Embed presentation
Downloaded 27 times

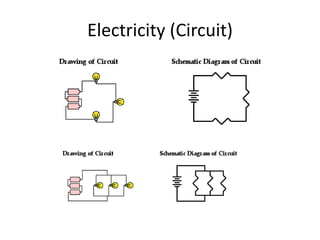
















This document discusses electricity, circuits, Ohm's Law, and series and parallel circuits. It defines key terms like resistance (R), current (I), and voltage (V) and explains how they relate according to Ohm's Law (I=V/R). It discusses how total resistance, current, and voltage are calculated for series and parallel circuits. Key facts about resistivity and how it affects resistance are also summarized. Diagrams and examples are provided to illustrate these circuit concepts.
















