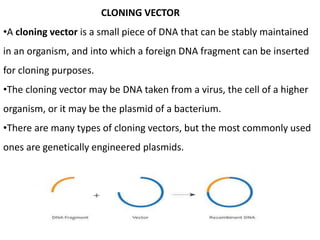
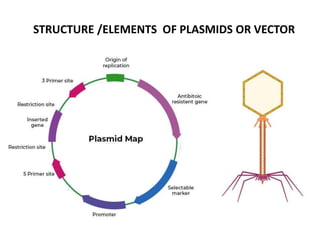
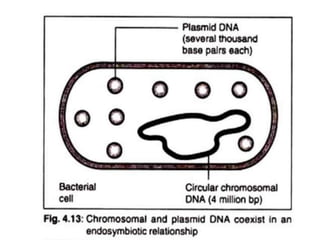
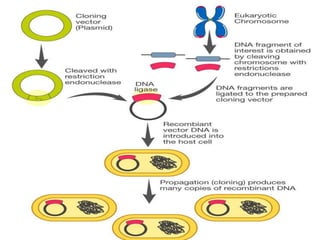
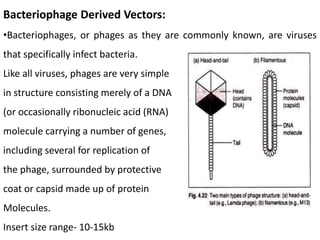
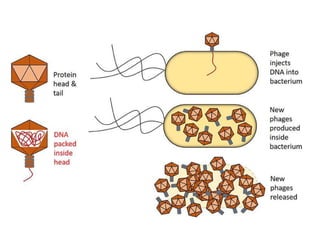
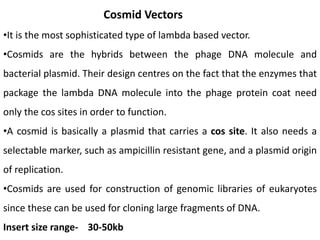
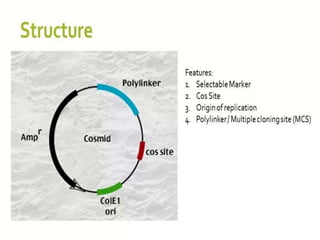
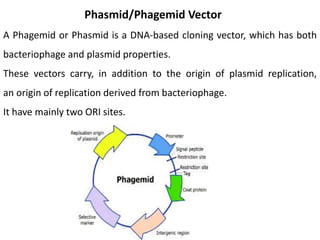
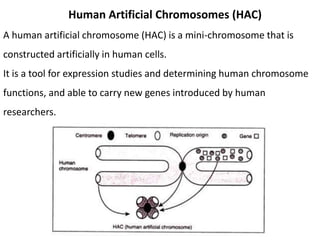
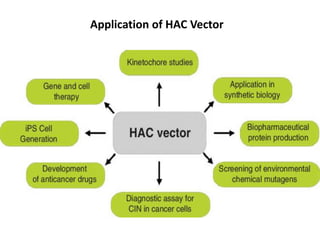
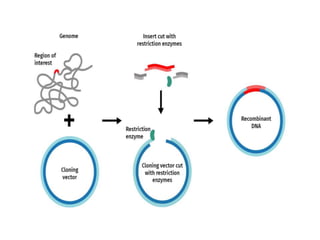
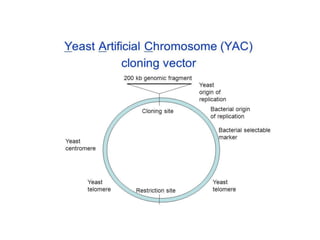
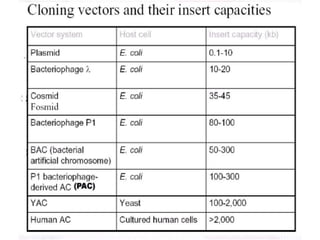
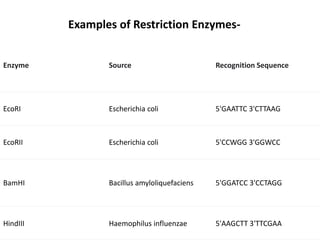
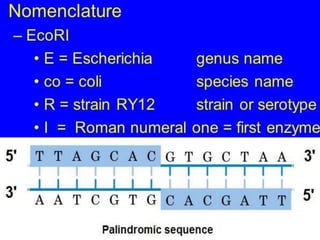
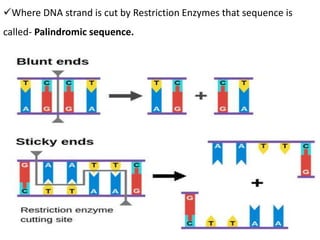
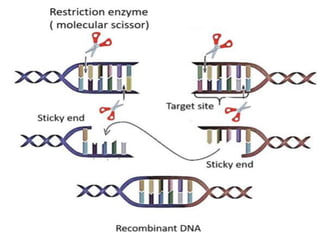
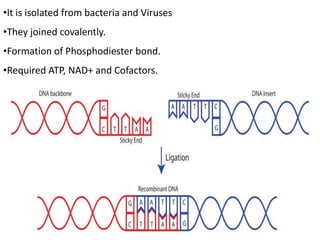
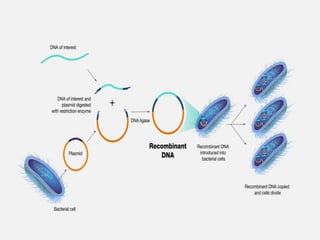
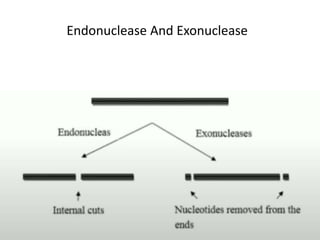
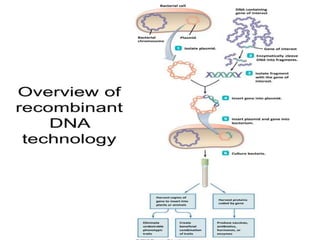
Cloning vectors are small pieces of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism and have foreign DNA inserted into them for cloning purposes. The most commonly used cloning vectors are genetically engineered plasmids. Plasmids are taken from bacteria and can replicate within bacterial cells. Other types of cloning vectors include bacteriophages, cosmids, yeast artificial chromosomes, and bacterial artificial chromosomes, which can accommodate larger DNA fragments. Restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are used to cut and join DNA fragments for cloning into vectors.