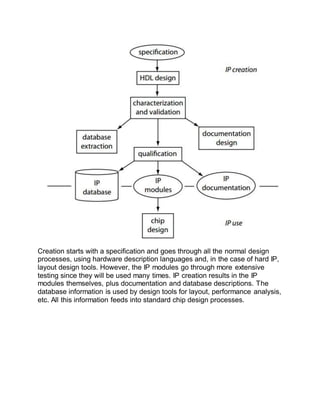
Intellectual property (IP) in VLSI design refers to reusable logic or functionality units that can be licensed and used as building blocks in chip designs. There are two main types of IP: hard IP, which includes a pre-designed layout, and soft IP, which is delivered as synthesizable code. Soft IP is more vulnerable to theft since it is in a synthesizable form. Memories are often delivered as hard IP since they require careful analog design and peripheral circuitry to be useful. IP differs from custom chip design in that it is created before a specific use, with the goal of reuse across multiple designs. The IP lifecycle involves initial creation through specification, design, testing, and documentation, followed by integration into