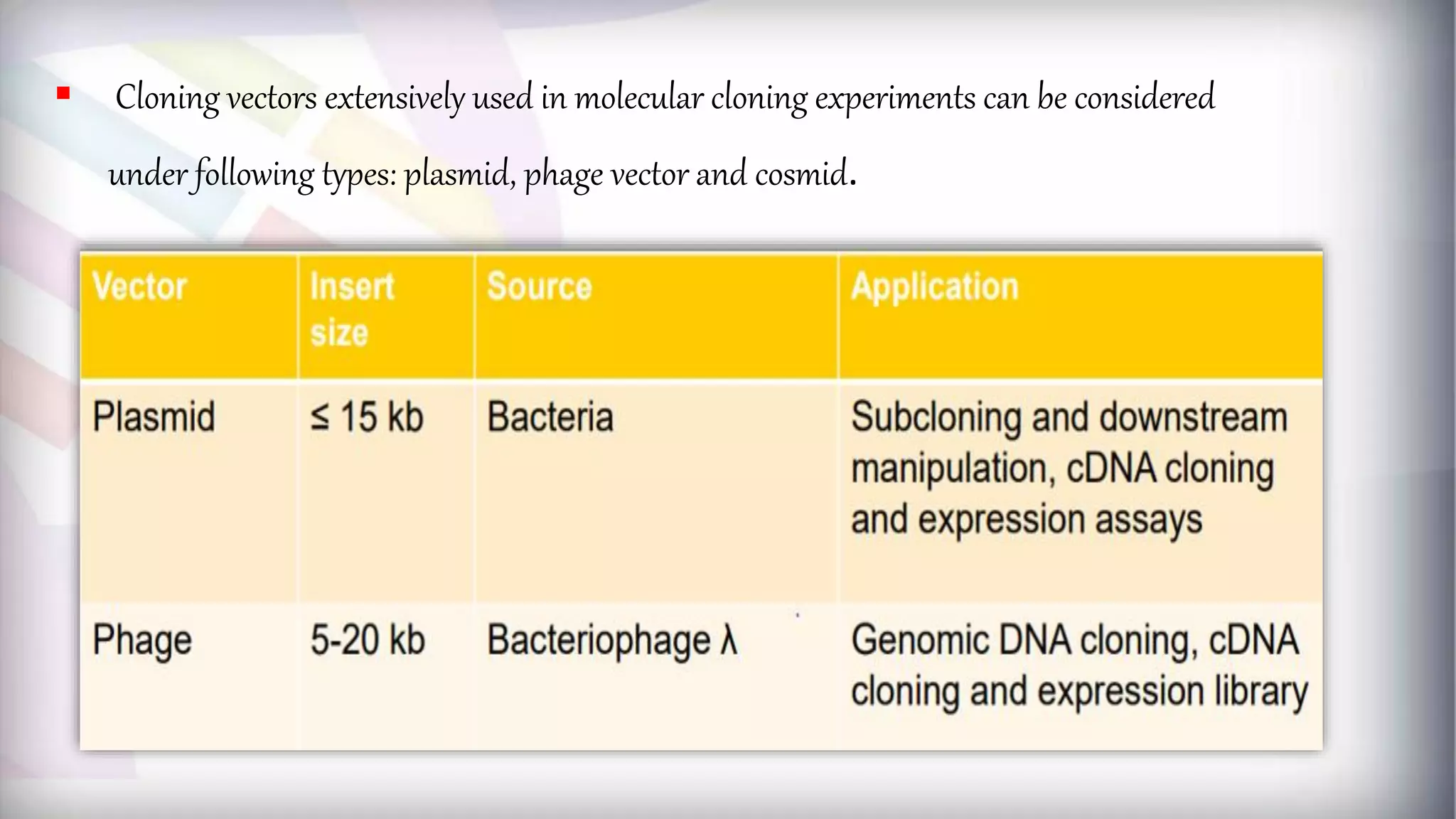
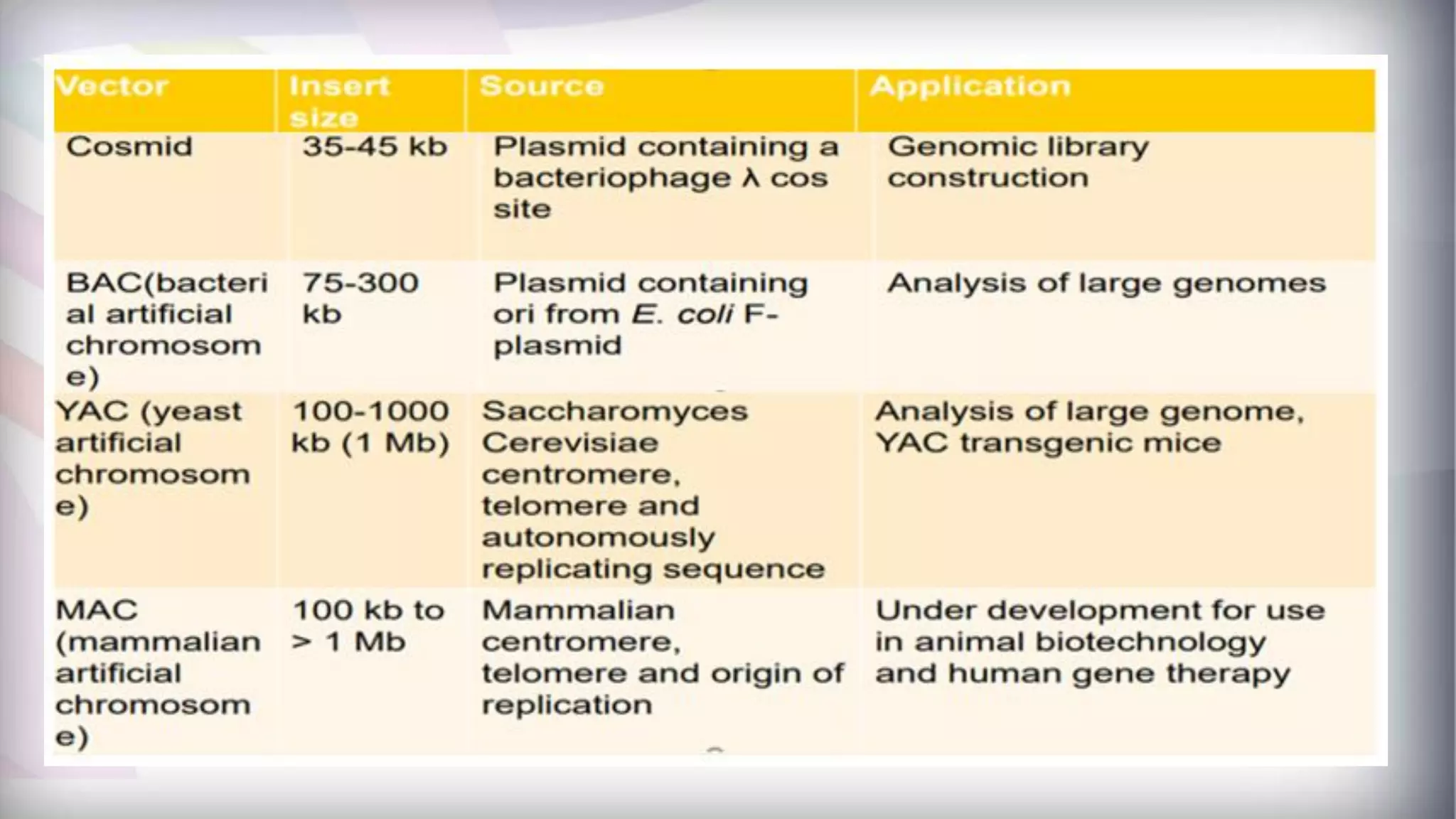
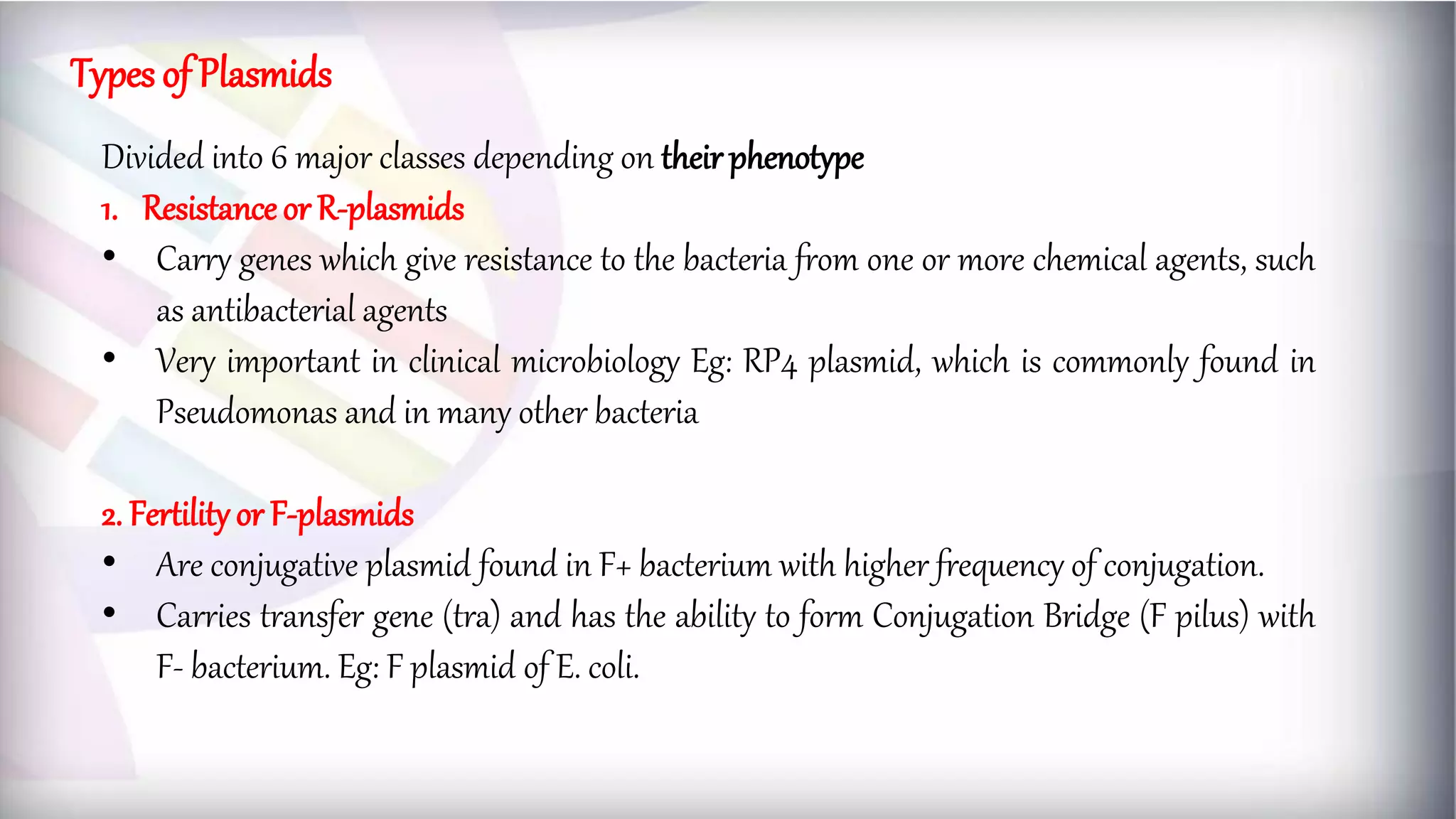
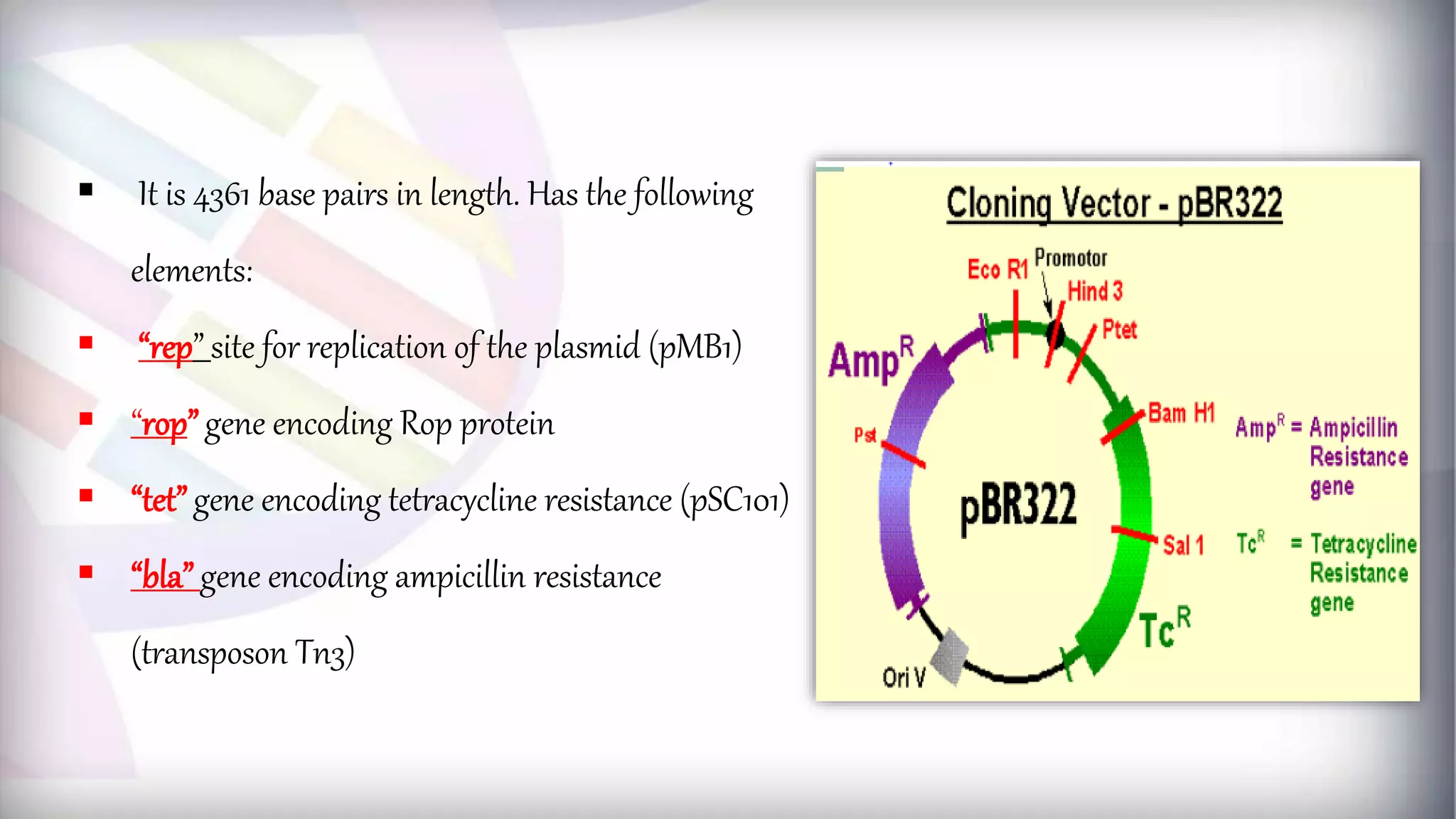
