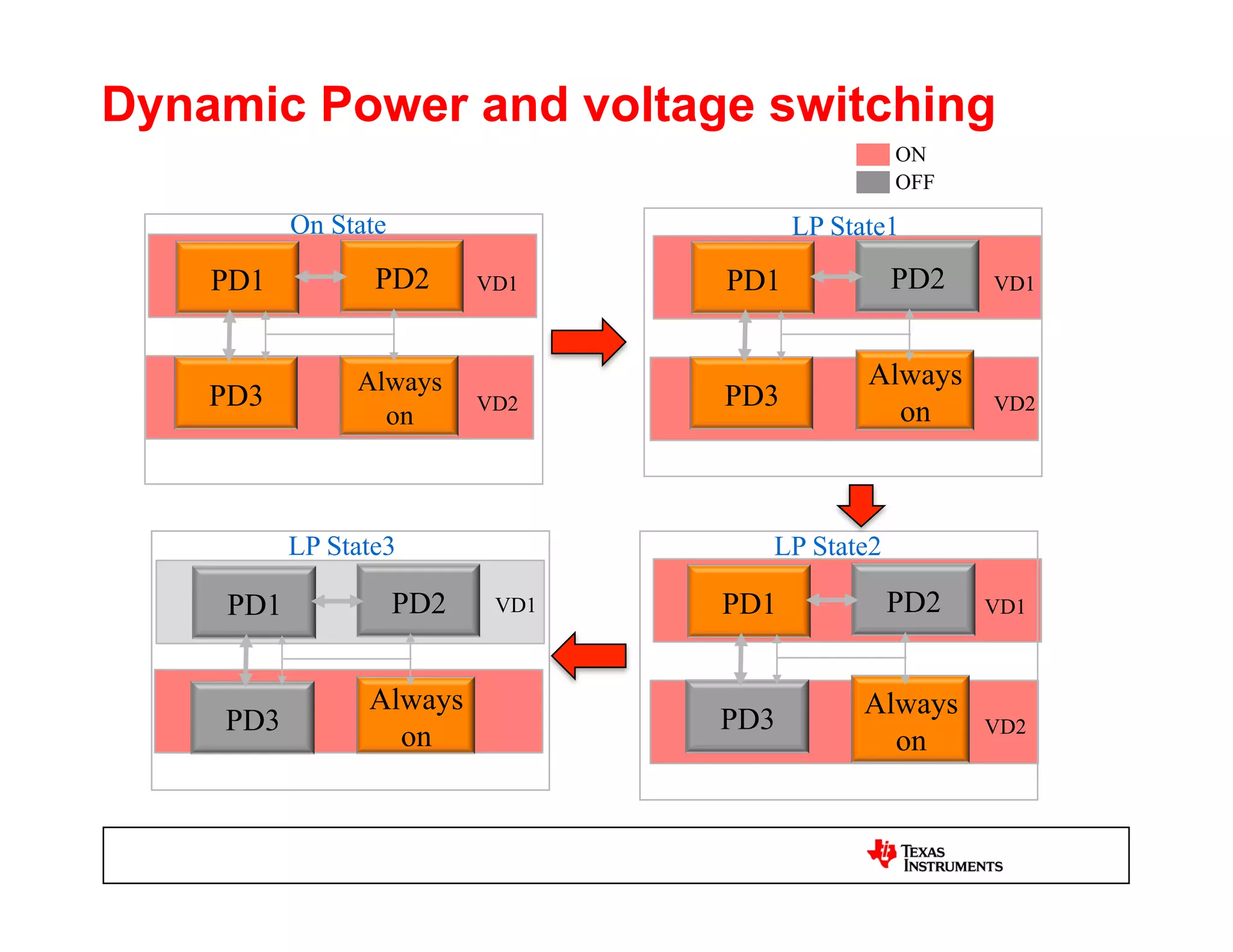
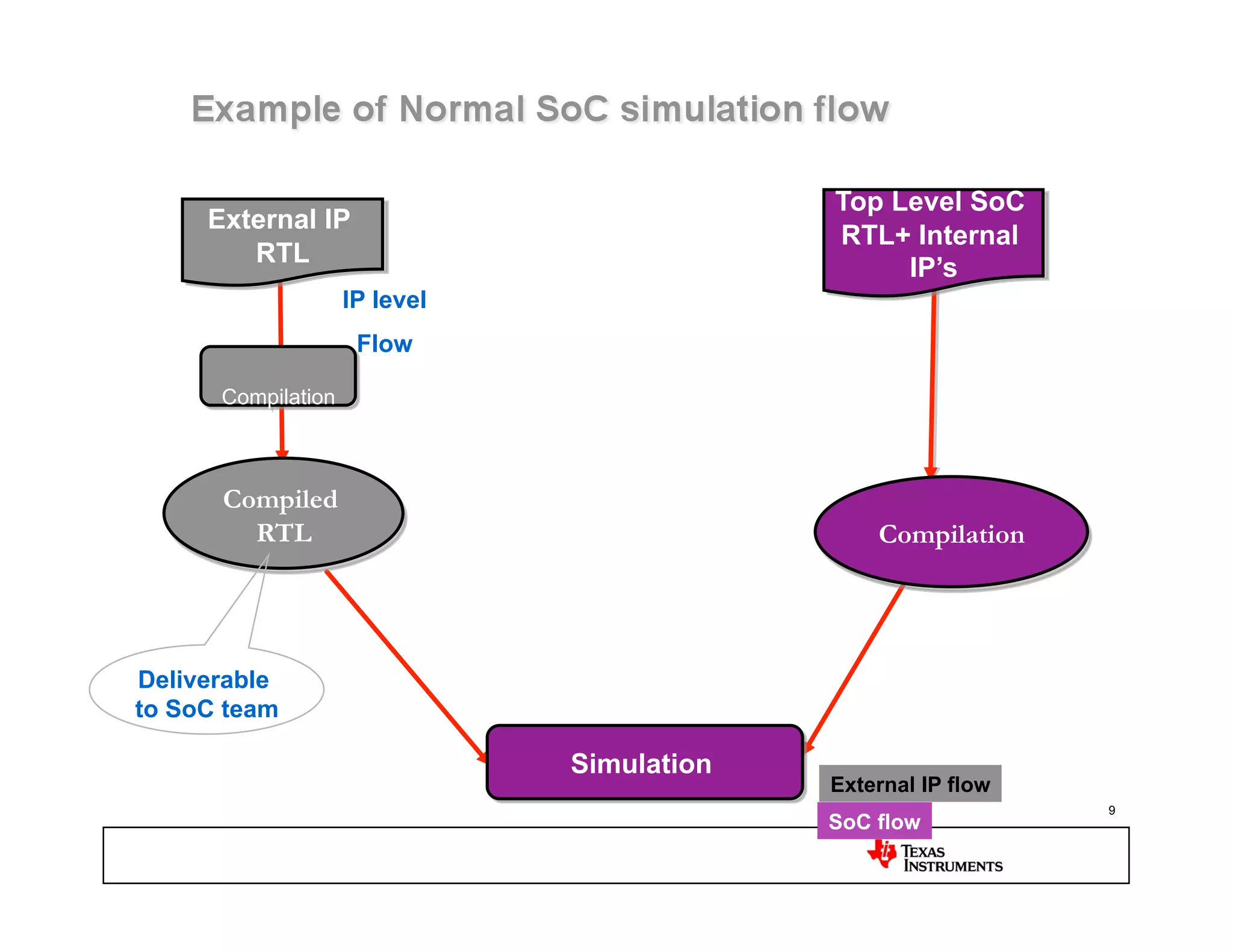
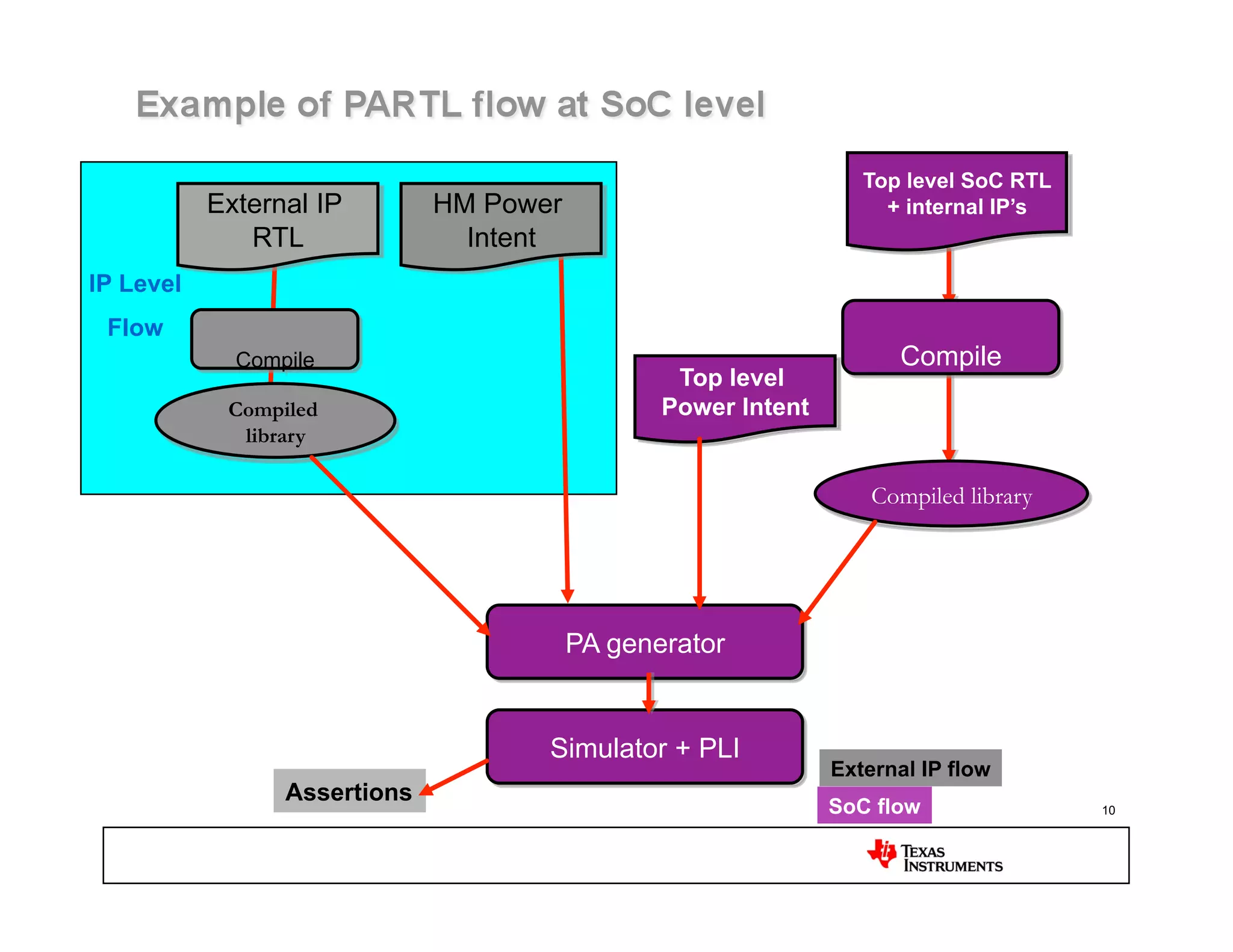
