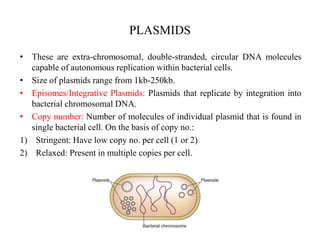
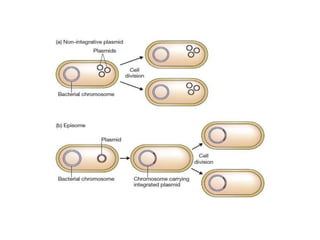
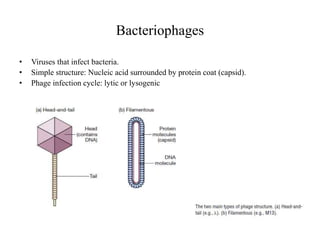
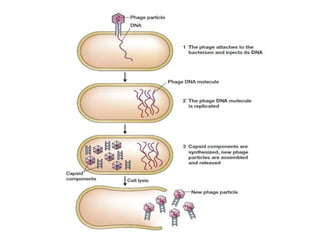
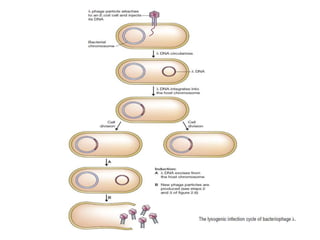
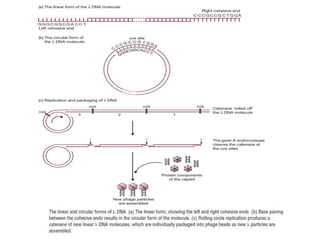
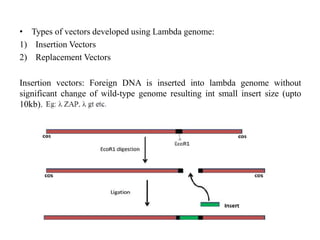
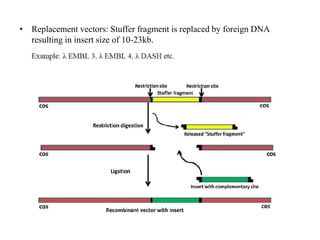
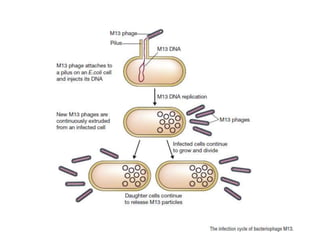
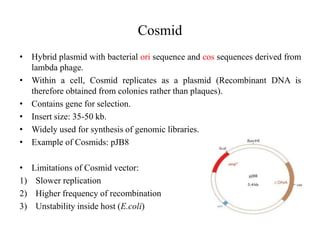
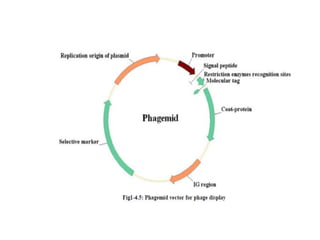
This document discusses various types of cloning vectors including plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, phagemids, and artificial chromosomes that are used to clone DNA fragments. It provides details on commonly used plasmid vectors like pBR322 and pUC, lambda phage vectors, properties of cosmids, phagemids and artificial chromosomes like BACs, YACs, and MACs. Components, applications, and limitations of these different vector types are summarized.