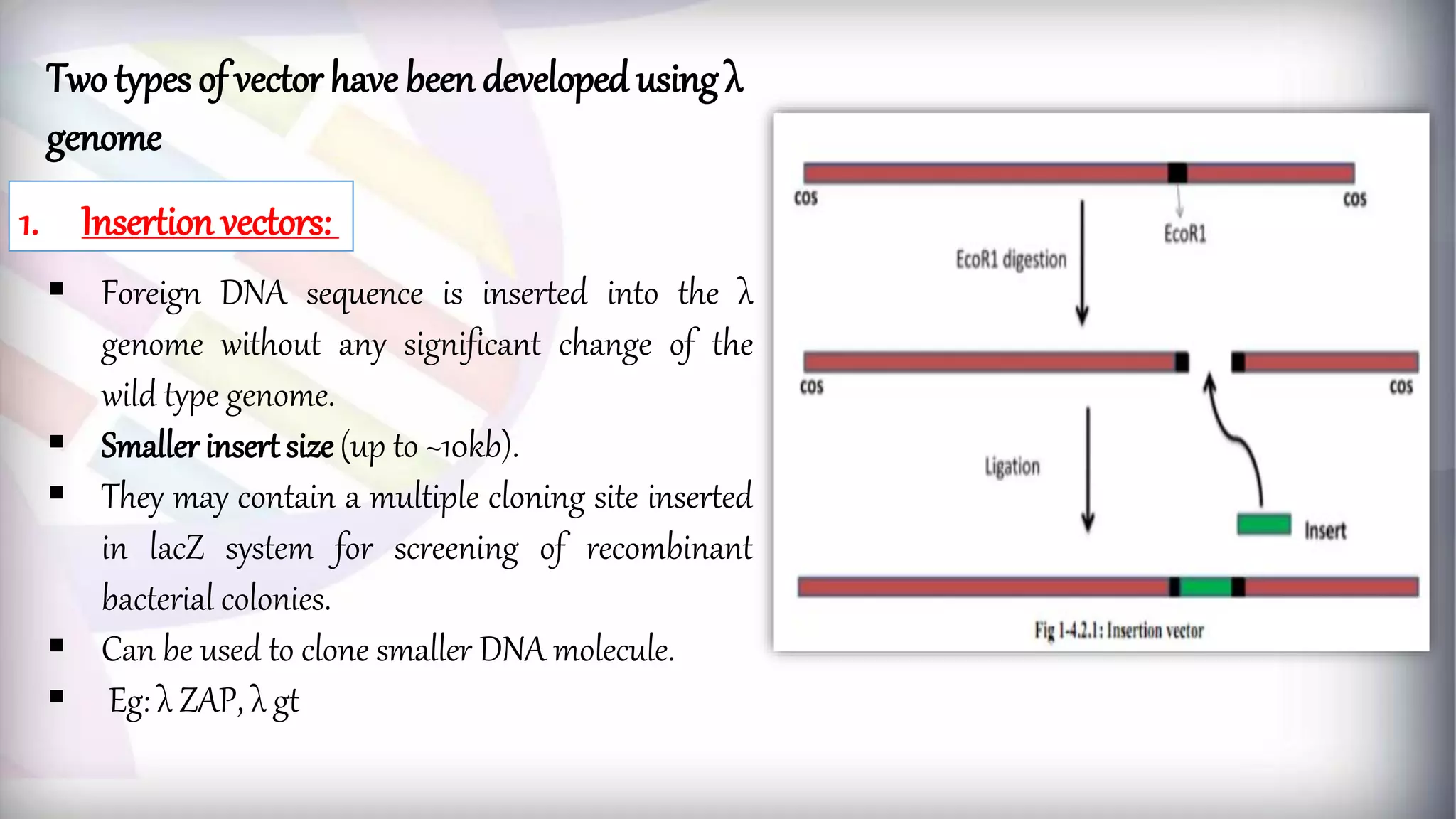
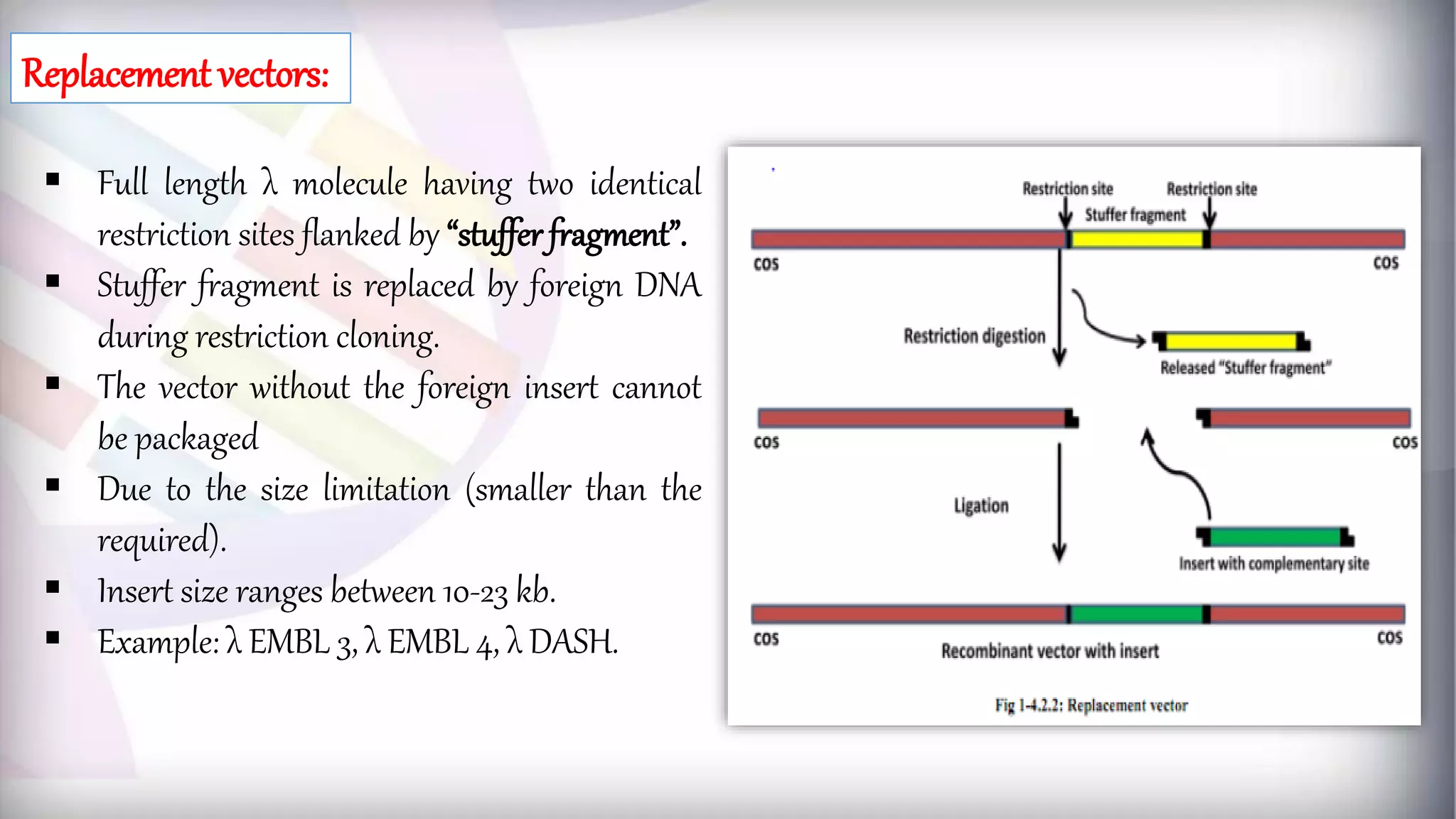
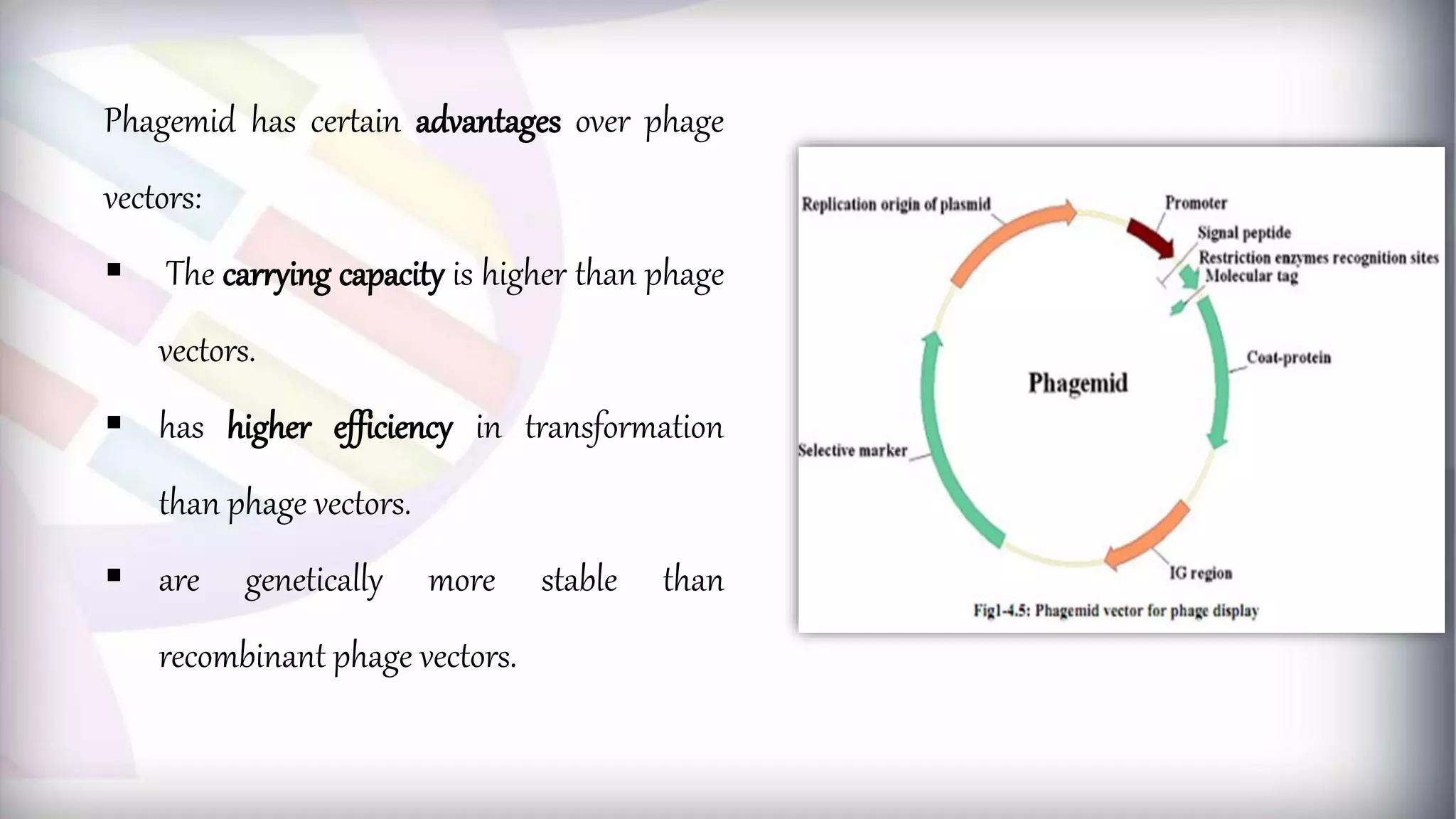
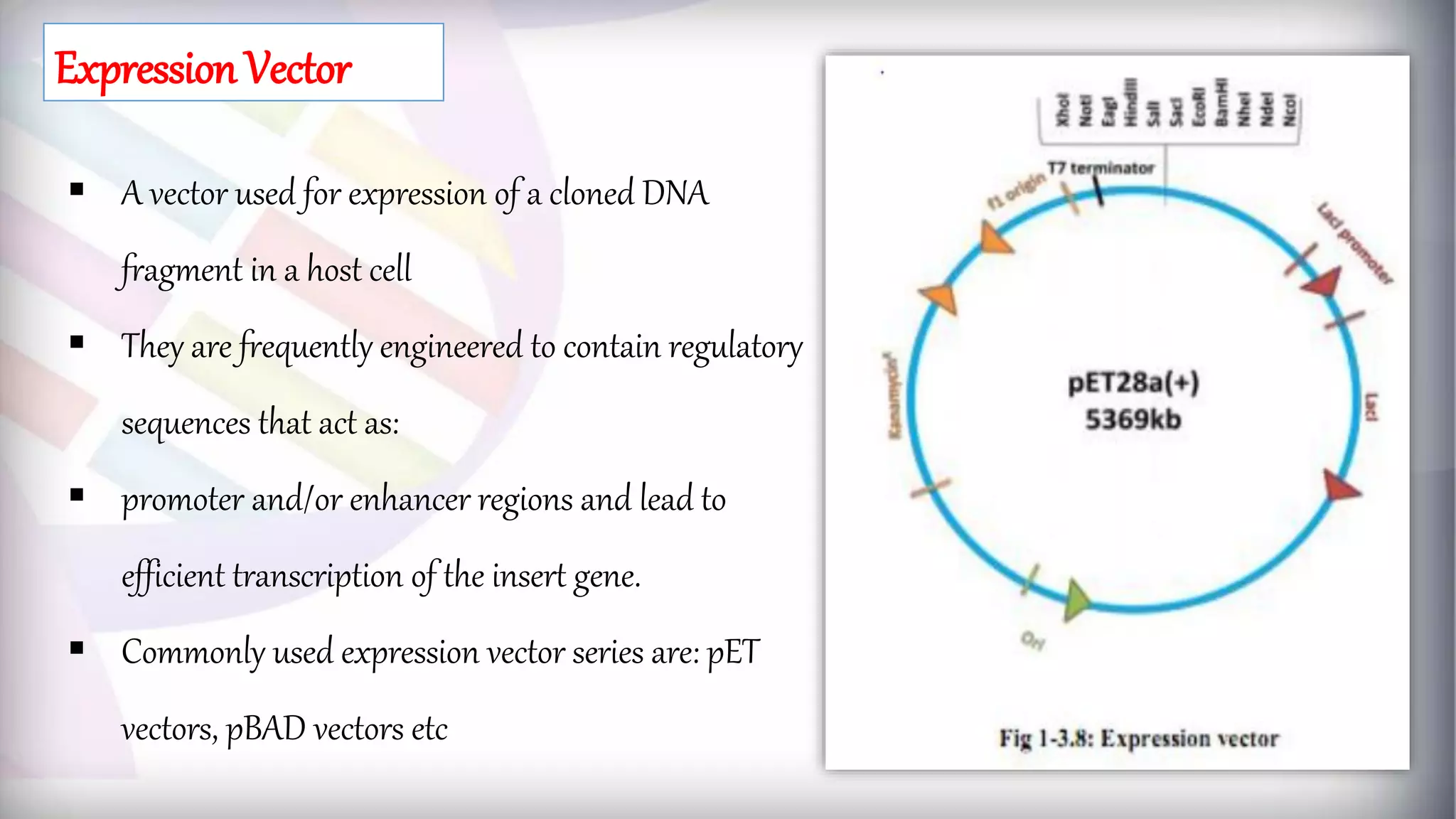
