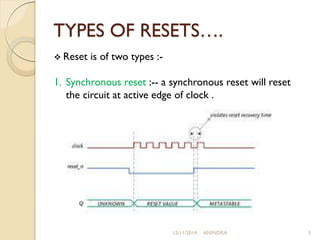
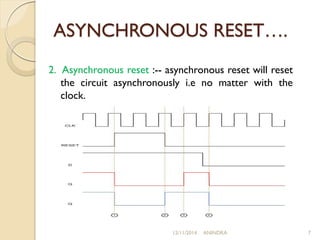
This document discusses synchronous and asynchronous resets. Synchronous reset will reset a circuit at the active edge of the clock, ensuring a completely synchronous circuit. Asynchronous reset will reset a circuit without regard to the clock, making it faster but also more susceptible to glitches. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of each type of reset.