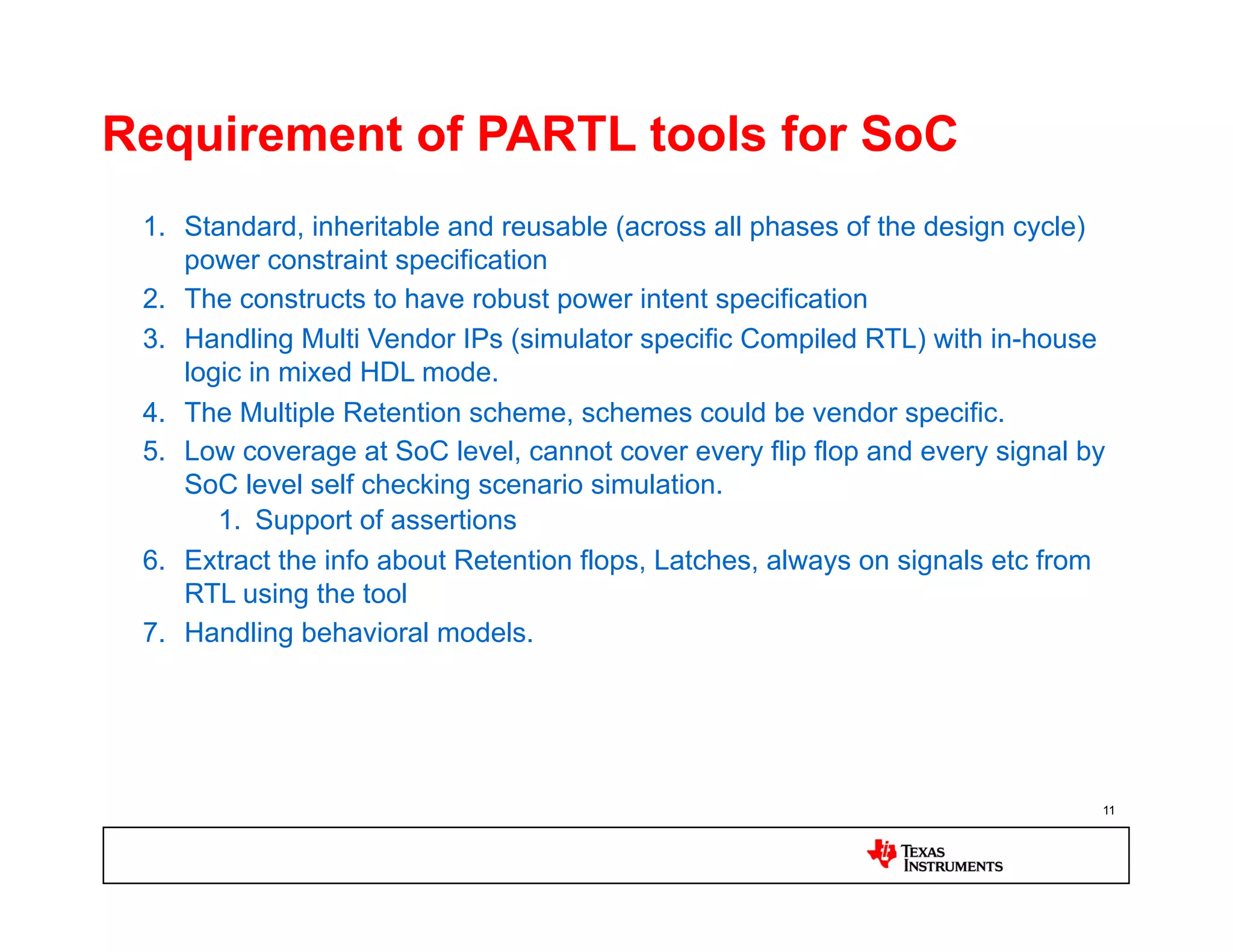
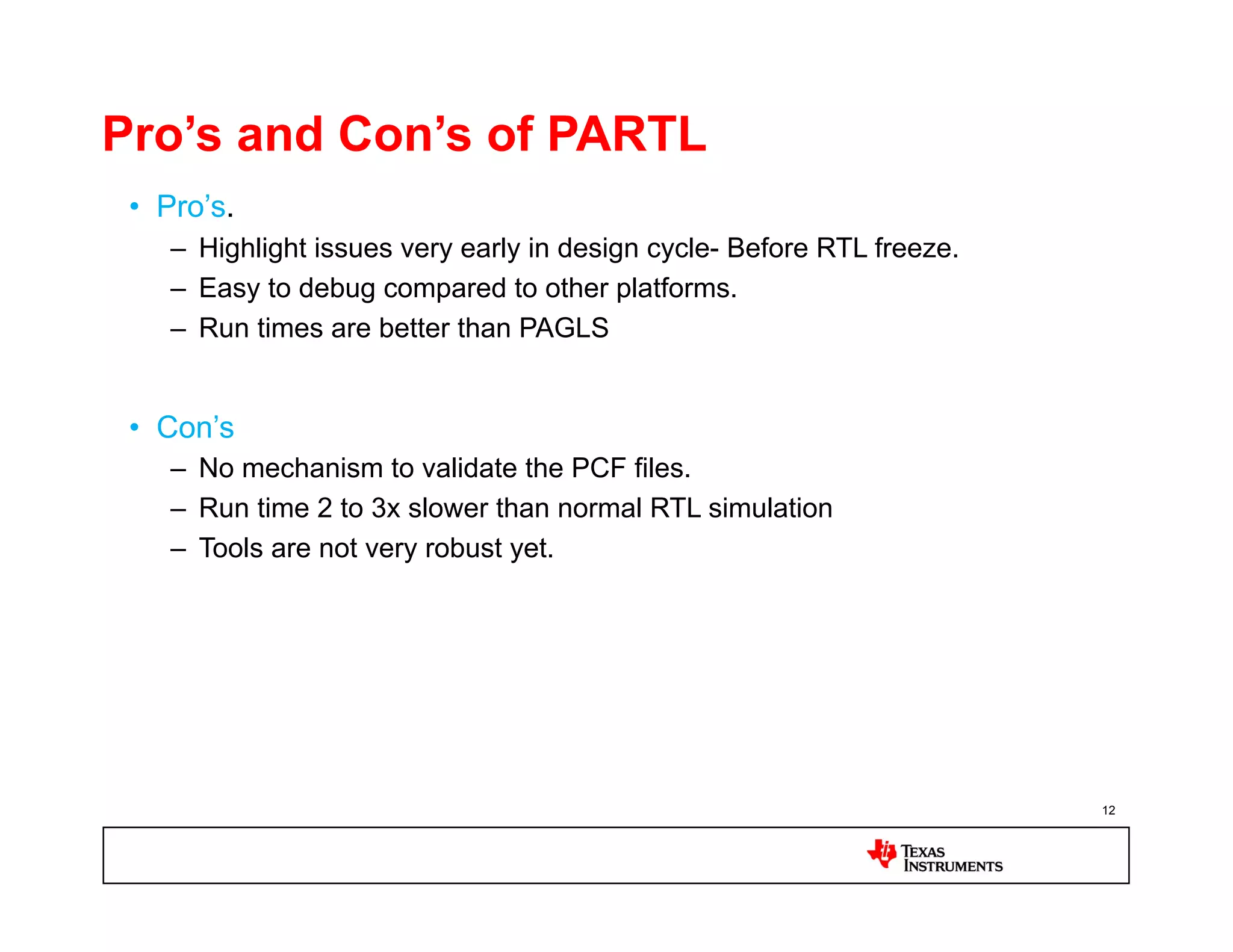
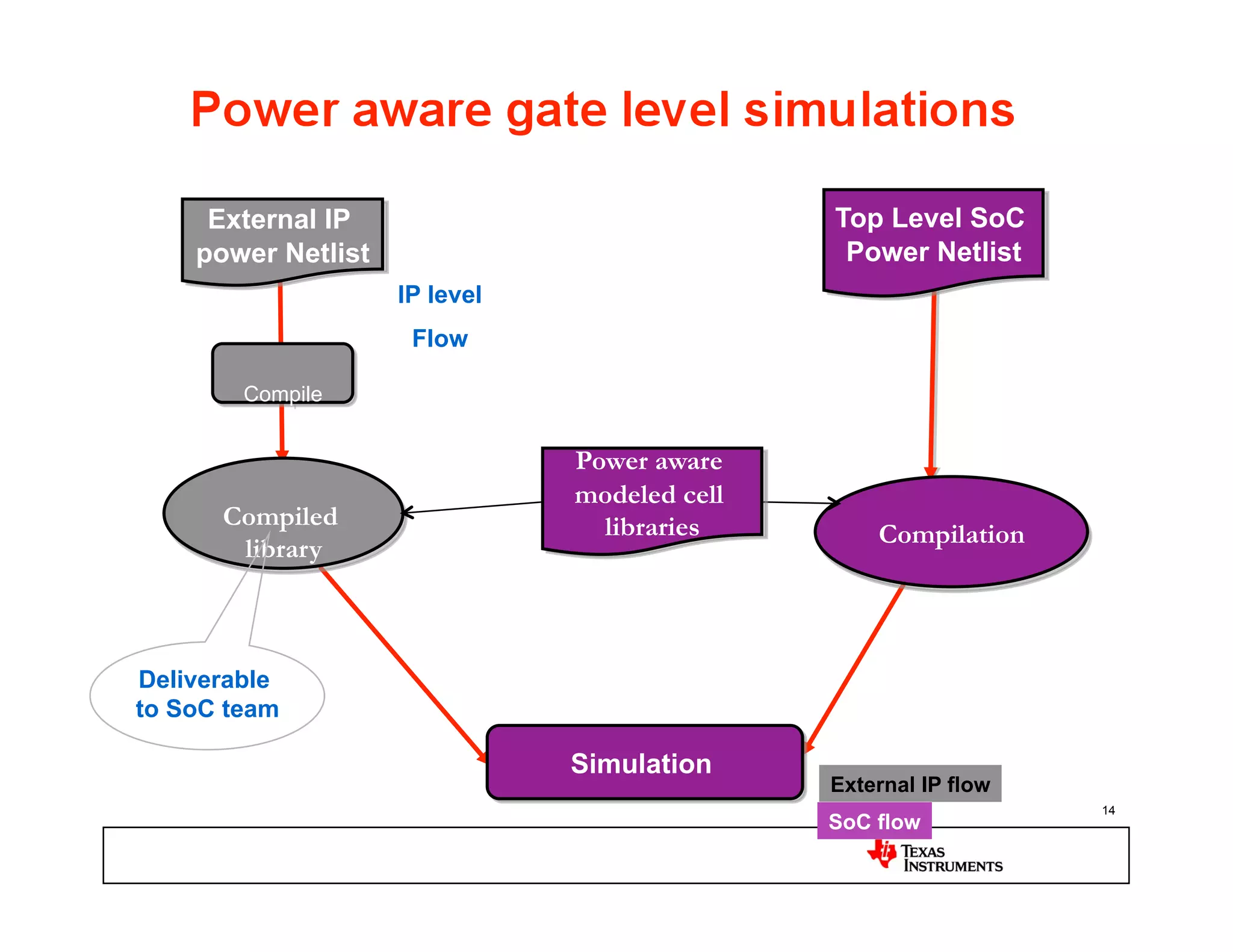