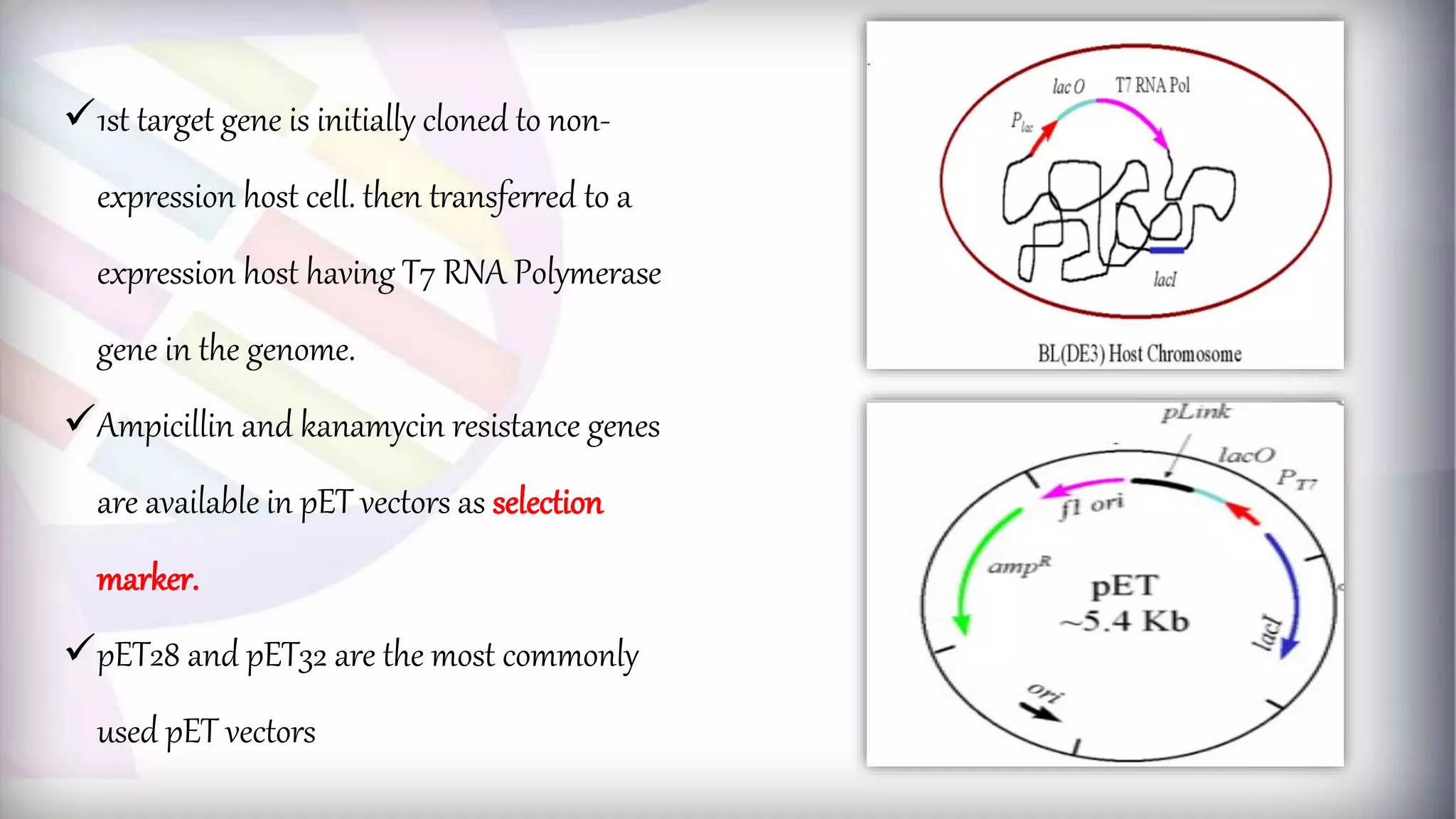
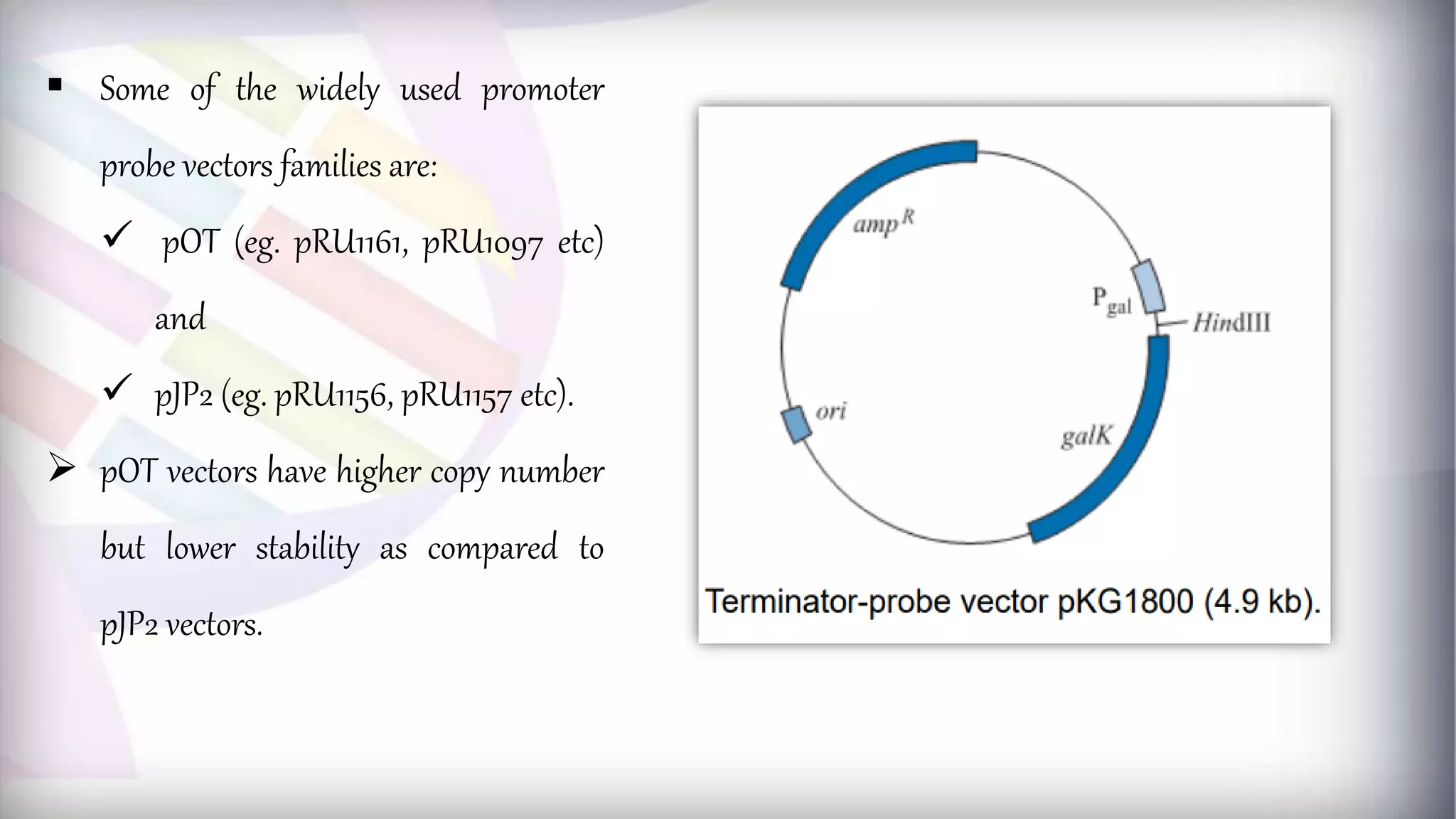
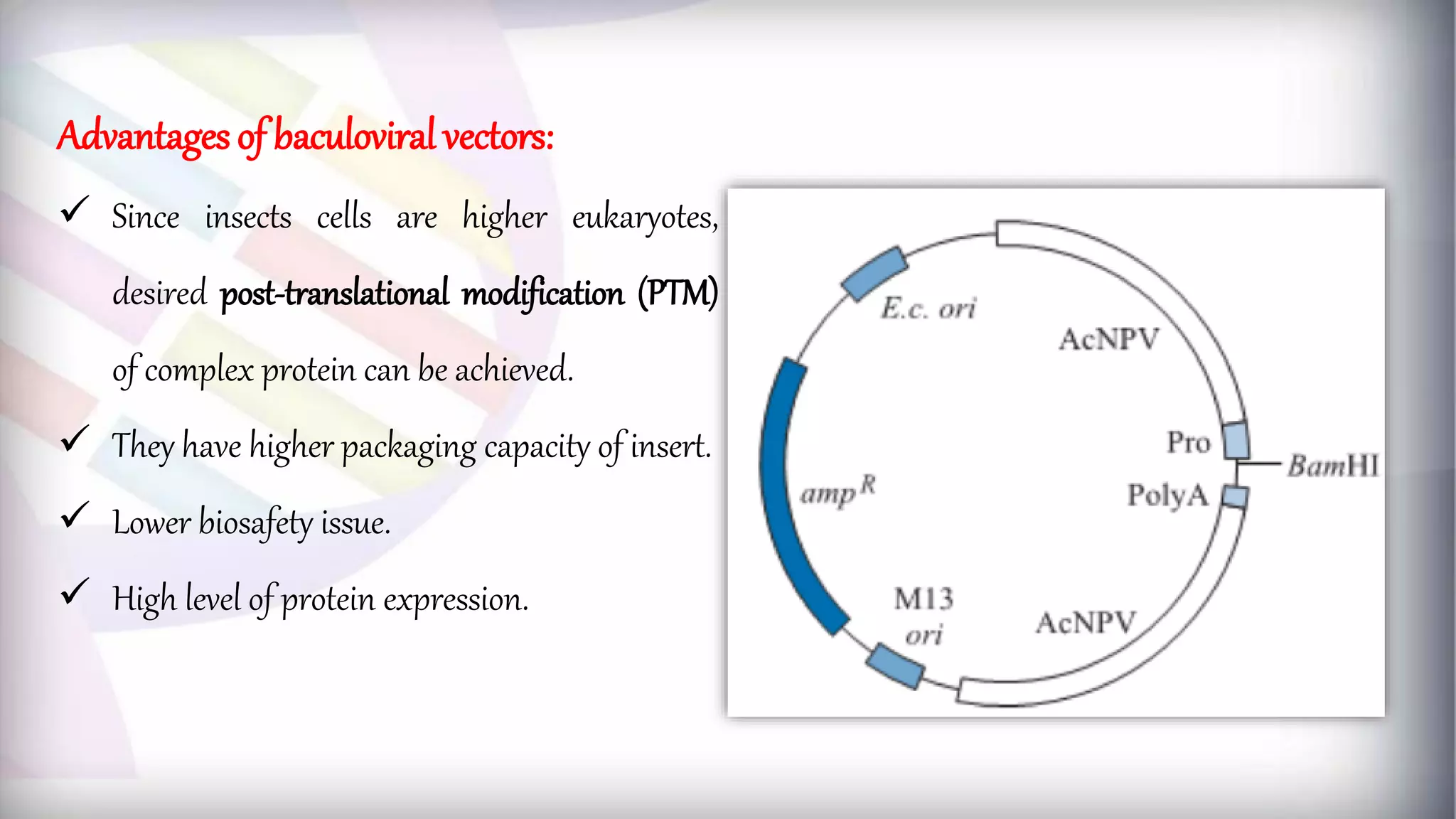
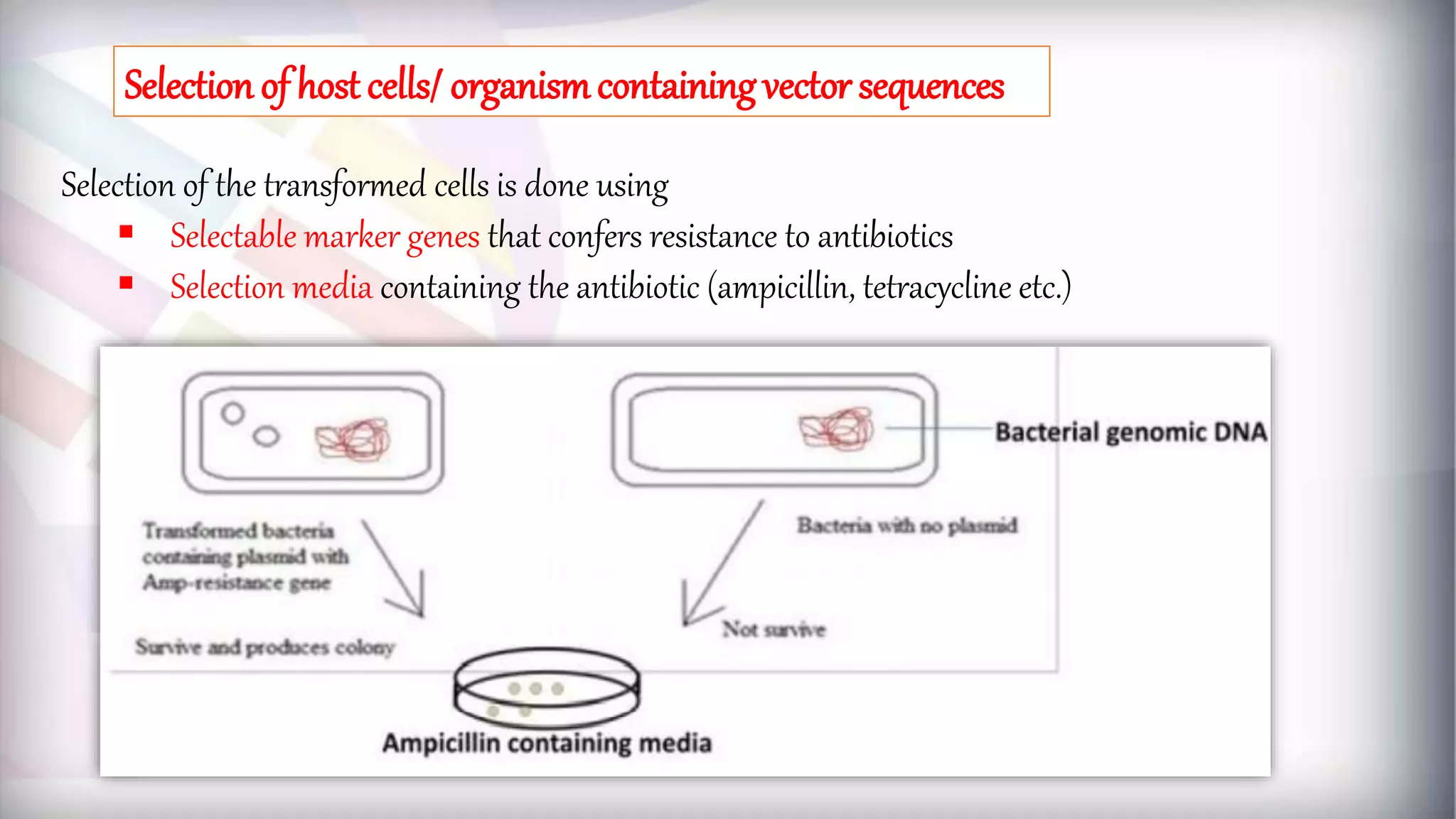
