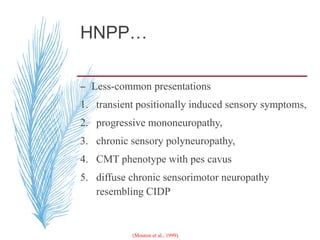
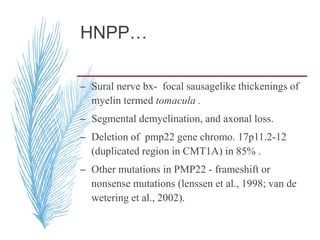
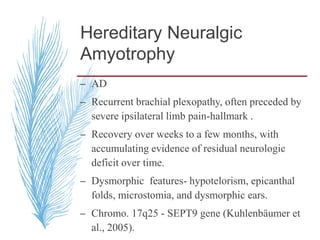
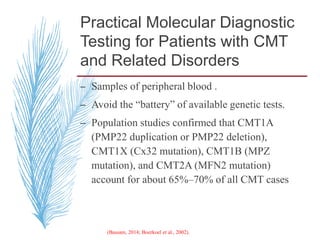
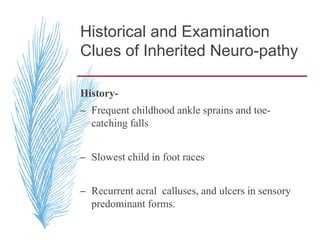
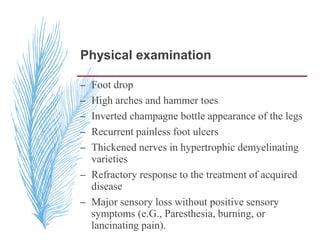
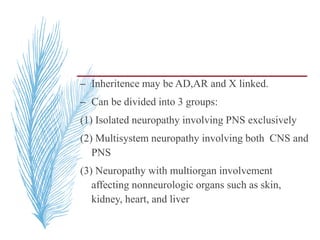
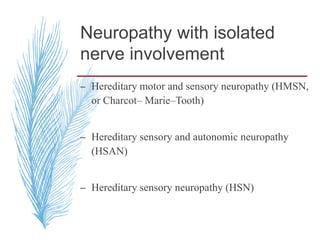
Hereditary neuropathies are a diverse group of inherited conditions affecting the peripheral nervous system. They are frequently underdiagnosed due to their indolent onset over decades and lack of clear family history in some cases. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is the most common inherited neuropathy, with two main types - CMT1 characterized by demyelination and CMT2 characterized by axonal loss. CMT1 results from mutations affecting myelin protein zero or peripheral myelin protein 22 genes, causing demyelination and onion bulb formation. Accurate diagnosis relies on detailed family history, neurological examination, and electrodiagnostic testing to distinguish inherited from acquired neuropathies.



![Acquired vs. Inherited
– More susceptible to injury from metabolic, toxic,
and other nervous system insults e.g. CTx.
– Major deficits with limited toxic or metabolic
exposure.
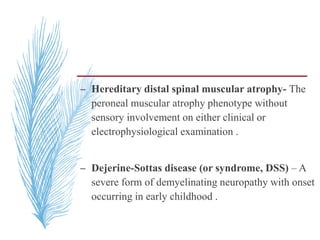
– HN frequently misdiagnosed as diabetic
neuropathy(less likely in the absence of
retinopathy or nephropathy).
Chaudhry V, Chaudhry M, Crawford TO, Simmons-O’Brien E, Griffin JW. Toxic neuropathy in patients with pre-existing neuropathy. Neurology. 2003; 60:337–340.
[PubMed: 12552058]
Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach JM, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in
a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993; 43:817–824. [PubMed: 8469345]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hereditaryneuropathies15-171102155131/85/Hereditary-neuropathies-9-320.jpg)
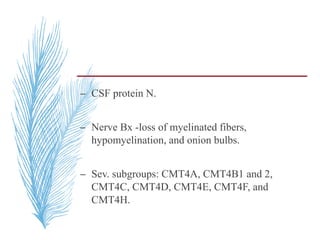
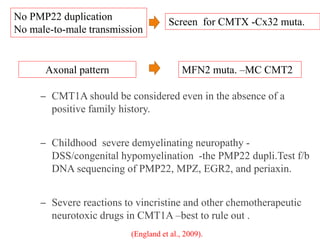
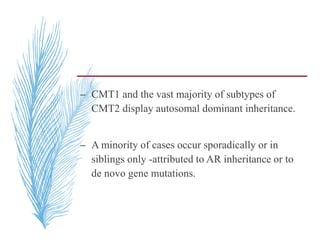
![Neurophysiology
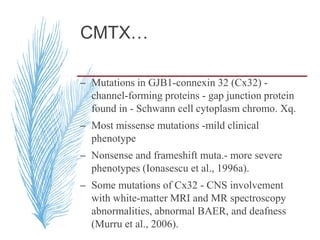
– Temporal dispersion and conduction blocks are
often absent Exceptions -CX32 mutations,
temporal dispersion can occur.