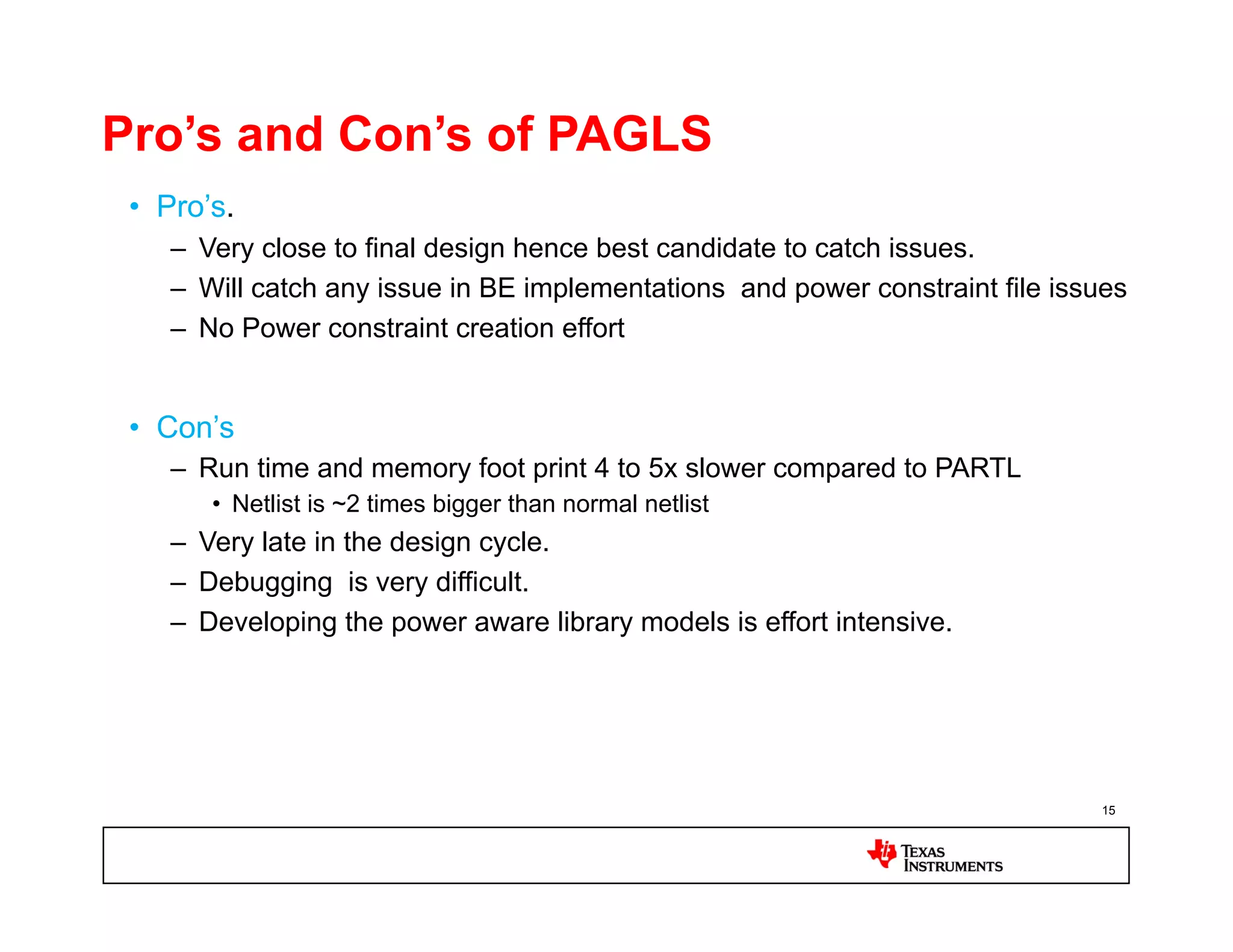
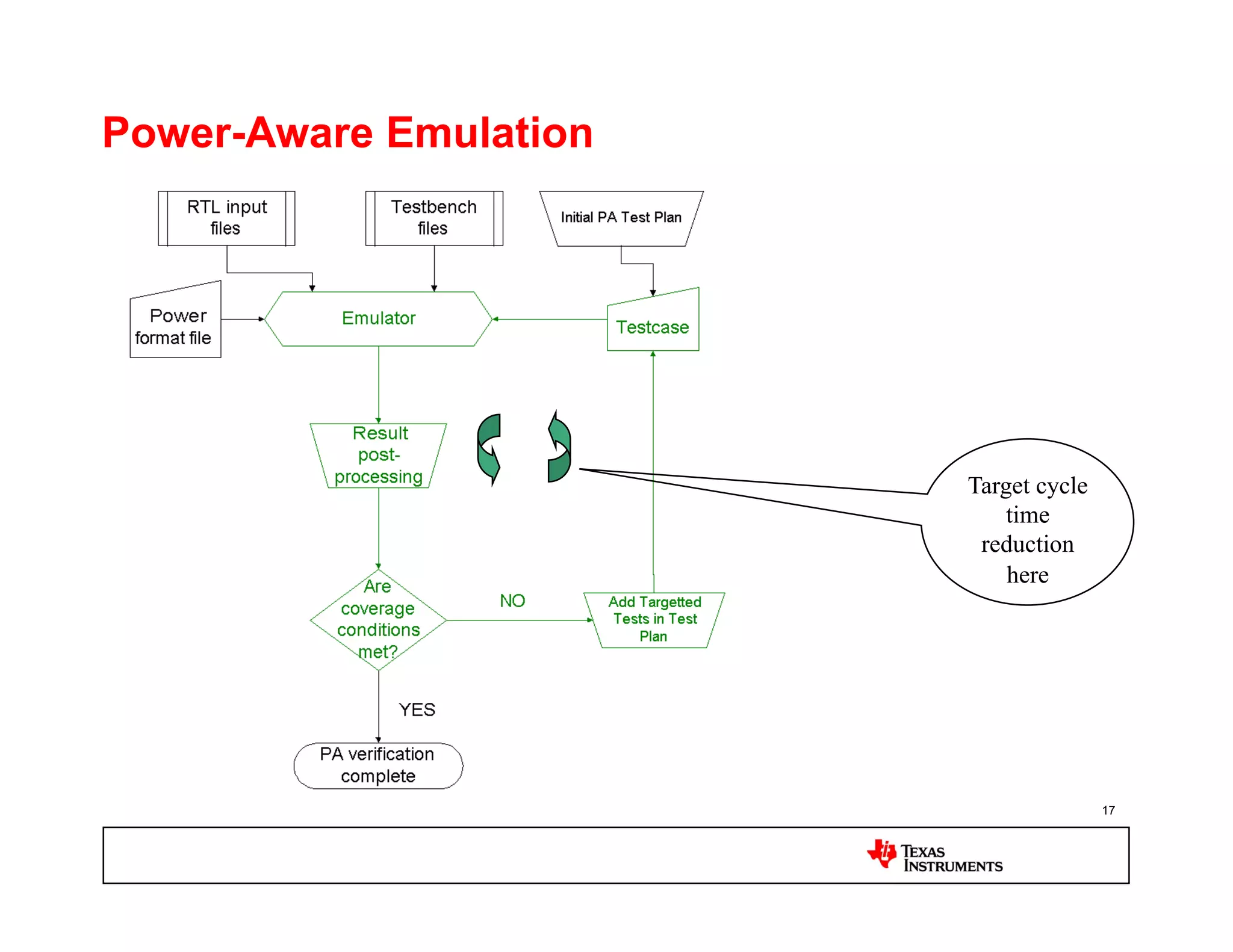