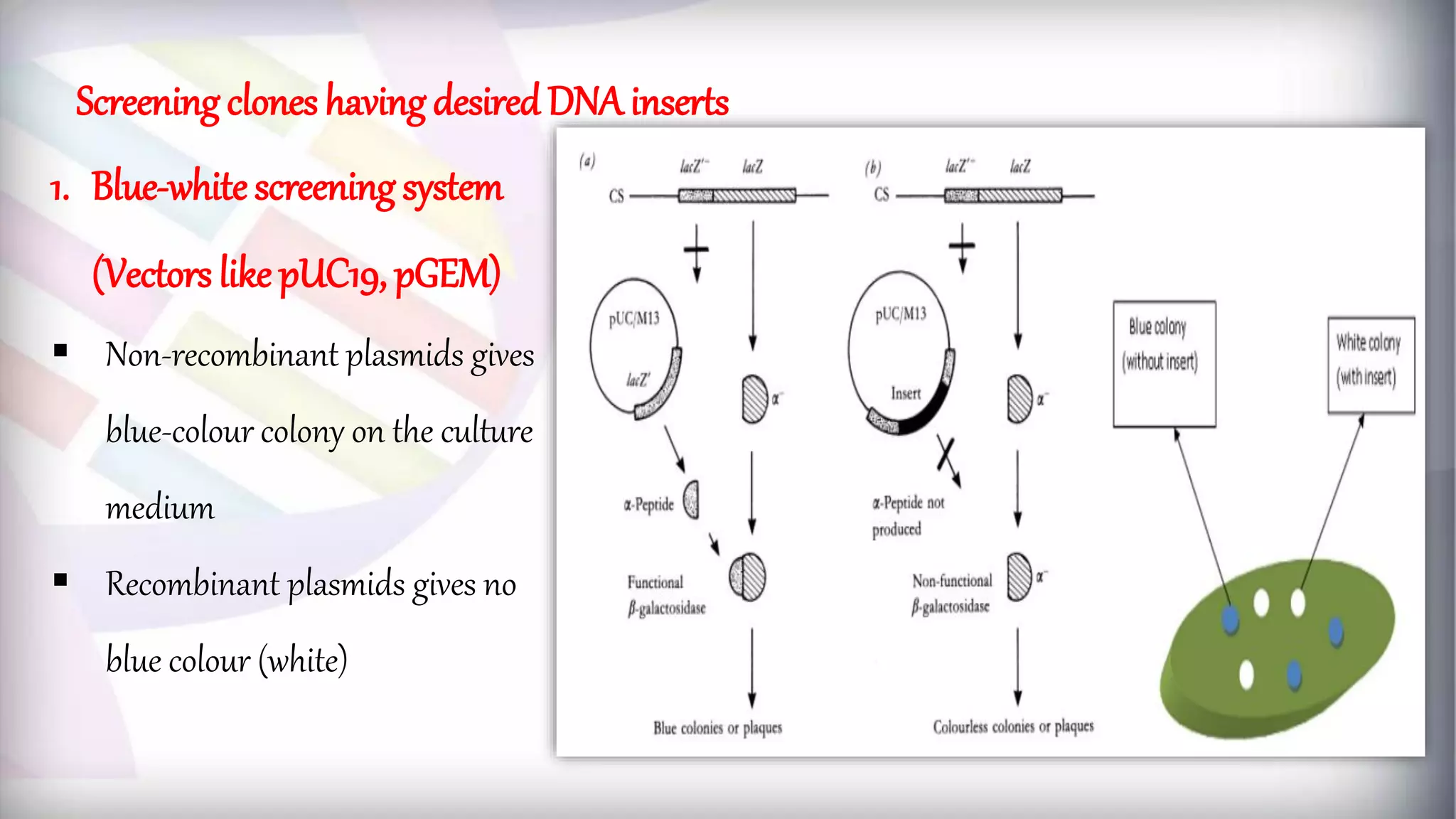
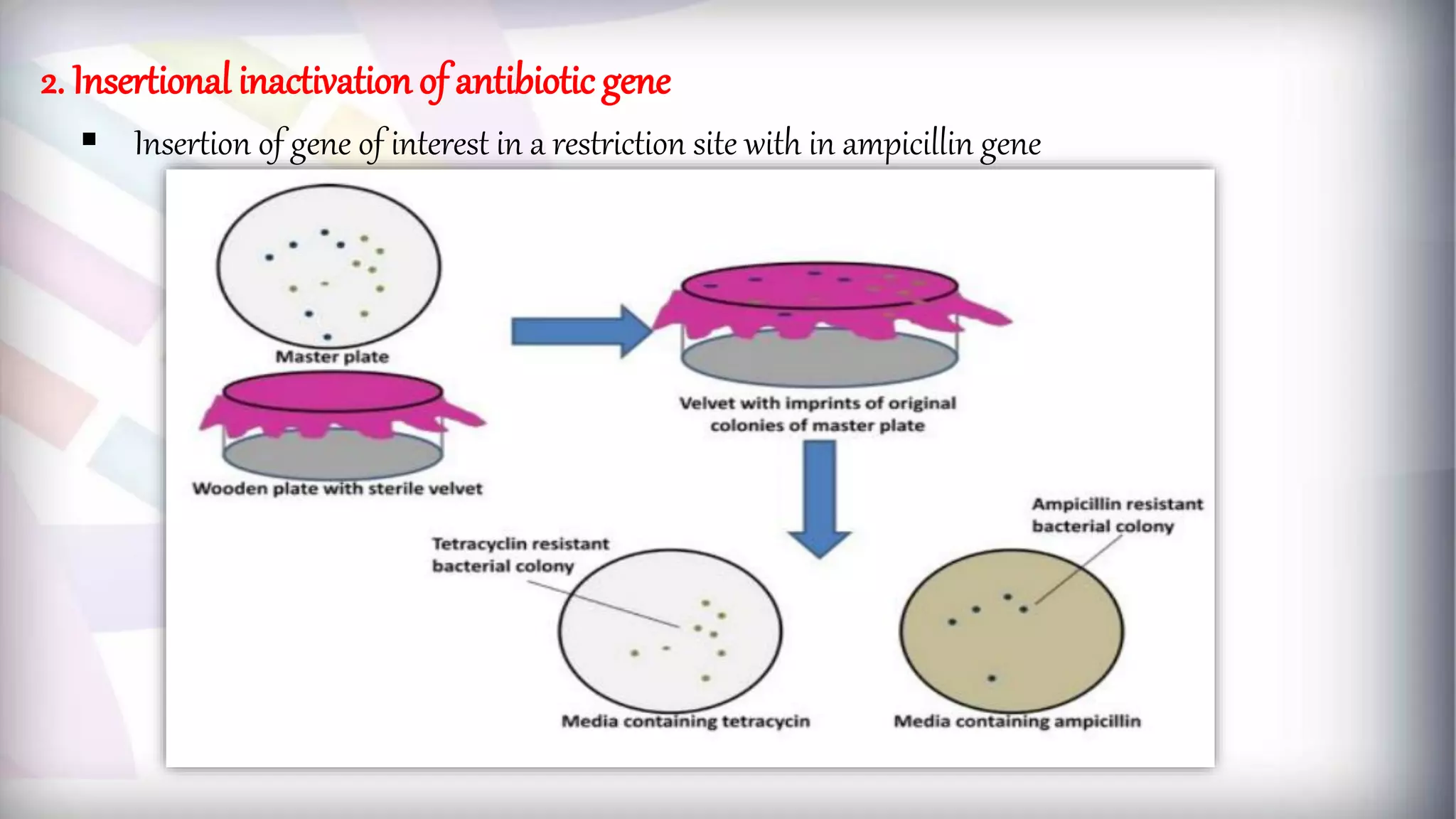
This document discusses different types of genetic vectors used in molecular cloning. It begins by defining vectors as DNA molecules used to artificially carry foreign genetic material into host cells. Vectors can be classified as cloning or expression vectors. Key features of cloning vectors discussed include origins of replication, selectable markers, and the ability to accommodate DNA inserts of varying sizes. Common vector types described are plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, fosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Specific examples like pBR322, pUC, and lambda phage vectors are explained in terms of their components and applications. The document provides an overview of genetic vectors for molecular cloning.