– NCV <38 m/s -demyelinating,
– NCV =38– 45 m/s-intermediate.
– NCV >45 m/s -primary axonal process
Lewis RA, Sumner AJ. The electrodiagnostic distinctions between chronic familial and acquired demyelinative neuropathies. Neurology. 1982; 32:592–596. [PubMed:
6283420]
Gutierrez A, England JD, Sumner AJ, Ferer S, Warner LE, Lupski JR, et al. Unusual electrophysiological findings in X-linked dominant Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease.
Muscle Nerve. 2000; 23:182–188. [PubMed: 10639608]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hereditaryneuropathies15-171102155131/85/Hereditary-neuropathies-12-320.jpg)


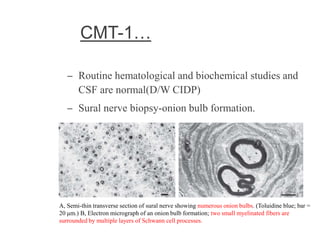
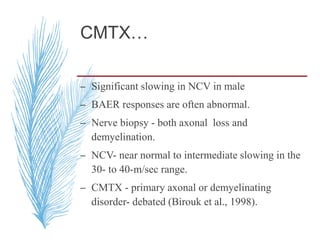
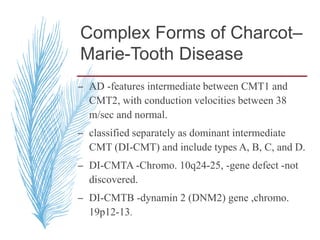
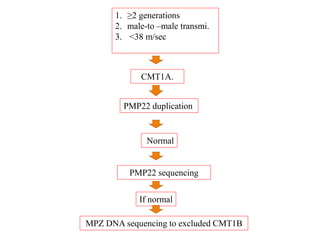
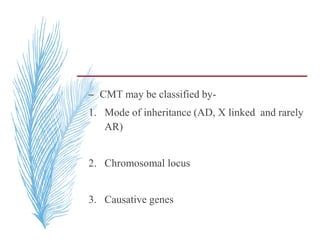
![– two main groups:
1. CMT1 [HMSN-I]- chara. By motor NCVs (<38
m/sec in forearm) and nerve biopsy findings of
demyelination and onion bulb formation
2. CMT2 [HMSN-II]- chara. By - normal or near
normal motor NCVs , and nerve biopsy reveals
axonal loss without prominent demyelination
(Harding, 1995).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hereditaryneuropathies15-171102155131/85/Hereditary-neuropathies-21-320.jpg)
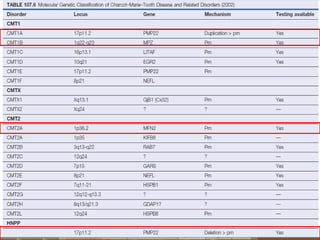
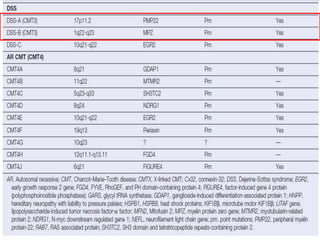
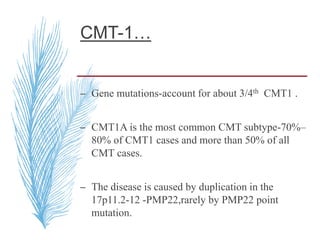
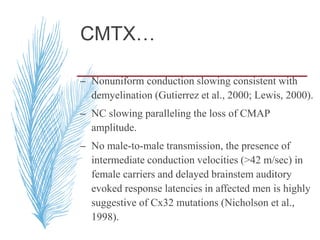
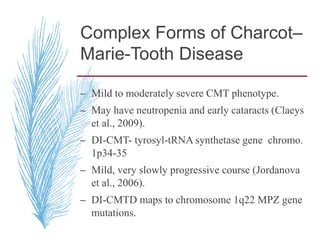
![A, CMT 1,HNPP,CMTX, DSS,CMT4-inherited disorders of myelin. CMT2 is a primary axonal disorder.
B, Point mutations of these genes (connexin-32 [Cx32], myelin protein zero [MPZ, P0], PMP22, EGR2,
periaxin) result in CMTX, CMT1B, CMT1A, DSS, and CMT4. Mutations of the LITAF gene result in
CMT1C.
C, Point mutations of the KIF1B and NFL genes and specific MPZ missense mutations result in CMT2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hereditaryneuropathies15-171102155131/85/Hereditary-neuropathies-28-320.jpg)