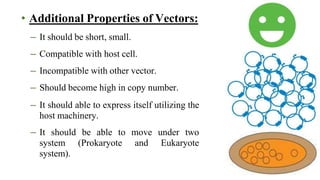
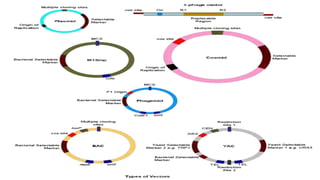
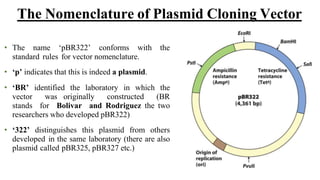
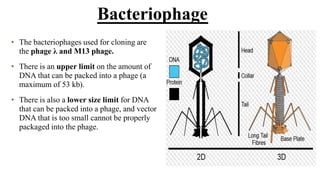
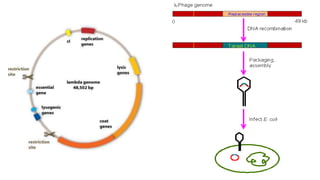
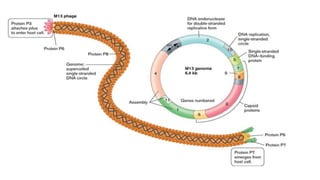
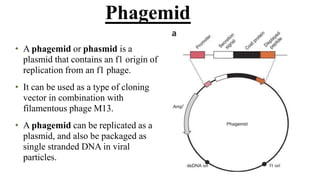
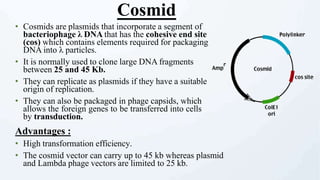
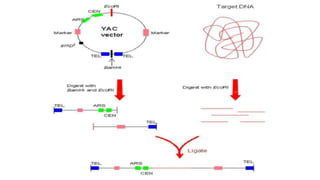
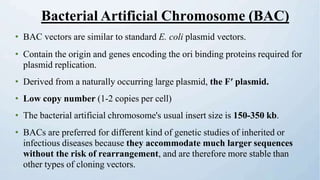
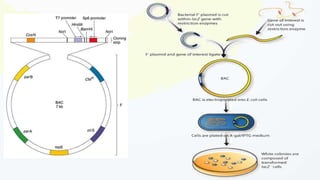
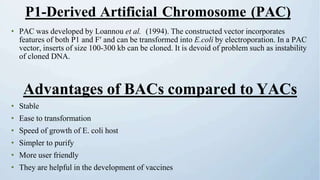
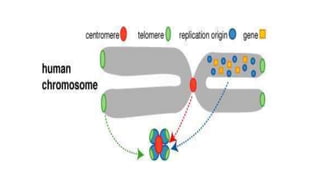
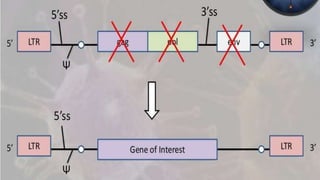
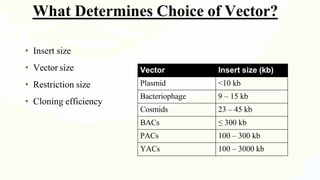
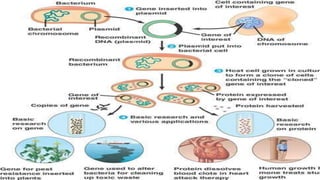
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA, such as a plasmid, virus, or artificial chromosome, that can accept foreign DNA and be replicated within a host cell. The summary describes the main types of cloning vectors, including plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, BACs, YACs, and retroviral vectors. It also outlines some key features of cloning vectors like origins of replication, cloning sites, and selectable markers. The choice of vector depends on factors like the size of the DNA insert and cloning efficiency.