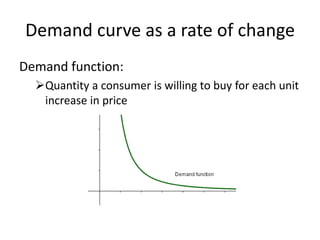
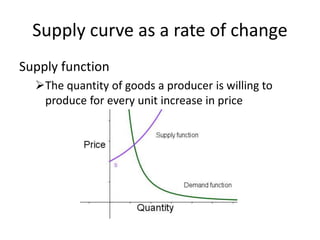
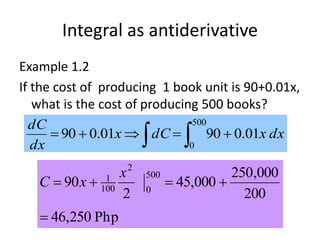
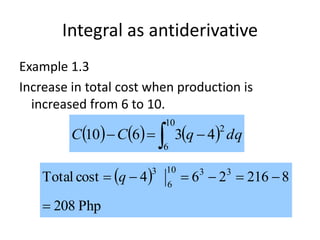
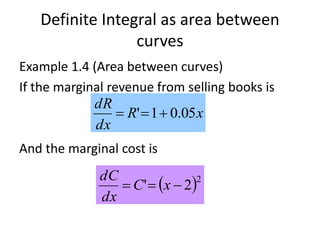
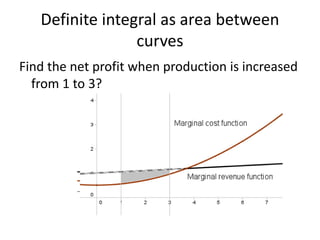
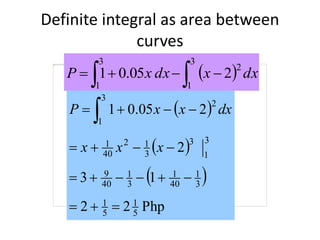
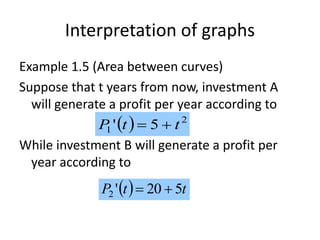
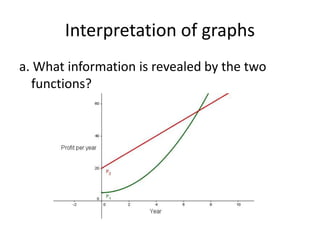
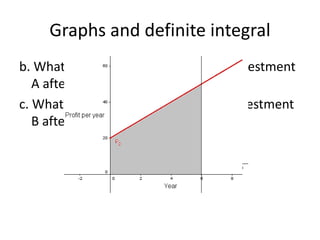
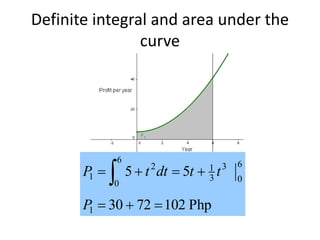
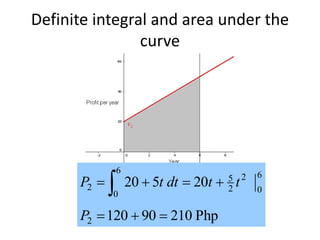
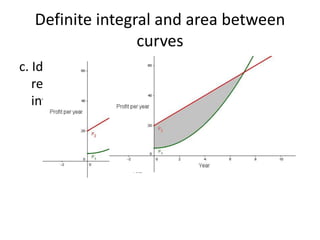
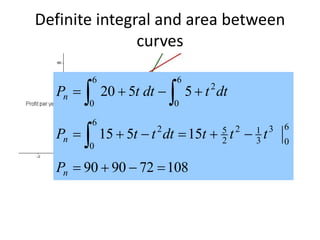
This document discusses the application of integration in business and economics. It provides examples of how integrals can be used to calculate total costs, profits, and areas between curves representing revenue and costs. Specifically:
1) Integrals allow calculating total costs by integrating marginal or incremental costs over quantity or time.
2) The difference between revenue and cost areas under their curves gives net profit over a range of quantities.
3) Investment profits over time can be found by taking the area under profit functions, allowing comparison of different investment options.