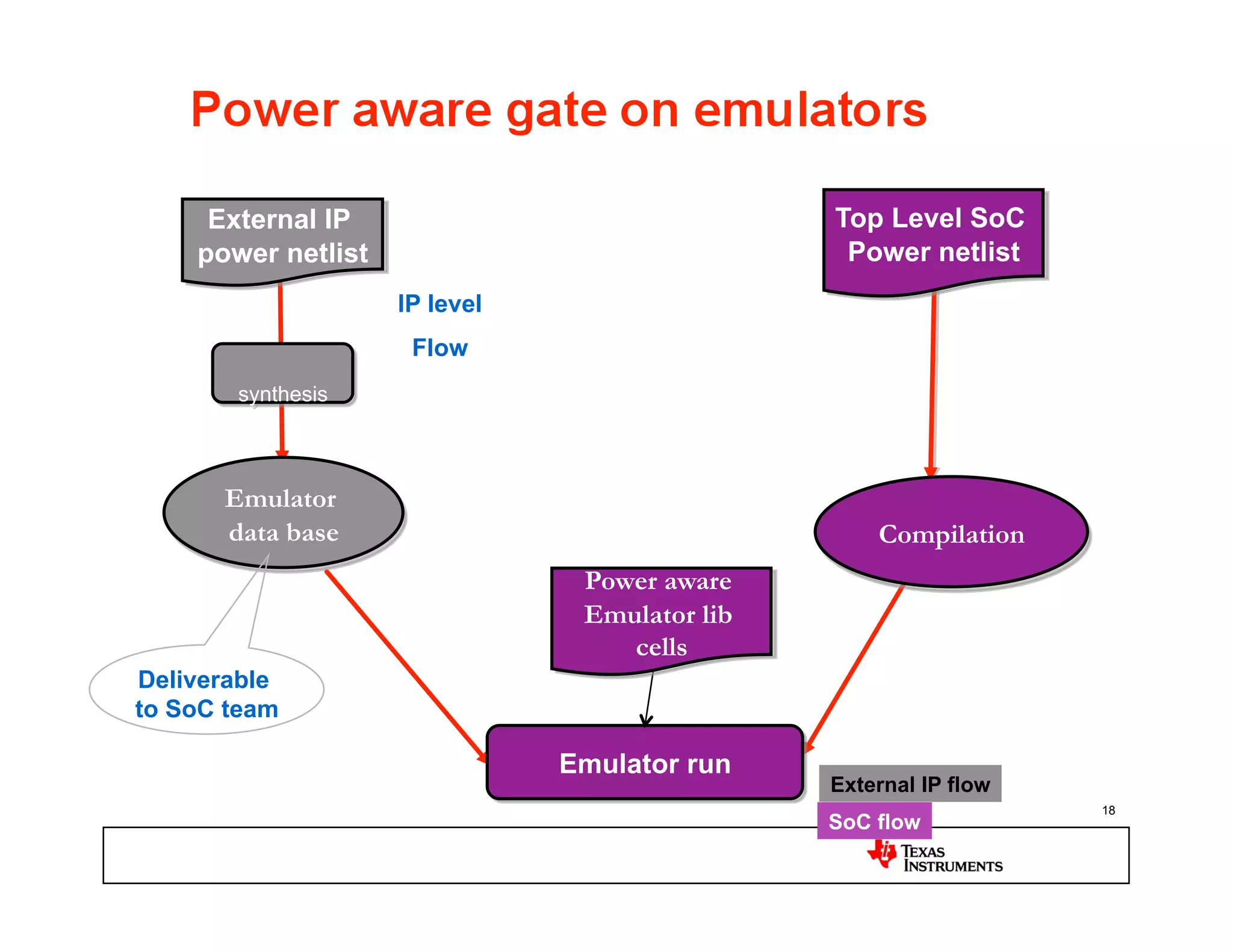
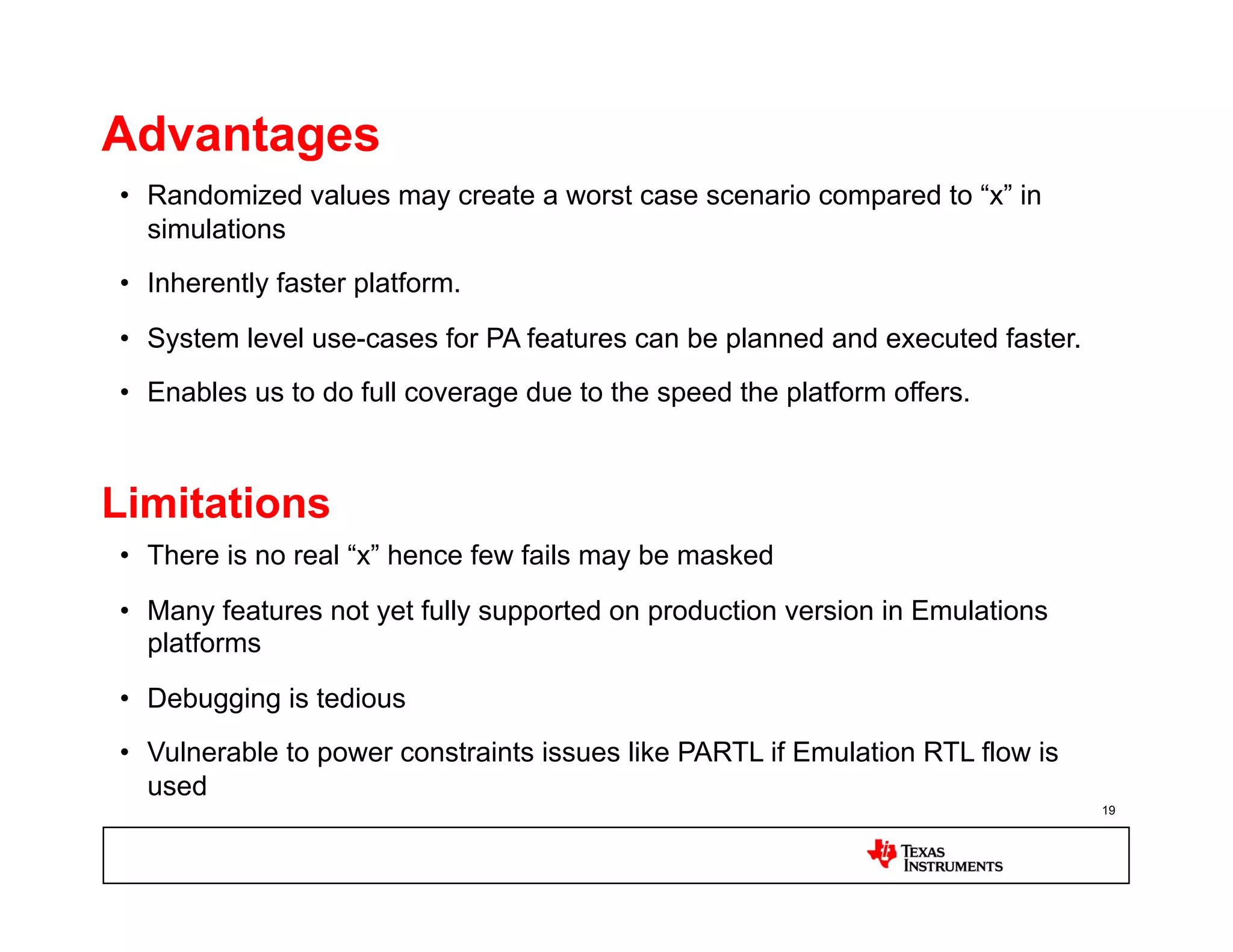
This document discusses approaches for power management verification of system-on-chips (SoCs) with dynamic power and voltage switching. It outlines the limitations of traditional simulators, and describes various tools and flows used at different design stages including dynamic simulation-based verification, static structural verification, and emulation-based approaches. Key challenges addressed include modeling of multiple voltage domains, retention behavior, and power-aware capabilities of different platforms.