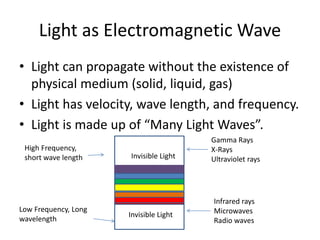
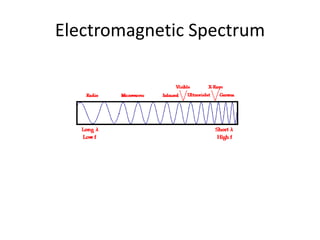
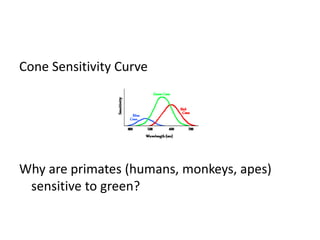
Light is responsible for photosynthesis and indirectly produces oxygen. It heats the ocean, air and land, initiating weather patterns and partly causing ocean currents and the water cycle. Light displays properties of waves as it reflects, diffracts, and refracts. It is an electromagnetic wave that propagates without a medium and has a velocity, wavelength, and frequency. The electromagnetic spectrum includes invisible forms of light like gamma rays and radio waves. In the visible spectrum, color is the reflected light wavelength, while white light is a combination of all visible wavelengths.