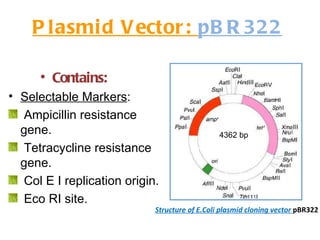
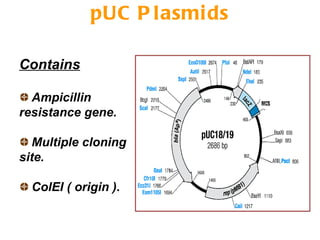
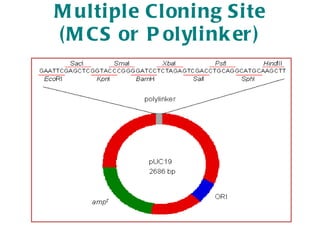
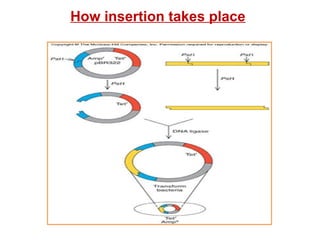
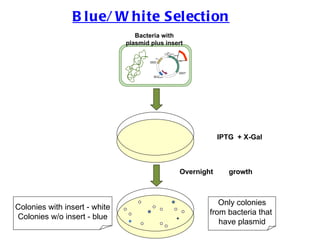
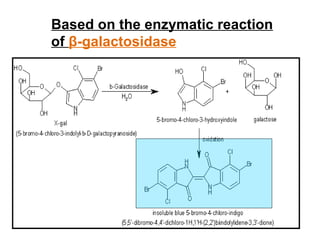
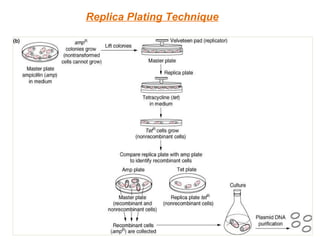
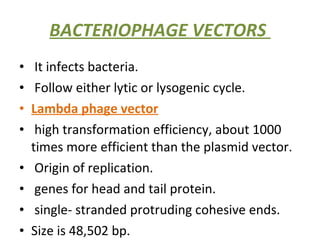
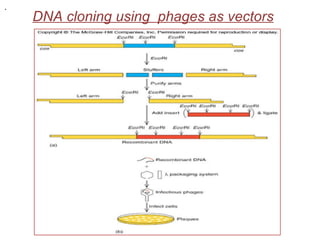
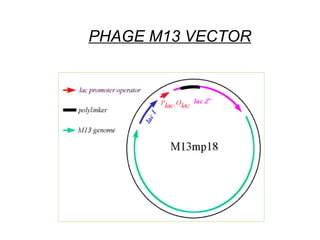
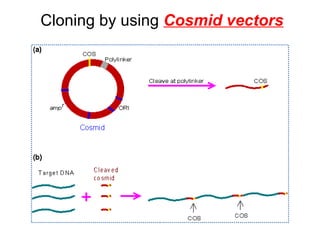
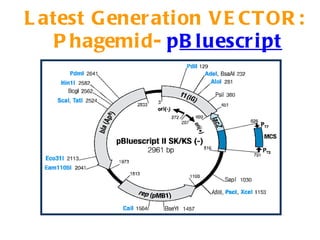
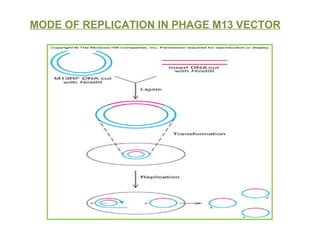
The document discusses different types of gene cloning vectors including plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, and phagemids. Plasmid vectors like pBR322 contain selectable markers and a multiple cloning site. Bacteriophage vectors like lambda phage infect bacteria and can carry larger DNA inserts. Cosmid vectors combine properties of plasmids and phages to clone fragments up to 50kb. All of these vector types allow cloning and replication of foreign DNA fragments in host cells.